Table Of Contents
C Corporation Definition
C Corporation (C Corp) refers to the type of business where owners and shareholders enjoy the liberty to frame separate legal structures to safeguard their personal assets and interest. In a C Corp, shareholders are taxed as separate entities and not part of the company. Such a business structure has limited liability, permanent existence, and improved credibility in the market.
C Corporations are one of the most popular business setups in the United States. These are subject to double taxation, with profits being taxed at the corporate and personal levels. With the provision of sale of stocks when required, these business structures are likely to get some good investors on board.
Key Takeaways
- C Corporation refers to a business structure where shareholders have separate legal status, which lets them safeguard their personal assets in the venture.
- There is no limit to the number of shareholders allowed to invest in such publicly traded entities.
- C Corps are subject to dual taxation – one is the corporate tax they pay as a business entity, and another is the personal income tax they pay as individual shareholders.
- The shareholders/owners have the liberty to choose the class of shares they want to issue in the name of the C Corp.
How Does a C Corporation Work?
C Corporations (C Corp) are publicly traded entities with a number of shareholders/owners. In this type of business structure, the company assets and shareholders’ assets are individually identified and separately taxed.
Forming a C Corp starts with registering an unregistered company name. The registrant can then prepare and file articles of incorporation with the Secretary of State and begin issuing stock certificates to the interested initial shareholders, who become the owners post-purchase. The next step is to apply for a business license and other relevant and required certifications.
Finally, the C Corporations must obtain an Employer Identification Number (EIN). Thus, they must file Form SS-4 or submit the EIN application at the Internal Revenue Service’s official website. Once the registration process is accomplished, the C Corp entity sets up a board of directors to monitor its operation and performance. The shareholders/owners are the ones who elect these directors.
C Corps do not have specific criteria to restrict people from owning shares. Therefore, any interested entity or individual from anywhere globally has the liberty to become a shareholder. In addition, these business structures do not impose any restrictions on the number of shareholders they can have.
Though the formation of the C Corps is a formal process, once the setup launches, it never stops, even if an owner expires. Therefore, the change in the ownership or shareholder status doesn't affect the working of these business types. In addition, the legal status of each shareholder not only shields their personal assets, but they also enjoy limited liability for the debts and financial obligations of the company as a whole.
In short, all the shareholders are equally responsible for anything happening in the organization, be it good or bad.
Taxation Laws
C Corporation tax laws vary from state to state. The tax treatment given to such business entities makes them different from the rest. As already stated, C Corps are subject to double taxation – corporate tax and personal income tax.
The company’s profit is taxable under corporate income tax with a deferral tax return (Form 1120). After paying the corporate taxes, shareholders receive their share of returns on which they pay personal income tax at the individual level.
Recently, the new budget proposal introduced in the United States stated that there would be an increase in the tax rate for C Corps in 2022. According to the plan, for Dec 31, 2021, and onwards, the C Corporation tax will be 21% to 28% more than earlier.
Advantages
A C Corp offers a wide range of benefits to the shareholders. Here is a list of C Corporation advantages to look at:
- These are separate entities, which means the units remain segregated from the owners/shareholders.
- The shareholders/owners have limited liability in such business structures as all share the accountability, be it directors, officers, employees, or shareholders themselves.
- The change in the shareholding or ownership status doesn’t affect the existence of a C Corp. It can exist even if an owner expires.
- The credibility of such entities is significantly higher as more and more investors are willing to invest.
- Such business structures have immense growth potential as they can sell shares and stocks as and when required.
- There is no restriction on the number of shareholders investing in C Corps. However, as soon as the number reaches a threshold, the entity has to register itself with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) as per the provisions under the Securities Exchange Act.
- C Corporations enjoy numerous tax benefits, including tax-deductible business expenses.
- These entities impose no restrictions on shareholding. People from all across the globe are eligible to invest, buy shares, and become C Corp owners. In addition, they can choose to offer any type of shares, be it common shares or preferred stocks.
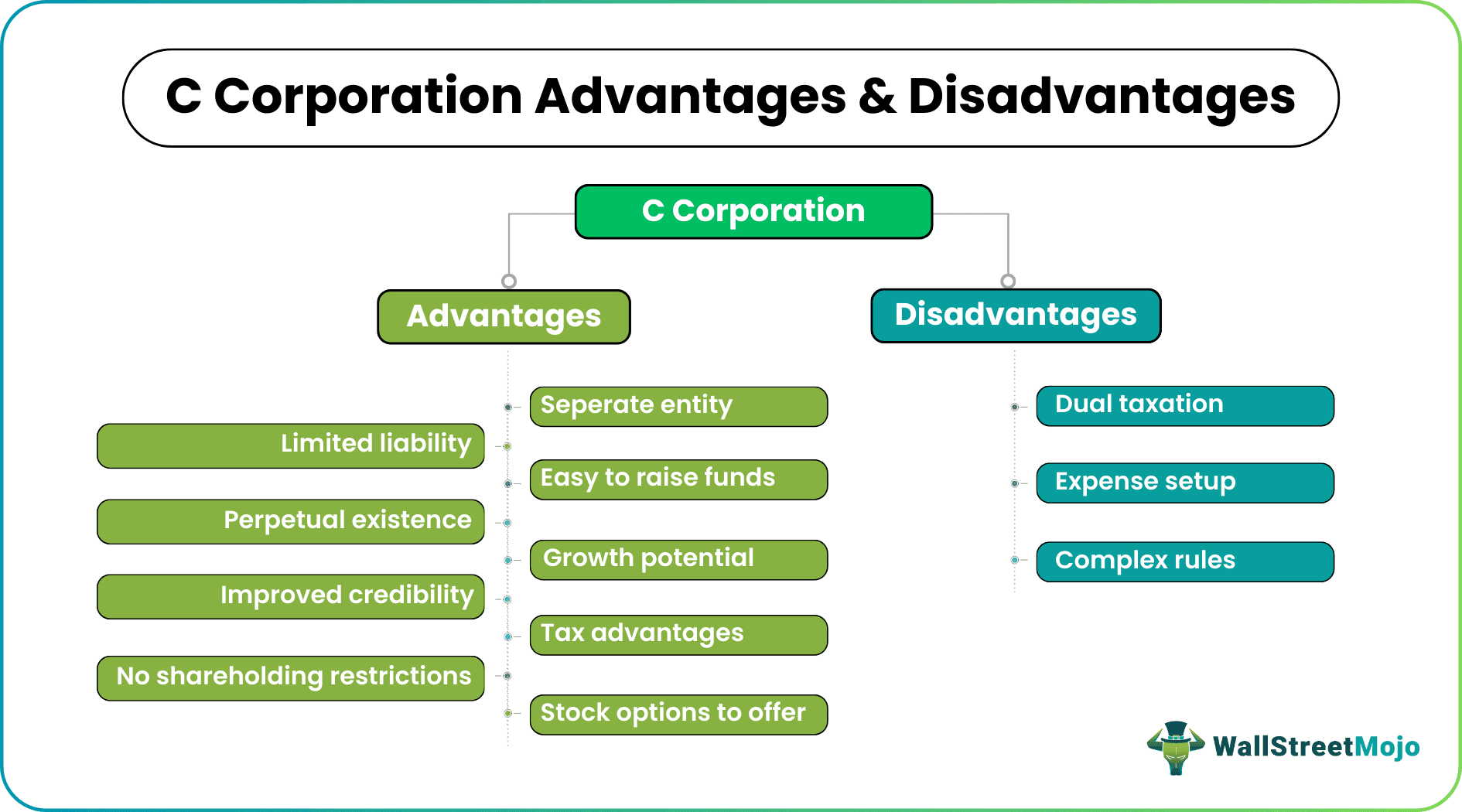
Disadvantages
With numerous benefits, these business structures have some limitations as well. So, let us check some C Corporation disadvantages quickly:
- They are subject to paying two taxes consecutively. The shareholders pay corporate tax as a business entity and personal income tax as individual earners.
- Setting up a C Corporation is an expensive affair with the registration and other fees involved in the process.
- As an autonomous entity, a C Corp remains overlooked by the state and federal authorities. As a result, the regulations guiding these structures are complex, especially the tax rules.
Example
Let us consider one of the conceptual C Corporation examples to understand the concept better:
Anna registered Company A as a C Corp and filed articles of incorporation with the Secretary of State. She issued shares to four investors, including herself. This resulted in limited liability protection, ensuring that the C Corp would continue to operate even if the original registrant leaves the entity or changes her ownership status.
As per the dual taxation rule applicable for C Corps, the shareholders paid the corporate tax. Then, after deducting the taxable amount from the total C Corp income, they distributed the profits among themselves and taxes were applicable again to their personal income as individual shareholders.
C Corporation vs S Corporation
C Corporation and S Corporation are two business structures similar to a great extent but with a fine line of differences.
Similarities
Both the C Corps and S Corps must file articles of incorporation. Shareholders, directors, officers, and employees comprise both corporations. Moreover, these two business structures offer limited liability protection to all shareholders involved.
Dissimilarities
C Corporation and S Corporation differ with respect to tax treatments and ownership rules.
In a C Corp structure, the taxation is dual. The corporation first pays corporate tax as an entity and then pays personal income tax as individual shareholders.
Secondly, a C Corp allows and invites any number of shareholders to purchase shares and become an owner. However, it has to register with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) once it reaches a threshold. On the contrary, S Corps allows only up to 100 shareholders to invest in the firm.
Thirdly, a C Corp cannot own an S Corp. But, on the other hand, C Corp has no such restrictions. Therefore, anyone can become a shareholder and own the C Corp entity.
