Table Of Contents
Borrower Meaning
A borrower refers to an individual or business entity that receives a financial loan, asset, or service from a commercial lender on credit. They receive it on a pre-determined agreement on fixed tenure and repayment terms along with a necessary guarantee based on the debtors' credit score. Borrowers help to circulate money in the economy to fight inflation and its growth.
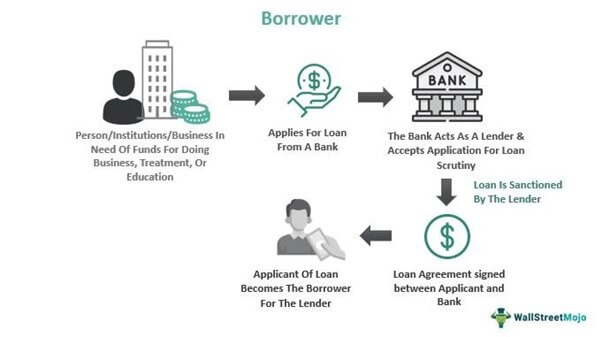
Many big business or industrial projects like mining need huge fundings, which is only possible through borrowing from lending institutions. Even expensive medical treatments, education, and homes result from debtors' lending from banks. Borrowers are the backbone of banks as they earn through interest accrued on debtor’s accounts.
- The borrower is any business entity or person who seeks the help of financial institutions called lenders to borrow the desired funds for investment or personal use.
- The lender and the debtor must sign a legal loan agreement regarding repayment terms and the payment schedule for the loan.
- A debtor has the right to full disclosure of the terms and conditions of the loan by the lender. Also, they must repay the loan as per the loan agreement without fail and get the closure done.
- Debtor and lender are two faces of the same coin, with both earning from each other's needs like the debtor needs a loan for business to earn, and the lender needs debtors to earn profit through interest on the loan-related charges.
Borrower Explained
A borrower describes an individual, entity, or organization applying for funds, i.e., a loan from a lender under an agreement to repay the same later. They are also called the debtor, the legal entity that owes a debt. The loan comes with the payment of interest at agreed terms and conditions between the two. The lenders, also known as creditors, can be an individual entity, a firm or a business, a government, or an organization. Moreover, the lender can demand funds from the debtor as per the nature of the loan granted.
Furthermore, the debtors can borrow money from the lenders for any purpose like marriage, treatment, education, and business.
If the debtor fails to abide by the loan agreement, the lender has the legal right to demand the loan amount and charge certain penalties and interest to the debtor. For any loan, the debtor has to provide all the details to the bank, accept the loan agreement, and use the loan amount for the loan taken from the bank.
A mortgage co borrower is a person or an entity who shares the liabilities with the prime debtor. The lenders hold both of them responsible for loan repayment. In some cases where the debtor has a poor credit rating, a co borrower gets used to granting a loan to the debtor. And in many cases, people also prefer borrowing 401k from their retirement funds due to the lower interest rate. However, in the long run, it has negative effects on the retirement corpus, contribution to the 401k fund gets stopped, and the payable taxes gets doubled.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Rights And Duties Of A Borrower
With every loan comes the rights and duties of borrowers towards the loan. The debtor's rights and duties are different as per agreements. Debtors' rights include:
- The loan agreement must conform to the debtor's needs.
- A debtor must get the loan agreement and the documentation in hard copies from the lender.
- The debtor shall get monthly loan statements where the intermediaries record the proof of payment.
- The lender must provide the credit score to the debtor.
- Lenders must not take hidden charges or terms besides those listed on the loan agreement.
The debtor's duties are as follows:
- Give consent to the lender for extracting credit score from credit rating agencies and pay for it if any charges are involved.
- All the documents related to personal information and financial information must be bonafide without any forgery.
- A debtor must honor the loan agreement.
- They must pay the installments within the stipulated time.
- They must not default on repayment of the loan.
- The debtor must utilize the loan amount for which the bank has sanctioned the loan.
