Table Of Contents
What Is A Brokerage Firm?
A brokerage firm is an entity that links buyers and sellers of financial securities. They act as the middlemen in executing transactions and transferring asset ownership. Financial experts capable of offering complete investment services such as financial advice, risk management, etc. constitute these firms.
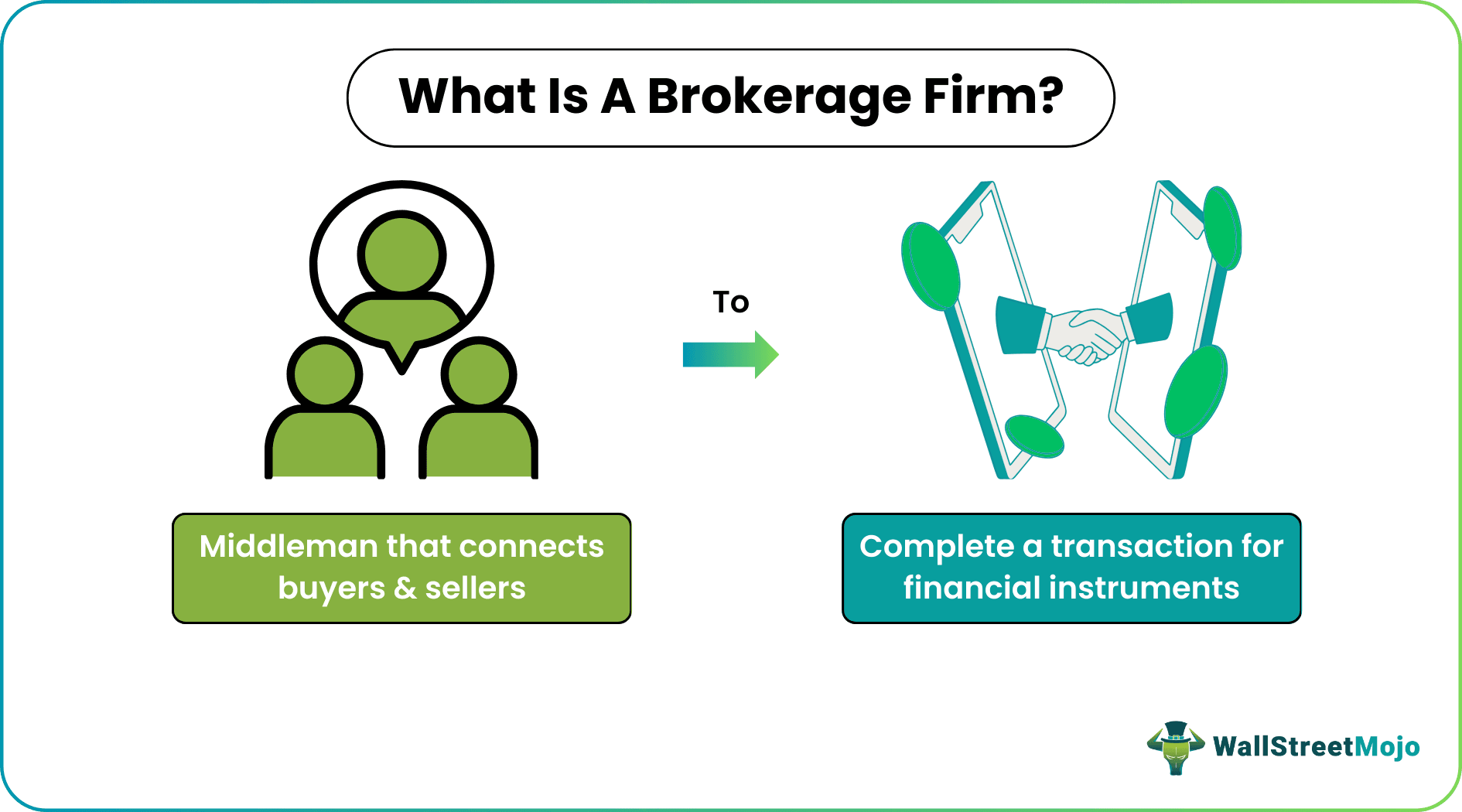
Also known as a brokerage company, they collect commissions or fees based on the extent of the services they offer. Stock brokerage firms have become essential players in trading due to the complexity of the process and the increasing number of buyers and sellers from different geographical regions.
Key Takeaways
- A brokerage firm is a business entity that acts as an intermediary between sellers or issuers of stocks and buyers. Its primary function is to provide a platform for these parties to engage and facilitate their transactions.
