Table Of Contents
Bookrunner Meaning
A bookrunner is an entity, normally an investment bank that is the lead underwriter or coordinator during initial public offering (IPO) or issuance of new equity or debt. They collect bids from investors and close the bid at an issue price during an IPO. A bookrunner can also coordinate the running of a leveraged buyout (LBO).
The bookrunners are also responsible for keeping an investor's books in order. Their role can also extend to determining the position of other parties, such as investors. The bookrunners often syndicate with other banks to reduce their own operational risk. Due to the heavy workload, they also collect the largest fees.
Key Takeaways
- A bookrunner is the principal underwriter in the issuance of debt, initial public offering (IPO), or other financial transaction that has a large value. They also coordinate a leveraged buyout (LBO). In the case of an LBO, the bookrunner represents one participating company.
- The bookrunner plays a significant role in minimizing the risks associated with the process for their client and ensuring that there are no hitches on the way. The bookrunner is also burdened with monitoring the process without stressing the client.
- Bookrunners may need to work with and lead other underwriters. In this case, the group of underwriters working for a company is known as a syndicate.
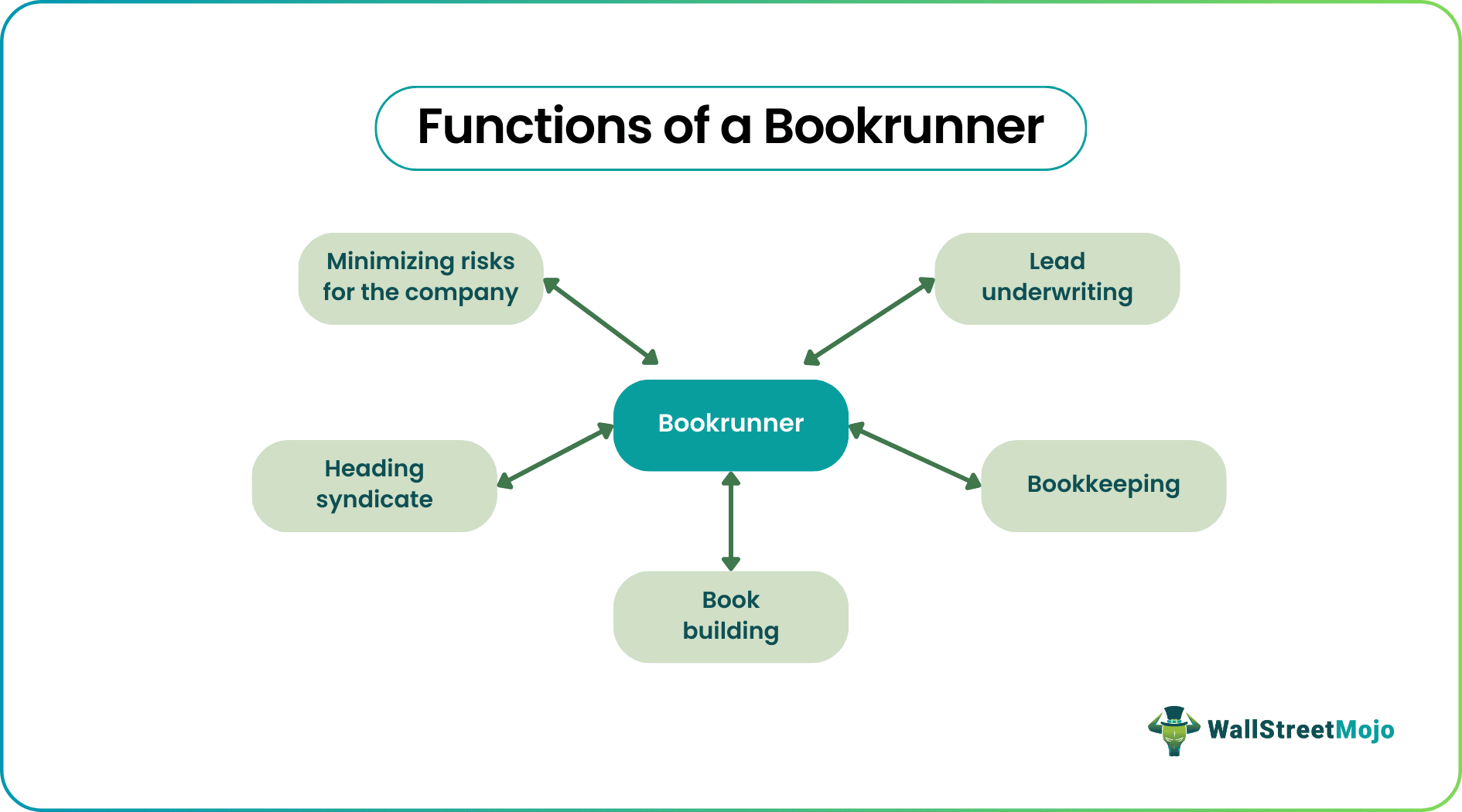
What Does a Bookrunner Do?
Bookrunners are an integral part of the underwriting of major investments. A bookrunner institution has several roles to execute with precision lest the investor sues them. They include:
- Primary underwriting- Large investments often need more than one underwriter. However, the bookrunner remains the primary underwriter, and they are in charge of keeping things organized.
- Initial offering- If an investor wants to issue bonds or IPOs, they often need a bank or a similar financial institution to assist them. The Bookrunners also have the role of issuing the bond either actively or passively. It is important since issuing IPOs and bonds requires a lot of work in terms of legal technicalities and financial responsibilities during the issuance process. Without stressing the investor, a good bookrunner would carry out the issuance properly. They may also need to ensure there are zero hitches before and after the issuance.
- Bookkeeping- Bookrunners are also in charge of bookkeeping. They must ensure that the financial records are current, up to code, and a truthful representation of the firm's or investor's financial position. Any false information is likely to lead to legal problems in the future since these books are the basis of tax obligations.
- Risk reduction- Bookrunners reduce an investor's or borrower's overall risk. They ensure this by working with a syndicate, a group of similar financial institutions. It is a common step during the issuance of equity and other securities.
- Head of the syndicate -Bookrunners are the head of the investor's syndicate and therefore represent the other firms in meetings and negotiations. During the latter, they consider the interests of the investor, other firms, and their own interests.
- Leveraged buyouts- In the case of an LBO, the bookrunner coordinates the participation of firms while representing one of them. They are also in charge of roadshows, discussions, etc.
These are just some of the functions of a bookrunner. Depending on the situation, these functions can cover a broad range, and some of them can even be unusual depending on the investor's or borrower's needs.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Example
Let us say a large company is looking to issue several IPOs. It will surely need several underwriters and other professionals to oversee the entire process. In such a case, the presence of the bookrunner will be enormously helpful to the company. The issuer can then concentrate on doing other IPO-related things, such as marketing.
In such a role, the bookrunner will serve multiple purposes. First, they will be responsible for the financial records related to an IPO. Before issuing an IPO, the regulating body (in this case, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)) has to go through the firm's books before giving the go-ahead to issue the IPO. It is to make sure that the company is fit to issue the IPO. The bookrunner is responsible for going through the books, correcting any errors, and keeping the books after the issuance of IPO.
If the IPO is large enough, it will need more than one underwriter. The team of underwriters, in this case, is called a syndicate. The bookrunners will act as the lead syndicate, representing all the other firms and making sure that they meet their interests. The issuer may sometimes require that the syndicate be a collection of only specific firms. In this case, they would provide their requirements to the bookrunners, who would then find other underwriters who fit the issuer's needs. All the underwriters in the syndicate need to get their license from SEC.
Issuing an IPO involves a lot of risks. If not managed properly, the issuance could flop, and the issuer could incur huge losses. One of the primary goals of the bookrunner is to first assess the issuer's risk and then reduce this to a minimum during the process. They also have to provide basic ideas for advertising campaigns to attract people to buy the shares. A good bookrunner should have experience in marketing and the psychology of the market they are dealing with, especially that of the issuer.
Joint Bookrunner
Joint bookrunners are the members of the syndicate who are also underwriters. Though they play a secondary role, they are a vital component in providing underwriting services in the syndicate. Typically, the lead bookrunner or arranger assigns the duties of a joint bookrunner. The lead bookrunner is also responsible for ensuring that joint bookrunners meet all their expectations. Since major financial exchanges need joint bookrunners, they must have an excellent reputation. If the situation demands, the joint bookrunner should also be capable of handling the role of a lead bookrunner.
Bookrunner vs Underwriter
An underwriter is a party (a bank or financial institution) that buys the shares sold through IPO and then sells them to the public. A bookrunner is typically the lead underwriter who is in charge of overseeing the process. The bookrunner is listed first among all the underwriters and controls the syndicate.
Bookrunners vs Lead Manager
Bookrunners are responsible for everything that has to do with underwriting. The role of a lead manager is to find leads to buy the IPOs and make sure there are no hurdles in the way. They also play a part in drafting the proposal for the IPO so that it is accepted by the SEC. Lead managers can also provide input in marketing the IPOs and help getting listed in the stock market.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The bookrunner acts as a primary underwriter while issuing new equity, debt, or other securities. They are in charge of bidding the shares of a company to the public and overseeing the process. They are also in charge of the books associated with the process.
An underwriter is an entity that buys the shares sold through An IPO and sells them to the public. A bookrunner is the lead underwriter in the initial public offerings and leveraged buyouts.
Lead coordinators are mostly associated with the operational and regulatory works of a company. They can also play a vital role in the marketing and listing of a company in the stock market. The bookrunners are primarily concerned with underwriting and controlling the team of syndicates. Bookrunners do the majority of work and collect the largest fees.

