Table Of Contents
What Is Business Management?
Business management entails overseeing the organization and coordination of corporate operations. It involves both marketing and innovation and the production of equipment, money, and materials. In addition, it aims to unite people to work toward the same goals and objectives by making the most effective and efficient use of resources.
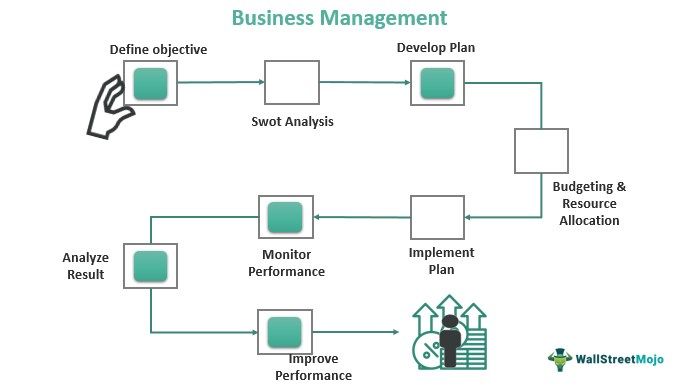
It keeps an eye on execution-related tasks and encourages workers to be as productive as possible. In addition, a manager can assist a company in achieving its operational and financial goals by supervising or training new staff. Therefore, it emphasizes the organizing, planning, and analyzing of business activities needed to manage and operate a business effectively manage and operate a business.
Key Takeaways
- Business management is the coordination and arrangement of corporate activities. Operations are overseen by managers, who also assist staff in maximizing production.
- It involves the creation of tools, cash, and materials, as well as marketing and innovation.
- Thus it reduces cost, helps resource management, and establishes a robust organization.
- It is more people-centered and heavily relies on managerial abilities in the workplace.
- Some of the famous management types are financial management, marketing management, and sales management.
Business Management Explained
Business management is the administration of resources, tasks, and activities inside an organization to accomplish a specific goal. This includes managing personnel, controlling basic operations, and planning infrastructure for the business's long-term success.
Experts claim that balancing work and talent is the secret to successful business management. For example, the respect of your coworkers is earned by technical proficiency, but maintaining that respect requires soft skills. Furthermore, effective leadership involves continuity, communication, empathy, and developing and maintaining strong working relationships. These qualities work together to form a successful corporate management plan.
A crucial business management role is maintaining the structure and administration of an organization's resources, especially talent. Therefore, it is more people-focused and strongly depends on a manager's business management skills. Business managers are strong leaders who are in charge of maintaining employee efficiency. They also have outstanding communication skills and are receptive to new ideas. Thus, managers develop the company's vision and work to provide their best efforts in assisting the organization in reaching and exceeding objectives. In addition, they are skilled at analytical thinking and problem-solving.
Types
Here are some significant business management types -
- Financial Management - The goal of financial management is to strike a sound balance between profits and risks so that, notwithstanding a setback, the enterprise remains profitable over the long run. This management style entails organizing, overseeing, and managing a company's accounts, investments, banking, insurance, securities, and other similar financial activities.
- Marketing Management - Marketing management is concerned with effectively deploying marketing strategies and controlling a firm's marketing resources and initiatives. Company, partner, competition, and consumer analysis are the four main pillars of marketing management. Along with marketing strategy and pricing, marketing management also involves brand management.
- Human Resource Management - Recruitment and staff management are the prime areas of focus for human resource management. This covers wages, hiring practices, health and safety, benefits, and other facets of managing employees.
- Information And Technology Management. It focuses on watching over and managing a company's technological resources to fulfill its demands and priorities. Information technology (IT) teams and managers ensure that a company's technology aligns with its business objectives. IT configuration, services, and financial management are the three main components of IT management.
- Sales Management - Leading and managing sales teams is a part of sales management. As sales managers, sales agents are pushed to develop solid bonds with prospects, turn them into leads, and advance them down the sales pipeline. In addition, marketing management and sales management frequently cooperate.