- The term 'brokers' is also used for intermediaries or middlemen holding stocks and other instruments. Irrespective of this, the broker or firm has to adhere to the capital requirements.
- They facilitate transactions and offer various services, such as investment advice, market analysis, and access to trading platforms.
Brokerage Firm Explained
Brokerage firms are significant components in investing. They provide a common platform for issuers, sellers, and buyers to fully understand what they are buying, other options, and prospective parties with whom they can engage in transactions. It is the most basic function of brokers.
Currently, there are many financial instruments worth trillions of dollars with thousands of companies and millions of investors. With brokerage companies, the math becomes simpler. Buyers do not have to interact with sellers or issuers but engage in financial transactions that provide value.
Brokers enhance the number of alternatives with investors and companies. Reputed and authorized brokers can also protect investors from falling prey to fraudsters. Another advantage of trading through brokerage companies is their margin account facilities, which enable investors to buy securities using borrowed funds.
Some top brokerage firms include Charles Schwab, E*Trade, TD Ameritrade, etc. Professionals in these firms have brokers who stay in contact with companies and depositories, financial advisers, and tax experts who mainly focus on customers. These companies are often contrasted with investment banks.
Real estate brokerage firms are of different types – full-service brokers offering comprehensive services from money management to tax advice, online discount brokerages, and robo-advisors that are automated and algorithm-based.
Brokers of any type charge commissions or fees. It forms a significant portion of their revenue. The prices depend on the range of services they offer clients or the transaction amount they execute. The fees are mostly charged as a percentage. While no standard rate changes from company to company, most firms charge around 1-2% of transaction value.
Nowadays, it is straightforward to avail brokerage services online using websites and mobile apps. These are available 24x7 and also charge significantly lower fees.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
How To Start?
The most basic requirement for starting a brokerage company is the people. The company should constitute professionals who can provide comprehensive services to their clientele – such as financial professionals, tax experts, brokers, etc.
Brokerage companies must register with the financial regulatory authority of the country where they operate. For instance, a brokerage company in the United States should be registered with FINRA. It allows the power to monitor the company and their activities. It is also essential in protecting investors from fraudsters.
Their capital requirements are another significant point stressed by the regulatory authority. Brokerages offer margin loans to their customers. They also need a minimum amount of money to finance other activities. FINRA specifies a minimum capital requirement of $250,000 in the United States.
Finally, as with any business organization, the company has to adhere to laws about income, taxes, human resource management, customer management, etc.
Examples
Refer to the examples given below to understand the concept.
Example #1
Suppose ABC is a stock brokerage firm. The firm's clientele mainly includes publicly listed companies, investment banks, and experienced investors. It offers essential brokerage services by linking issuers, sellers, and buyers of stocks. It does not provide any other services. Therefore, its revenue mainly comes from commissions. The fees are charged based on the transaction amount and volume.
Example #2
In 2019, Charles Schwab, the largest brokerage firm in the United States, substantially altered its revenue structure by removing trading fees. These fees had comprised a notable portion of its earnings at the time. The move was intended to help the firm manage against low-cost competitors.
Initially, the company planned to gain a larger market share through low fees and invest the cash from its platform for profits. It made the company the largest broker in the country, with client assets worth $7.4 trillion. However, surging interest rates by the Fed have adversely affected the firm's plans. Consequently, its shares have plunged by over 40% in 2023.
Brokerage Firm vs Investment Bank
While investment banks and brokerage companies share similarities and offer overlapping services, their fundamental objectives and functions diverge.
Let us understand the differences between them.
- Brokerage companies primarily focus on connecting buyers and sellers within financial markets. In contrast, investment banks are driven by the goal of maximizing returns for their clients.
- Brokerage companies assist clients in executing investments of their preference. Conversely, investment banks are pivotal in guiding investors' decisions regarding asset purchases or sales, relying on analysis and strategic insights.
- Brokerage companies act as intermediaries to facilitate transactions between parties. On the other hand, investment banks provide a broader range of financial services that extend well beyond facilitating transactions.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The applicability varies. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), a U.S. government agency, offers insurance for bank deposits. Consequently, solely brokered certificates of deposit are eligible for FDIC insurance, excluding other instruments like stocks, bonds, and similar assets.
Yes. While changing brokers is slightly complicated, there are a few ways to do this. Investors can transfer their investments from one brokerage account to another, sell their assets, and transfer their cash.
Brokerage firms maintain copies of trade confirmation for three years. Details of transactions are kept for at least six years.
Individuals can invest in publicly traded brokerage firms by purchasing stocks on stock exchanges. It allows individuals to benefit from the firm's performance and growth potentially.