Examples
Let us take a closer look at some of the borrowers' examples to understand the topic better:
Example #1
Suppose a student named Martha wants to pursue higher studies in one of the best management colleges. But she does not have enough money. Hence, she applies for an education loan in a leading American bank, provided she has:
- Filled out the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
- Obtain a student aid report (SAR) containing the expected family contribution (EFC).
- Afterward, colleges will send appropriate student financial aid per EFC and SAR.
- Then, the student has to accept one of the proposals and move forward with acceptance.
- As a result, the college will inform the student of the loan amount in the award letter it sends to them.
- Students sometimes require entrance counseling when they are first-time debtors.
- Suppose the student is qualified for federal loans. In that case, the federal student loan will forward the amount to the student's college for disbursal of the loan amount covering fees per semester, cost of books, and supplies, including living costs.
In this case, Martha is the debtor, and the American bank is the lender. The approval of the loan will depend on the terms and conditions of the bank, acceptance by the student, and qualifying for a federal student loan.
Example #2
In case of person A intends to apply for a home loan from an American bank, then it has to provide the following details:
- Social security number
- Employers' details
- Annual gross income
Then the person has to visit the branch with the details to apply in the bank format. After the credit scoring process, a loan agreement containing the payment schedule, rate of interest, and other details get finalized.
In this case, A is the debtor, and the bank is the lender.
Example #3
In the United States, on August 16, 2022, the Education Department announced that it would cancel federal student loans worth $4 billion for those who attended ITT Technical Institute. The popular for-profit institution defrauded 208,000 borrowers. Thus, the department will discharge student loans that borrowers received to participate in ITT from January 1, 2005, till the institution's closure in 2016.
The Federal Student Aid chief and former director of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, Richard Cordray, said that this action would remove the unnecessary, unfair debt burden and allow them to resume their education.
Differences Between Borrower And Lender
A lender and borrower, i.e., debtor, get linked up with the common factor of loan amount and its related interest. However, there are certain differences between lenders and borrowers, as listed in the table below:
| Particulars | Lender | Borrower |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | A lender is a person or entity that seeks funds from a lender. | A Borrower is a person or financial institution providing monetary credit to the debtor. |
| Role | They must repay the loan amount to the debtor. | They have the right to ask for loan repayment from the debtor. |
| Rate of interest | They must pay the interest rate for the loan amount till the closure of the loan. | They are obligated to collect the interest rate besides the principal amount. |
| Tenure | The debtor can pay the full term per the loan agreement or even foreclose the loan. | The lender can also ask for debt settlement per the agreement but cannot force the debtor to foreclose the loan. |
| Loan sanction | A debtor cannot force the lender to borrow the funds against the lender’s approval. | Lenders are free to approve or reject the loan application of the debtor. |
| Inflation | Debtors benefit from the inflation | Lenders suffer from the inflation |
| Credit score | Debtors' application depends on their credit score and financial status | Banks have the freedom to use any credit rating agencies and credit rating models to judge the debtors' capacity for a loan. |
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A co borrower is a person without which the co debtor, the primary loan applicant, may not get any loan. As a result, the co borrower is equally liable to pay the loan if the primary debtor fails to do so. For instance, the father can become the co borrower for his ward's education loan.
Investors doubt the borrower’s creditworthiness when the latter has a lower credit rating. In case investors doubt the creditworthiness of a debtor, then the price of the security bond will climb down, resulting in higher yields for the bond.
Debtors benefit from the inflation compared to lenders as the debt services, and their repayment does not depend on a country's inflation rate. Moreover, to ease inflation, central banks reduce the bank rates to ease the flow of money, forcing the lenders to reduce the rate of interest rates on all loans.
Normally, the primary debtor is entitled to take the car and use it. However, the co borrower has no right to take the car.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Borrower and its meaning. Here we explain its rights and duties and differences with the lender with examples. You may also find some useful articles here:

