Table Of Contents
Capital Deployment Meaning
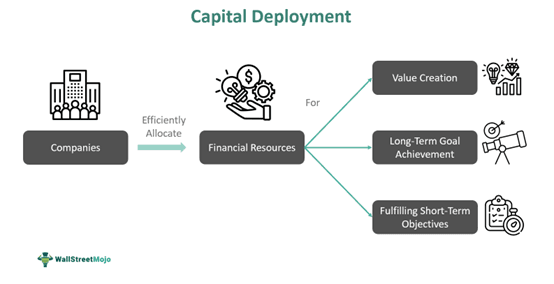
Capital deployment refers to the strategic allocation of financial resources by a company such that it successfully achieves its long-term and short-term objectives. Such decisions involve efficiently investing funds in assets, research, expansion activities, infrastructure development, business operations, and other potential projects with a fair return on investment.
These are critical business decisions that are irreversible and involve the cost of capital and opportunity costs, determining an entity's long-term success or failure. Moreover, companies aim to foster business growth, create value for their stakeholders, manage and reduce risk, enhance return potential, and become more competitive by efficiently deploying their capital.
Key Takeaways
- l Capital deployment is a well-planned strategy for allocating funds to efficient investment opportunities to achieve short-term and long-term business goals.
- l Such financial resources can be employed for the purpose of buying assets, business expansion, infrastructure development, fulfilling operational needs, acquisition and mergers, etc.
- l Some of the fundamental principles to consider for effective capital deployment include focusing on business survival, organic investment, product margin, strategic approach, and limited debts.
- l It is critical for business growth, huge returns, risk management, value creation, being competitive, and enhancing the company's overall efficiency.
Capital Deployment Explained
Capital deployment is the process of strategically planning the financial resource allocation by companies for building long-term stakeholders' value, ensuring growth, and becoming the market leader. However, organizations find it a challenging task because of the trade-off between various investment opportunities and the risk and return profile of each of them. Therefore, it becomes crucial to analyze and compare the risk-return profiles of the available investment options to ensure efficient capital allocation.
Given below are the different capital allocation approaches:
- Traditional Approach: Earlier, businesses used to invest in projects that provide the best return on investment (ROI).
- Risk-Adjusted Approach: This concept focuses on calculating the risk and reward profile of the various investment opportunities to select the one that generates the highest shareholders' value.
- Strategic Approach: The strategic approach ensures that the financial investment should often align with the company's long-term objectives and strategies.
- Value-Driven Approach: It emphasizes the capital allocation approach by selecting assets, projects, and investment opportunities that derive maximum value for its stakeholders, including employees, customers, associates, suppliers, and communities.
- Opportunistic Approach: This capital deployment approach focuses on employing funds towards exceptional business or growth opportunities, thus responding to changing market scenarios.
Deploying capital efficiently is necessary for the companies to grow and succeed. However, the management and the directors should carefully plan such decisions since these are irreversible and, if gone wrong, may significantly affect the business's reputation, earnings, and even its existence. Moreover, the business needs to consider the opportunity cost of a project to know what it is letting go of.
Principles
The decisions regarding capital deployment involve trade-offs since the financial resources are limited, and there can be various investment opportunities. Therefore, the companies need to consider the following factors before strategizing such decisions:
- Prioritize Survival: The primary focus should be business survival, and the companies should ensure that they have sufficient funds to maintain their liquidity and fulfill their operational needs. Also, they should not take too high a risk that it stakes their existence.
- Buy Low, Sell High: The organizations should focus on availing or producing the goods or services at low prices and selling them at high prices, making an exceptional return.
- Avoid Herd Behaviour: No capital allocation strategy should be driven by crowd behavior, i.e., because the majority of competitors are doing the same or are under the pressure of creditors, investors, or shareholders.
- Investment Beats Financial Engineering: It is proven that in the long run, investments in assets and projects offer incremental returns that are much higher than those of financial engineering.
- Focus on Organic Investment: Organic investments resemble the undertaking of those projects or opportunities in which the companies hold the expertise, as well as the ones that have a balanced risk and return profile.
- Strategize Acquisitions to Grow and Spinoffs and Divestitures to Shrink: It is crucial to align the acquisition strategy with the business goal to ensure success. Similarly, the business should plan its spinoffs or strategically divest from a loss-making unit or the ones that don't align with its core competencies.
- Leverage Prevents Investment: Remember, if the company is in high debt, it may not have sufficient financial resources to fund its growth and investment prospects.
- Apply Buyback Execution Rules: Companies often use a share buyback strategy when they know that their shares are undervalued in the market, and repurchasing them would generate more value for their remaining stockholders.
- Dividends Are Value-Neutral: The regular distribution of dividends to the shareholders cannot be undertaken as a capital deployment strategy since it creates no value for the shareholders.
- Hard Work Results in Value Creation: The firms need to put a lot of effort into planning and executing their capital allocation strategies, whether it is starting a new project, producing new products, making capital expenditures, acquiring a target company, or performing research.
Examples
Businesses often devise capital deployment strategies to meet their investment goals with precision. Given below are some examples of efficient capital allocation for business growth and success:
Example #1
Suppose ABC Ltd is a bone china crockery manufacturer with a valuation of $5 million. The company secured $1 million from a Series A funding round. Now, for capital deployment, it has two investment opportunities; the first one is to buy a small clay crockery firm, which is into losses for $7,00,000, and invest the remaining funds in reviving the unit and acquiring the vast potential market in the vicinity.
The second option is to buy nearby premises for $3,00,000 and invest the rest of $7,00,000 in buying machinery, raw materials, funding working capital, and marketing campaigns. The company would then export its crockery to countries where there is a high demand for such premium-crafted products. On calculating the risk and reward profiles of both these opportunities along with their return on investment (ROI), the Board of Directors opted for the second project, I.e., to expand locally and sell globally.
Example #2
The semiconductor industry is experiencing robust growth, with an anticipated annual expansion rate of 6 to 8 percent until 2030, driving projected annual revenues to $1 trillion. To meet this escalating demand, semiconductor manufacturers are planning capital deployment for the construction of new fabs in the United States. Currently, the combined value of US-based semiconductor projects stands between $223 billion and over $260 billion until 2030. The federal government has allocated $54 billion in grants for domestic semiconductor manufacturing and research through the US CHIPS and Science Act.
Notably, challenges for US fab construction include a scarcity of construction talent, emphasis on sustainability, supply chain complexity, and navigating federal and local incentives. Nevertheless, opportunities exist to revolutionize fab construction through innovative financing, modular design and prefabrication, strategic negotiations, generative scheduling, and project control towers.
Importance
Companies often implement effective capital deployment strategies since it is the key to long-term success due to its following significance:
- l Risk Mitigation: Capital deployment across different assets, projects, and markets helps the companies diversify their investment, thus reducing the risk arising from economic fluctuations, recession, and unforeseen events.
- l High Returns: When businesses expand their productivity, market reach, and profit generation prospects by effective capital allocation, they ultimately enhance their income potential.
- l Provides Competitive Edge: The organizations that invest in the latest technology and processes are able to become more competent and differentiate themselves from the other companies in the industry.
- l Improves Efficiency: When businesses invest more in infrastructure, technology, innovation, research, and development, they tend to enhance their overall efficiency of production, sales, and profit-making.
- l Fosters Growth: The companies often leverage financial resources to develop new products or services, expand the market, increase sources of revenue, fulfill working capital needs, and perform research and development.
- l Ensures Value Creation: The firms aim to build long-term value for their shareholders, investors, creditors, employees, customers, and other stakeholders by increasing the return on investment, reinvestment prospective, dividends, etc.
