Table Of Contents
C-Suite Meaning
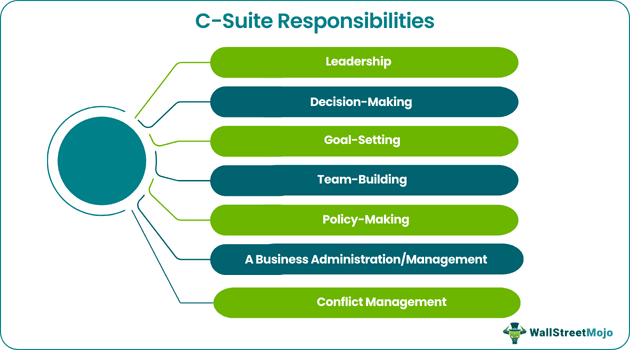
C-Suite sometimes referred to as C-Level, represents a class of high-ranking executives or officers in a corporation. These top senior management officials demonstrate business expertise, leadership skills, and decision-making ability, making them the most influential people in the organization.
Since these professionals act as “chiefs” of their respective departments, hence the term C-Level. Chief executives ensure the proper functioning of the company while leading the business. Other functions include business communication, team-building, and working with group members. Based on their role, they are responsible for devising business plans, recruiting human resources, overseeing financial activities, resolving business conflicts, setting strategic goals, etc.
Key Takeaways
- C-Suite or C-Level refers to the group of top-level management executives who, with their extensive business expertise, administer and manage the organization and ensure its success.
- Some of the most commonly found C-Level titles in the modern organizational setups are Chief Executive Officer, Chief Operation Officer, Chief Finance Officer, Chief Marketing Officer, Chief Technology Officer, Chief Information Officer, etc.
- The educational qualification and experience required by candidates applying for the C-Level positions must match the nature of the business.
- The responsibilities and risks associated with the C-Suite positions are high, so the executives serving the roles are offered significant compensation with numerous high-end benefits.
Explanation
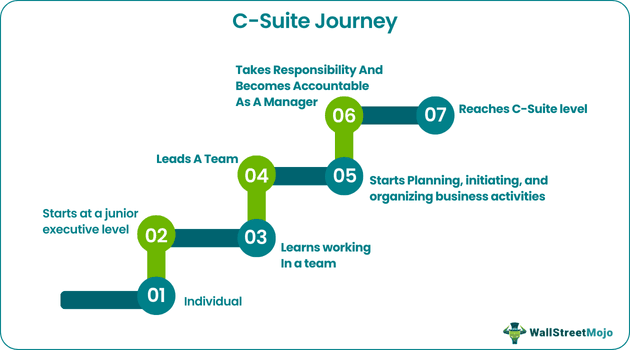
The corporate journey of any individual starts with junior executive level, and they climb the corporate ladder by gaining extensive business experience. The step-wise gradual growth allows lower and middle management employees to understand how an organization functions.
C-Suite executives are the high-ranking officers in an organization. They exhibit extraordinary ability to make strategic decisions and to administer and manage the organization. Executives must be a leader, manager, initiator, planner, and organizer to join the C-Level. Some of the commonly known C-Suite titles are Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Chief Operating Officer (CIO), and Chief Marketing Officer (CMO).
Every organization follows a different protocol while creating C-Level positions. Although C-Level executives guide the rest of the executives and professionals working in the company, their titles may differ. For example, there is a Chief Medical Officer or CMO in a healthcare firm. In contrast, a Chief Technology Officer or CTO is in charge of the technical operations of an IT company.
Hence, a C-Level title represents the products or services offered by a company and the industry in which it operates.
The changing business environment requires organizations to create new chief executive positions or expand beyond traditional executive titles from time to time. An analysis of C-Level appointments in the U.S. in 2020 by LinkedIn revealed a growth of 84% in the hiring for such positions, for example, chief diversity officer. Events like the murder of George Floyd and growing sentiments for racial injustice influenced these business decisions. Similarly, the COVID-19 pandemic let many companies rely on chief revenue officers, chief growth officers, and chief medical officers.
Essential Qualification And Compensation
The educational qualification and extensive business experience determine whether a candidate is suitable for the C-Suite level. Depending on the niche in which a particular organization operates and the type of services it provides, the eligibility criteria might differ. For instance, a medical company would need C-Level executives having extensive qualifications in pharmaceutical sciences. Likewise, a core financial company would look for someone with a degree in finance.