Levels
Let us go through the levels of business management in the following section.
- Top-Level Management - The most senior executives and decision-makers within an organization make up top-level management. The direction and expansion of the business are the responsibility of each higher leadership member. Therefore, the performance and destiny of a corporation are determined by its top management.
- Middle-Level Management - The leaders of numerous departments within a company make up middle-level management. These executives are in charge of enabling interaction between top-level and lower-level management. They control most of the executions and micromanagement in an organization.
- Operational-Level Management - The cooperation between the operational workforce and middle-level management falls under operational-level management. They supervise teams and give out detailed tasks to workers in real-time. However, middle-level administration typically issues instructions, and operational-level management needs more decision-making authority.
Examples
Let us understand the concept through the following examples.
Example #1
Imagine that Mobicon Ltd., a smartphone manufacturer, realized it had squandered the chance to pioneer the smartphone revolution. After that, it appointed a new chief executive officer (CEO) and started a process to redefine itself. The focus turned to connectivity and mapping technologies when the faltering mobile device segment was sold to another large company, Amacon Ltd.
Later, Mobicon Ltd. created a thruster program that assisted the business in keeping up with the competitors' new technological developments and the constantly evolving needs of its customers. As a result, they reduced operations to just three departments and reduced the number of business units from nine to four.
It also bought small rival companies in the industry. As a result, all components of a small firm were coordinated and aligned as part of small business management. As a result, shareholder value increased by billions, and Mobicon Ltd. transformed into a full-service infrastructure supplier.
Example #2
In 2009, Domino's Pizza had trouble since its stock had dropped to an all-time low. Despite the company's value of upholding a positive image, its difficulties rendered this a significant problem.
However, Domino's Pizza was revived in 2012 due to an effective change management implementation. The major participants in the digital transformation successfully persuaded top management to join, which was the foundation for the organization's successful turnaround. Their enthusiasm eventually spread throughout the entire company.
The company adopted new technology to help the opportunity. Although there were only 150 DXPs on the road at the time, they served as an advertisement for a new specialized delivery truck with a heating oven.
The business also increased its initiatives in digital marketing. For example, customers can buy pizza through messages, Amazon, Google, Twitter, Facebook, Smart TVs, and other platforms.
Domino's used its unique operating system to take advantage of the vast amount of consumer data. This gave Domino's information on its clients while also lowering transaction expenses. Additionally, loyalty programs can be created to increase sales, and special offers can be made.
Importance
The importance or purpose of such management can be understood in the following ways.
- Reduces Costs - Management ensures maximum outcomes with less input from proper planning. Business management functions combine physical, human, and financial resources in the most straightforward way possible. Cost-saving benefits result from it.
- Resource Management - Management makes productive use of all available physical and human resources, resulting in effective management. In addition, by choosing the least difficult viable alternative labor inside the industry and avoiding other services, management provides maximum utilization of finite resources.
- Establishes Sound Organization - Effort duplication is absent. Establishing a sound organizational structure is one of the management's goals that will align with the company's goals.
- Prosperity of Society - Effective management results in better economic output, which in turn helps to raise the welfare of the general populace. In addition, a proper business management system prevents the wastage of scarce resources.
Business Management vs Business Administration vs Project Management
Project management is carrying out one or more projects successfully while adhering to time, scope, money, and quality constraints. While company management entails monitoring certain business operations to ensure everything is going correctly. This may involve manufacturing, marketing, sales, and other activities.
At the same time, business administration, which is sometimes focused on specific industries, concentrations, or job titles within a corporation, is the study of business relating to operations and leadership.
| Basis | Business Management | Business Administration | Project Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Overall operations | Daily operations | Single projects |
| Purpose | Manage and organize operations | Manage departments | Manage single projects. |
| Role of manager and team members | Temporary | Permanent | Permanent |
| Complexity | More complex | Less complex | Less complex |
| Management | Permanent | Permanent | Limited as per the deadlines |
