Table Of Contents
What Is Bill of Materials (BOM)?
Bill of Material, also known as product structure or BOM, is a comprehensive list of items required for the manufacture of the end product, containing details of raw materials required, components, assemblies that are required either to construct or manufacture a product and which is used as the communication medium of manufacturing team with stores team.
Preparing a BOM can be considered one of the initial stages of the manufacturing process. Without this list, the manufacturing would not begin, given the significance of the list of materials to be assembled to begin the manufacturing or production process.
Table of contents
Bill of Materials Explained
Bill of materials (BOM) is a list of items that are required to manufacture a product. Until this is prepared, the businesses do not start the manufacturing process. This list contains the raw materials, parts, components, etc. to be brought together to begin the process.
This bill of materials not only contain the names of the items required to produce or manufacture a product, but also instructions on how to assemble them properly to make the best finished product out of them.
The bill of materials contains the specification of every item required to manufacture the end products. Hence, not only the raw materials but also subassemblies, subcomponents, sub-parts, and consumables are enlisted therein.
The top level of BOM represents the finished product. Further, it is broken down into parts to define the requirements. It is important to have a BOM accurately made to ensure no future issues arise because of errors. If this list is inaccurate, it would put the manufacturing process on hold, thereby disturbing the entire production, distribution, and sale schedule. In addition, it would involve high operating costs in controlling the damage done. This shows how crucial bill of materials management and preparation are.
Elements
Any Bill of Material should serve the purpose of manufacturing the end product without any hustle on the procurement of even a single item.
Following elements are required to create the same -
- Quantity: The BOM should specify the number of parts procured or manufactured for each assembly. Make sure that the optimum purchase order is placed. Quantity is the foremost requirement of BOM.
- Unit of Measurement: Per unit, inches, grams, kilograms, liters, square feet, cubic feet, etc., should be specified for each quantity. The purchase cost should be under the budget set for the project. It ensures that exact quantities are ordered.
- BOM Level: This helps understand all the elements of the Bill of materials. BOM level provides the number or ranking for each part. It may be Single-level BOM or Multi-level BOM.
- BOM Notes: This provides additional information regarding the bill of material other than the description of parts.
- Part Number: This helps track each part. Thus, a unique part number is assigned for each item for easy referencing.
- Part Name: The unique name of each item with a specific part number helps identify the item easily and more effectively.
- Raw Material: You should know the essential raw material for your end product. BOM should specify the same quality of raw material required in the manufacturing process.
- Description: Each part should have an adequate explanation about the part. It helps to distinguish between similar parts.
- Images: It’s good to have an image of a thousand words. It helps to cross-verify the BOM details with the image. Images of the end product help with an easy understanding of each component.
- Method of Procurement: The required parts or items may be purchased from an outsider or manufactured internally. Make sure that optimum discount is availed in bulk purchases of items from the same vendor.
Types
There are two types of bills of material.
#1 - Engineering BOM
It defines the design (i.e., drawing) of the end product. The engineering department makes such a design. The design itself specifies the requirement. It has alternate or substitutes for part numbers. The dimensions of each sub-assembly are also specified in such BOM. Each line of BOM specifies the description part, name of the part, part number, unit of measurement and its size, and other relevant specifications.
#2 - Manufacturing BOM
The requirements herein are specified from the angle of actual manufacturing rather than just designing. However, engineering BOM aids the manufacturing of BOM. MBOM specifies the processes which are required at the execution stage and thereby keeping all things ready for manufacturing activities.
#3 - Sales BOM
It is treated as a sales item rather than just an inventory item. The requirements are specified in the sales order document.