In short, the eligibility of the candidates would depend on the responsibilities they would be handling after being finalized for the position.
The role, responsibilities, and risks associated with the C-level positions are pretty high. Therefore, these top management executives get attractive compensation. Apart from lucrative salaries, they get the company’s stock ownership, health benefits, and other perks.
List of C-Suite Executive Positions
The number and titles of C-Level executives in an organization depend on its need, size, type, and vision. Here is a list of some of the most commonly found C-Level titles in the modern organizational setups, along with roles and responsibilities:
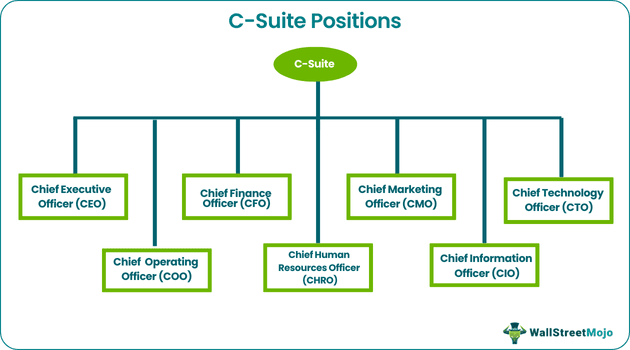
#1 - Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
It is the highest corporate title overseeing the administration and management of the organization. Sometimes the company founder or co-founder could serve the role. While managers, senior executives, and heads of different departments report to the CEO, they are accountable to the Board of Directors.
Due to their extensive business knowledge, CEOs are responsible for making strategic decisions and ensuring business success. They set business goals and create and implement company policies aimed at maximizing business value. Their leadership skills help them make difficult decisions in the best interests of the company.
#2 - Chief Operating Officer (COO)
In the modern corporate world, the COO is a position immediately next to the CEO. They make sure that company policies align with business strategies in the absence of the CEO.
Aside from curating business plans and governing business operations, COOs take care of human resources functions in some organizations, such as employee recruitment and training and payroll management. Other responsibilities include handling legal and administrative services.
#3 - Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
Some organizations appoint CFOs to handle core financial services. These high-rank officers are expert financial analysts and work in coordination with the CEO. Knowing accounting, investment, and portfolio management makes them the real asset for the companies.
The range of responsibilities they look after includes financial planning, financial reporting, and financial risk analysis. In addition to managing cash flow and preparing annual budgets, CFOs explore new business and investment opportunities.
#4 - Chief Human Resources Officer (CHRO)
Although rarely found in the modern organizational setting, some organizations prefer having a separate position for CHRO at the C-Level. They are forward thinkers who help companies preserve their most precious assets – employees.
Their roles include employee recruitment, training, evaluation, and promotion as part of talent acquisition and succession planning. They ensure all departments and tiers in the organization work collectively without any disputes.
#5 - Chief Marketing Officer (CMO)
The sales and marketing department is one of the most critical segments in any organization. Whether a company produces goods or delivers services, brand management is crucial for guaranteed sales. CMO in an organization makes sure the sales and marketing procedures are managed and taken care of properly.
CMO handles the company’s marketing strategy, from planning quality product development to promoting brands on various platforms. They are responsible for making consumers aware of the products or services through digital marketing, brand advertising, and marketing events.
#6 - Chief Information Officer (CIO)
In an organization, the backend department headed by CIO takes care of computer programming, coding, etc., to make the business information available to everyone. A CIO oversees and manages technological products and services in an IT firm or software development company.
Besides ensuring smooth IT operations across the business, they handle technology research and development per business goals. They are also responsible for applying their technical skills in other business areas, such as risk management.
#7 - Chief Technology Officer (CTO)
A few firms use the positions of CIO and CTO synonymously. However, when a company has a separate title for both, the CTO takes charge of researching, developing, and implementing innovative technological systems essential for smooth business operations. They are responsible for managing the security and technology infrastructure for the greater good of the company.
Besides the ones mentioned above, other C-Level positions in an organization can include:
- Chief Investment Officer
- Chief Supply Chain Management Officer
- Chief Data Officer
- Chief Diversity Officer
- Chief Growth Officer
- Chief Analytics Officer
- Chief Security Officer
- Chief Legal Officer
- Chief Research Officer
- Chief Compliance Officer, etc.
