Table Of Contents
What Is Brokerage Fee?
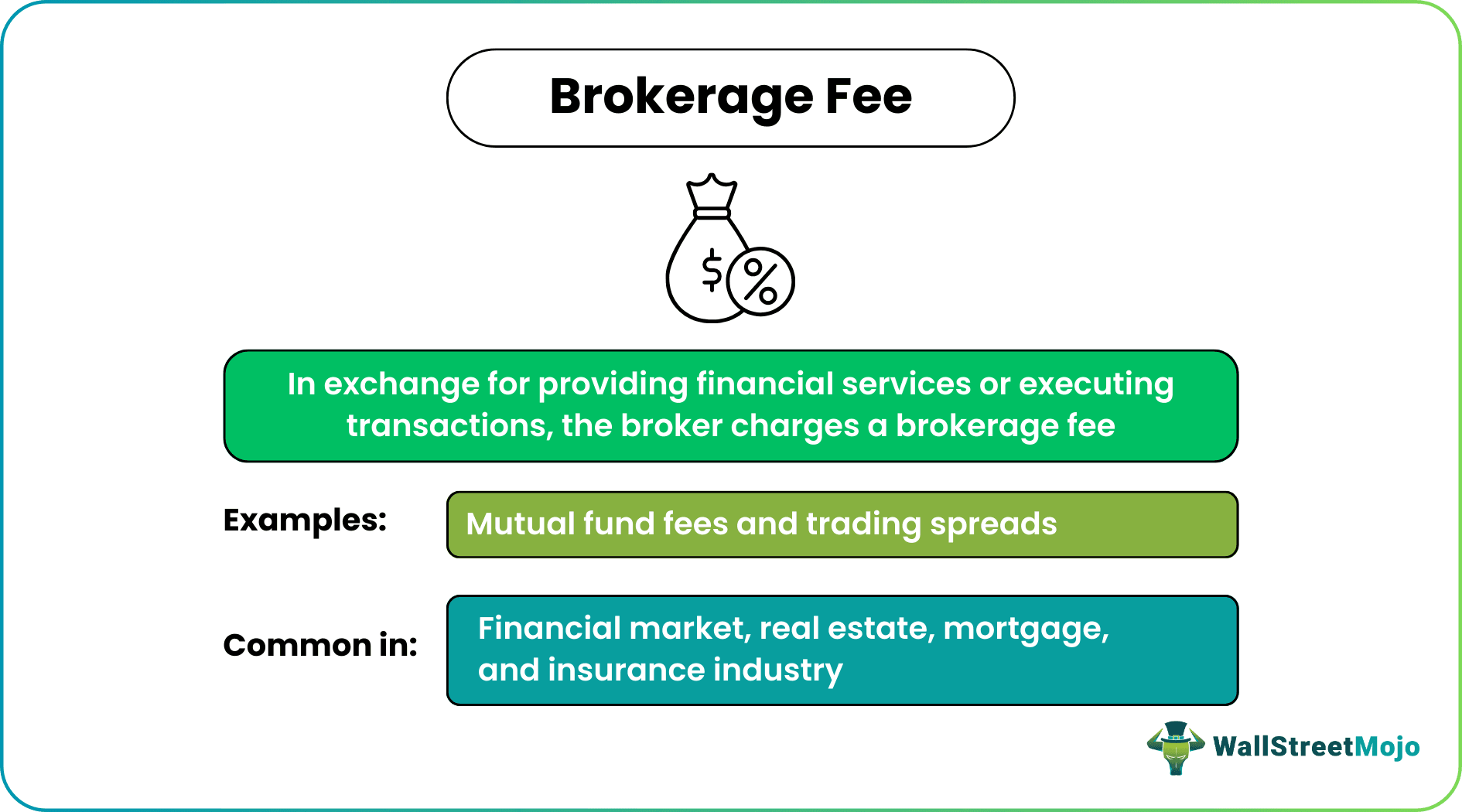
A brokerage fee refers to the broker's remuneration or commission for providing services and executing transactions based on client requirements. It is usually charged as a percentage of the transaction amount.
For helping investors find the best deals, brokerage fees are typical in real estate and financial services. For instance, fees are paid to a mortgage broker for arranging loans and real estate brokers for finding rental properties or assisting in the selling process.
Key Takeaways
- Brokerage fees are the compensation brokers receive for their services and can be a fixed value per transaction or a percentage of the transaction amount.
- Brokerage services provide benefits such as assisting clients in finding the best deals, fast transaction processing, and ensuring investment returns.
- Common types of brokerage accounts in the financial security industry include full-service, discount, and online brokerage accounts. Full service offers many services but is more expensive than other modes.
Brokerage Fee Explained
Brokerage fee agreement is the charge that the client has to pay to the brokers for carrying out any kind of financial transaction on behalf of the client. It may be related to both trading and non trading transactions. The fee, after being added up over a time period can become quite a significant amount. This can reduce the client’s return on their portfolio.
