Table Of Contents
What Is A Brokerage Account?
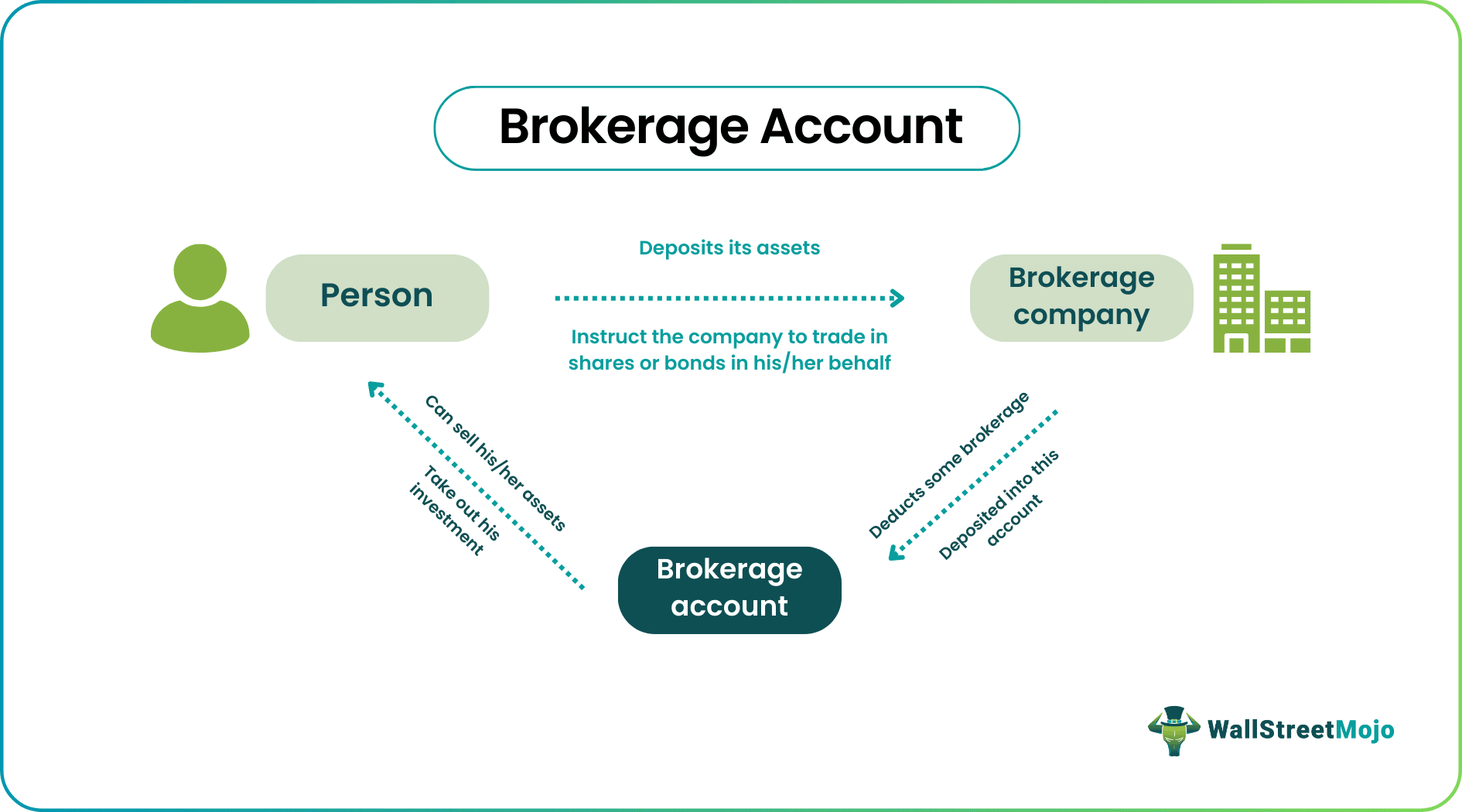
A brokerage account is one that investors/traders open with brokerage companies for the latter to handle the purchases and sales of securities on behalf of the former. The account is an investment arrangement that allows institutional and individual investors to deposit an amount for the brokerage companies to use when they find a fair deal.
A brokerage account is different from a tax-advantaged retirement account, with the former being a taxable investment system. The account deals with all assets, including stocks, mutual funds, bonds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), certificates of deposits (CDs), and other securities.
Key Takeaways
- A brokerage account is an account that holds the assets of the investor, and the investor instructs the broker/brokerage firm for the purchase, sale, trading, or operation of the assets held.
- The investor deposits the assets in the account and instructs the broker to buy/sell/trade on their behalf.
- The brokerage account can charge a monthly or annual fee or allow the investor to operate the account, featuring a low fee.
- A brokerage account can operate on either a Cash Basis or a Margin Basis wherein the brokerage account can also provide credit funds for investing/trading.
