Table Of Contents
What is Bottom-Up Forecasting?
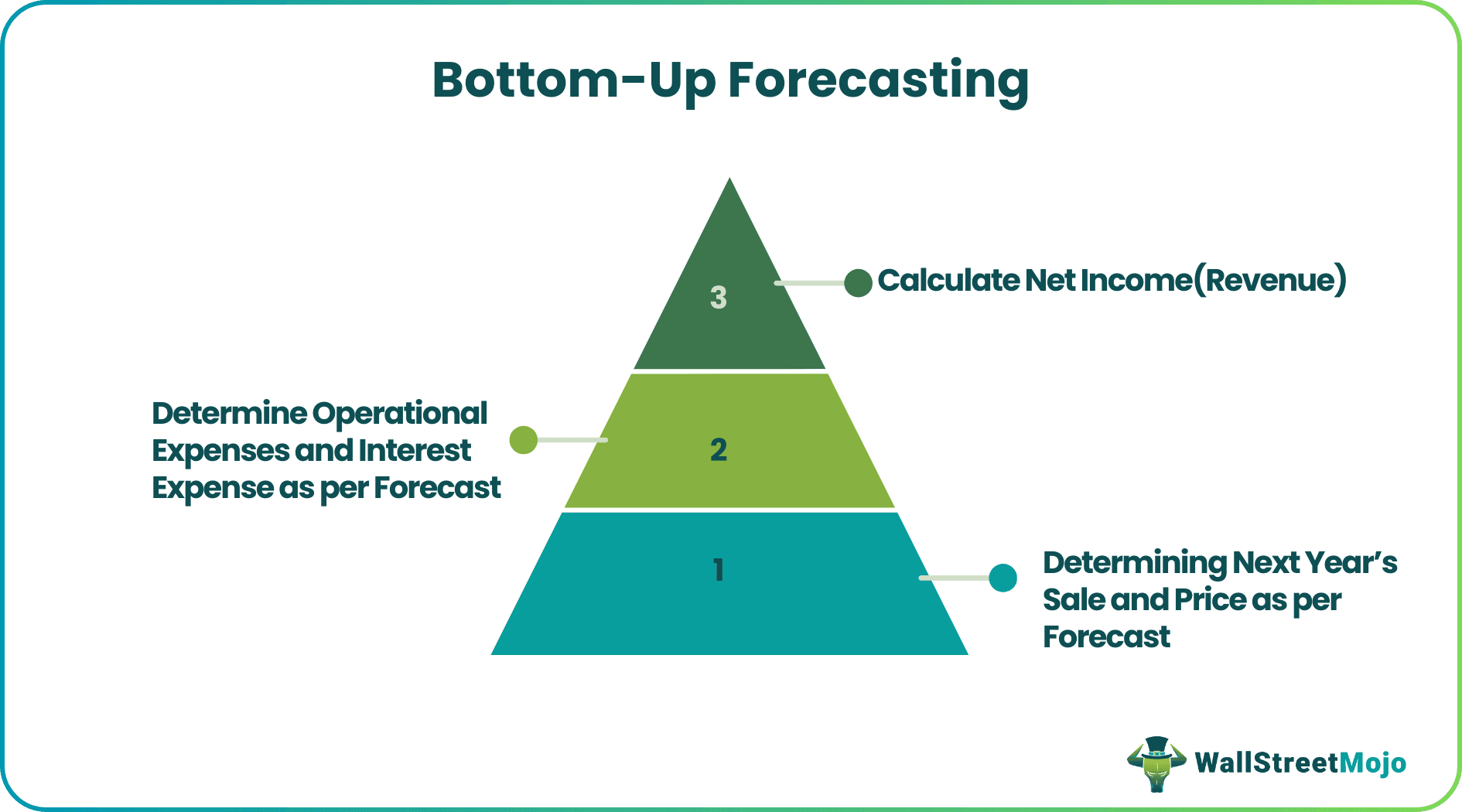
Bottom-Up forecasting refers to the projection of micro-level inputs of a company to reach the revenue and income for a particular year. However, estimation of these micro factors that leads to the payment is difficult to forecast as it is company-specific and depends on various factors.
Example of Bottom-Up Forecasting
Let's take an example to understand the concept:
Company ABC is a pen producing company. An investor is trying to forecast the company's revenue for the next year. The details are mentioned below:

Use Bottom-Up Approach to calculate the revenue
Solution:
Step #1: Determining Next year's sale and price as per forecast

Step #2: Determine Operational Expenses and Interest Expense as per Forecast


Step #3: The overall income statement looks like this -

Bottom-Up vs. Top-Down Forecasting
Bottom-Up Approach starts with Micro factors that are company-specific and reaches the revenue. On the other hand, the Top-Down approach helps forecast a company's revenue by using macro factors. In the Top-Down approach, the GDP is forecasted to determine whether the sell quantity of a company will increase or decrease. Sector-specific aggregate demand is forecasted to determine the demand for goods. Relaxation of export terms also increases the demand for goods. Depreciation of currency increases the demand for goods. So all these are macro factors that are considered while doing Top-Down Forecasting.
Advantages
- This approach is more practical than Top-Down. In Bottom-Up forecasting, the actual sales of a company are predicted by seeing its products' demand in the market as the demand is being compared from the previous year to the current year. So it is more realistic. It deals with the company's fundamental data.
- This approach is dependent on the company’s data, so they are accurate. A Financial Analyst will not have to depend on third-party data to do the forecasting. Real data makes the forecasting stronger as the trends can be validated from the company’s past data.
- Companies may have different segments. Bottom-Up finds the demand of each segment, so it will help companies allocate resources accordingly. It makes the company more efficient while making capital budgeting decisions.
- As the decision is based on micro factors, it gives a clear picture of the company's higher management. Management is aware of the expenditure being conducted by each segment and whether it will be possible to reduce the expenditure to improve productivity.
Disadvantages
- It involves several micro factors, so it takes time for the study to get completed. All micro factors must be properly forecasted for this approach.
- It is costly. It will require a team dedicated to gathering data from individual departments to carry out the approach. So it is costly to make the forecast.
- The specific department will provide the data collected as per their productivity level. If a decision is taken as per the data, then it may happen that the forecast will not match reality if the key members of the team change.