Brokerage fees are credited to brokers for making the investment practices smooth for their clients. A broker may be an individual broker or a brokerage firm connecting a buyer and seller. Through research, people can find brokers who offer great perks while not having high fees. However, this fee is not tax deductible.
People resort to brokers' services to execute a transaction or invest their money if unfamiliar with investment strategies. From their perspective, applying the broker's knowledge level will increase the likelihood of return by mitigating the potential risk associated with the investment choices.
There is no fixed brokerage fee agreement, and diversity in fee structure is prevalent across industries. Instead, brokers obtain the fee based on predetermined methods like fixed percentages, flat fees, and consignment fees. For example, under a fixed percentage commission system broker gets a fixed rate of the amount of trading as a commission. The brokerage fee for real estate transactions involving private homes in the United States is around 6% to 7%.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Fee Comparison
Let us look at the brokerage fee comparison in different sectors.
#1 - Real Estate
Selling real estate is hard work, and paying for the real estate brokerage fee is usually legal. Nevertheless, people depend on broker services to ensure a maximum return in the real estate industry.
Brokers are experienced in selling strategies enabling the faster sale of assets. Seller and buyer can have different brokers representing their side, while a single broker representing both buyer and seller is also typical. Conventionally, it is the seller who pays the commission. However, there are events in which both buyer and seller agents share the broker fee.
The price movement of real estate brokerage fee implies different trends in different countries. Usually, it increases with the value of the asset sold and the complexity of the sale process. However, in some countries like Finland, commissions associated with selling high-priced private homes are comparatively lower.
#2 - Financial Services
Brokerage services are essential to the financial services industry, and brokers charge their clients for assisting them in mortgage purchase, real estate transactions, helping investors buy and sell stocks, and so on.
Stock Market
Investors use brokerage accounts to trade securities like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds in the capital market. Brokerage handling the brokerage account connects the market and investors. Full-service brokers, discount brokers, and online brokers are the standard options available. Each one offers tailored services, but the cheapest options tend to provide a much lighter service.
Full-service brokers offer a fully-fledged pack of financial services, whereas discount and online brokerages provide only limited benefits. The fees also vary accordingly. The brokerage fee comparison discloses that the full-service one is expensive compared to discounts and online. Sometimes online brokerages have no brokerage fee offering for trading. In addition, there are a variety of charges associated with brokerage accounts changing with account types, for instance, advisory fee, trade commission, inactivity fee, and so on.
Insurance Fees
When it comes to insurance, people generally want the best overall policy. So, brokers utilize this opportunity and find suitable packages for their clients. Unlike agents, who work for the insurance company, brokers work for their clients. They act as the middlemen between the customer and the insurance company. Also, the brokerage fee percentage usually falls between 2% to 8% of the insurance premium in the United States.
However, it's essential to see that paying broker fees is not making the whole process of acquiring insurance expensive.
Thus the above brokerage fee comparison helps us to understand the real world scenario.
Examples
Let us try to understand the concept through an example.
For example, imagine that an individual without much industry knowledge finds a policy that requires to pay $2,000. Whereas, with the broker’s help, he could have found essentially the same services for $1,600, charging only $160. This way, people can save money despite the broker fees. It’s also possible to negotiate the prices to reduce the value. In this case it has become quite expensive for the client to acquire the insurance through a broker.
How To Calculate?
Calculating the fee based on the prearrangement between seller or buyer and broker is a straightforward.
Consider a house that is sold for $400,000, and the brokerage fee percentage is 6% of the selling price. So 6% of $400,000, that is $24,000, will go to the broker, and the seller will get $376,000 at the end of the process. On the other hand, if the firm has set a flat fee, say $5000, clients should pay that amount regardless of the size and complexity of the transaction.
Brokerage Fee Vs Commission
A brokerage fee is a charge that a broker takes to execute any financial transaction on behalf of their clients whereas a commission is a type of brokerage that they charge for stock trading.
The commission is based on the volume of trading done, or it might also be a fixed amount, whereas brokerage can be for trading and non-trading purposes.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Banks typically generate brokerage fees by acting as intermediaries in financial transactions, such as buying and selling securities on behalf of clients. They may charge a commission or fee based on the size or complexity of the transaction or through other arrangements, such as markup/markdown on securities prices or management fees for investment accounts.
Government organizations typically do not charge brokerage fees as they are not engaged in commercial brokerage activities. However, they may incur costs related to brokerage services when conducting financial transactions, such as buying or selling securities, which may be passed on to taxpayers or included in the overall cost.
Charging a brokerage fee may be considered illegal in scenarios that violate applicable laws, regulations, or industry standards. For example, charging excessive or undisclosed fees, engaging in fraudulent activities, or charging fees without proper client authorization may be considered illegal and subject to penalties or legal action.