How Does A Brokerage Account Work?
A brokerage account is accessed by the brokerage companies on behalf of the clients who invest in stocks and other types of securities. The latter deposits a certain amount of money into the account and allows the brokerage agents to use the funds to buy and sell financial instruments. The brokerage firms, in turn, keep a watch on the market and take trades on behalf of the investors/traders.
Investors can use this custodial brokerage account for short-term and long-term profits. It is termed as custodial as the brokerage agent or company holds the responsibility of maintaining and operating the account as a custodian for the securities on behalf of the actual owner. The process of opening the account is similar to that of any other savings or investments account that one starts.
Investors must apply with the required brokerage firm to open an account. First, they fill up their personal details and their Social Security number. As soon as the application is approved, traders can start depositing the money in the account for the brokerage firms to begin taking trades.
Though the accountability rests on the brokerage firms, the guiding force is always the investors. They are the ones who give instructions to the former in accordance with which they act. The brokerage unit buys and sells the securities, but the account holder decides where to invest for maximum profits.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Types
Before they choose the best brokerage account options, market participants should know the various categories in which they are available. These taxable brokerage accounts are classified based on ownership, deposits made, and fees paid.
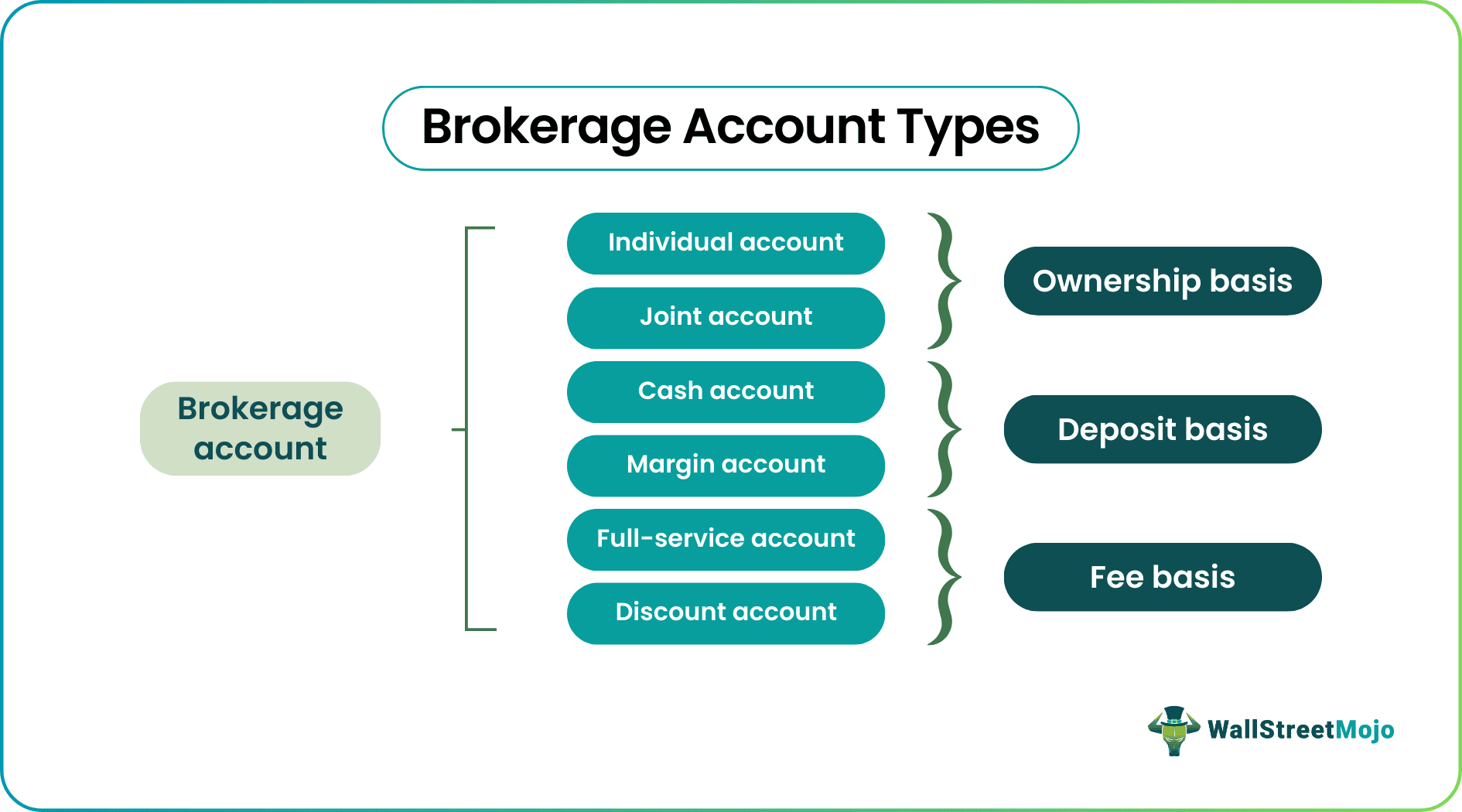
#1 - Ownership Basis
Firstly, these accounts offer different ownership facilities, giving investors two types of accounts segregated based on the ownership type.
- One is the individual account, which only one owner operates.
- Another one is a joint account, which more than one account holder use. Such accounts are co-held by spouses, family members, or relatives having similar financial goals. In case of the death of one owner, the other one has the right to have a share of the profits of the decedents.
#2 - Deposit Basis
Secondly, the segmentation is done based on the mode of deposits made.
- One is the cash account, where the traders should pay the entire amount to purchase the securities. In this case, the former cannot borrow any amount from the brokerage firm.
- The other is the margin account, in which investors can borrow money from lenders to buy securities. This loan is backed by the securities in question as collateral. This type of brokerage account makes investors liable to pay interest costs whenever the brokerage firms lend money for trade.
#3 - Fee Basis
Thirdly, the classification is done based on the fee structure. The taxable brokerage account is divided into full-service and discount accounts.
- The former provides investors with financial advice from experts from Morgan Stanley, Wells Fargo, etc.,
- On the other hand, the latter receives all investment options but no expert consultation.
Those with a full-service account get a chance to discuss the market conditions and trends with the best sources and then decide whether to make an investment. The brokerage firms pay the advisors for the advice they share with clients. Thus, these are highly recommended options for amateur traders.
How To Open A Brokerage Account?
Earlier, the process of opening a taxable investment account was time-consuming and required a lot of effort. However, investors can open a brokerage account and find brokerage firms that help in conducting the process online.
Users can open the account online easily in a few minutes:
- Interested investors/traders can fill in the application form, enter their personal details, and upload identity proof.
- In some cases, the users post the documents to the account address for verification.
- Once the authorities approve the application, the account becomes active.
- After account activation, the investor transfers the deposit amount from their savings account to these taxable accounts.
- At the account opening, the investors must choose the type of account they would like to open.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the brokerage account definition better:
Example 1
Mario decided to start with stock trading. However, he hardly knew anything about trading. Thus, he connected with a brokerage firm, Brook, nearby. At Brook, they recommended him to go for a full-service account, which was expensive but included expert consultation.
The amateur trader took it as an opportunity to learn and chose the full-service package over the discounted one. He learned from experts and invested after analyzing the trends and using the experience.
Example 2
Rachael has a margin account in which she had a deposit of $100. However, she monitored the market conditions and decided to buy stocks worth $150. As a result, she borrowed $50 from the brokerage firm. The additional stock worth the lent amount automatically became collateral backing those $50. This $50 was available to the trader for an interest payment until she returned the amount in full.
Opening a margin account is probably the best option for investors as they have an opportunity to borrow money from brokerage firms when they run short of funds. However, operating with such accounts could be riskier. Especially when the market is down, the brokerage firms might demand instant payment of the margin debt. This urgent demand for repayment of the loan is termed a margin call. The worst part is that the firm is not liable to notify investors of the early demand for debt payment.
Pros & Cons
A brokerage account has both advantages and disadvantages that investors and market players must know about.
Benefits
- This account is flexible and easy to use. It does not impose any income or contribution restrictions and offers a wide range of investment options to people opening it.
- There is no limit to the amount to be maintained in these accounts.
- Investors can withdraw money per their wish.
- There is one single statement to be maintained and investors do not have to have multiple statements to refer to finances.
Limitations
- The account is taxable. Investors are taxed when they sell a security or pay dividends.
- Based on the type of account held, investors may owe dividend taxes, capital gains taxes, etc.
Brokerage Account vs IRA
Often, a brokerage account is considered similar to a retirement account, like an Individual Retirement Account (IRA). However, the nature and type of these accounts widely differ. Here is a list of differences between the two.
| Parameters | Brokerage Account | Retirement Account |
|---|---|---|
| Law | No rules and regulations to guide the account operation | There are government rules that guide the operation of these accounts. |
| Taxes | Taxable | Tax-advantaged |
| Contributions | Unlimited | Capped annual contributions |
| Utilization | Trading various assets and securities, including stocks, bonds, CDs, mutual funds, etc. | Acts as retirement savings |
| Withdrawal | No limit | No withdrawal before a certain period |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A brokerage account does not offer a definite gain or increment in the assets held or investments. However, if the brokerage account is of a Full-Service type, it offers professional expertise and guidance.
To open a brokerage account, an individual/organization must have an Aadhar card, Pan card, and Bank Proof for all the proofs required to open and verify the account.
A brokerage account is necessary to buy and trade securities in India. You can open a Brokerage/Demat account with institutional brokers or online brokerages such as Swastika, Zerodha, etc.