Structure
The structure of the BOM differs based on the types of finished products to be manufactured and extent of clarity required in the list. Let us look at the types of structure of these bills:
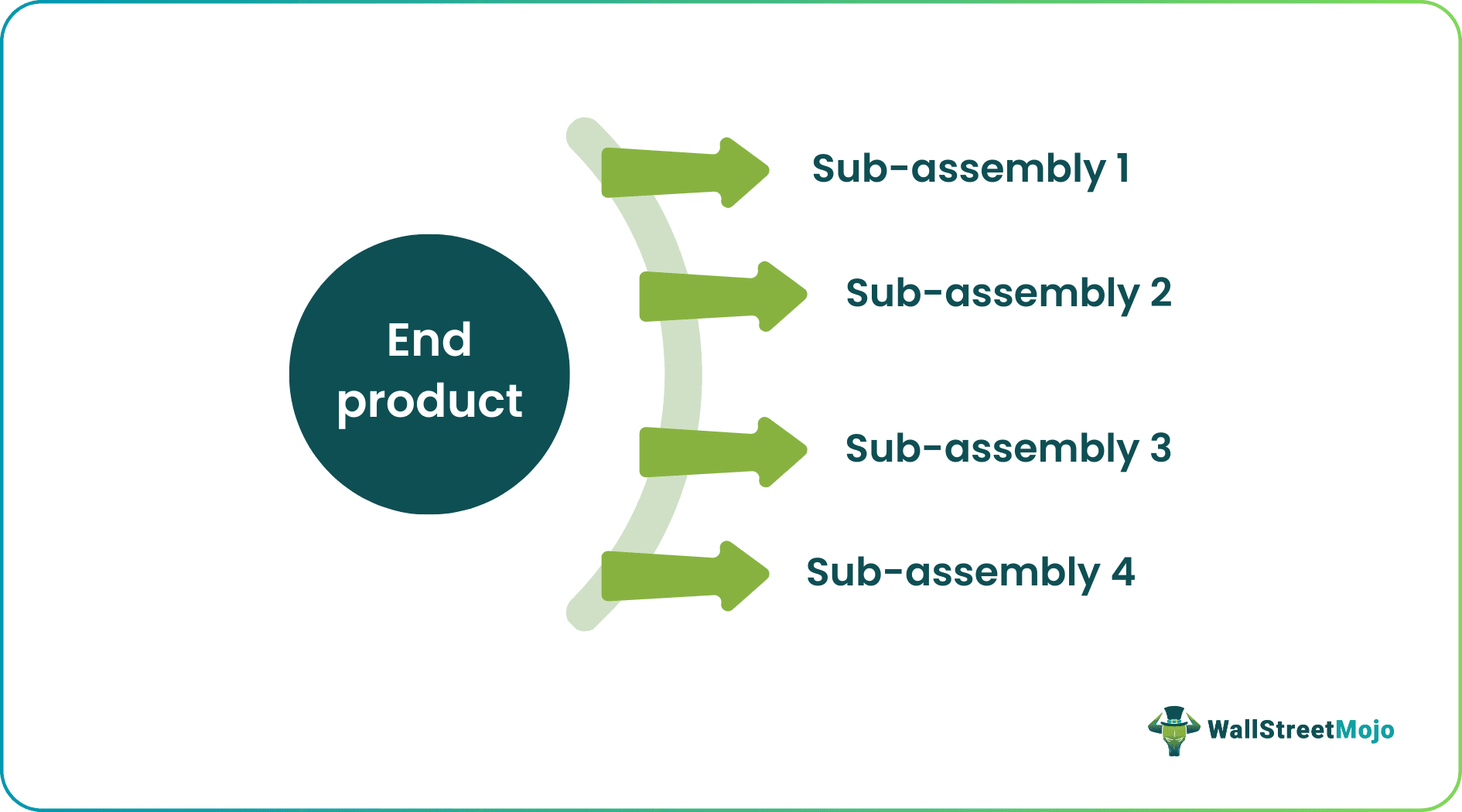
#1 - Single-Level
It is simple to prepare and use. However, in case of product failure, it is challenging to investigate which item requires replacement or repair. Further, such a structure of BOM is unsuitable for complicated products.
The basic structure has been shown below:
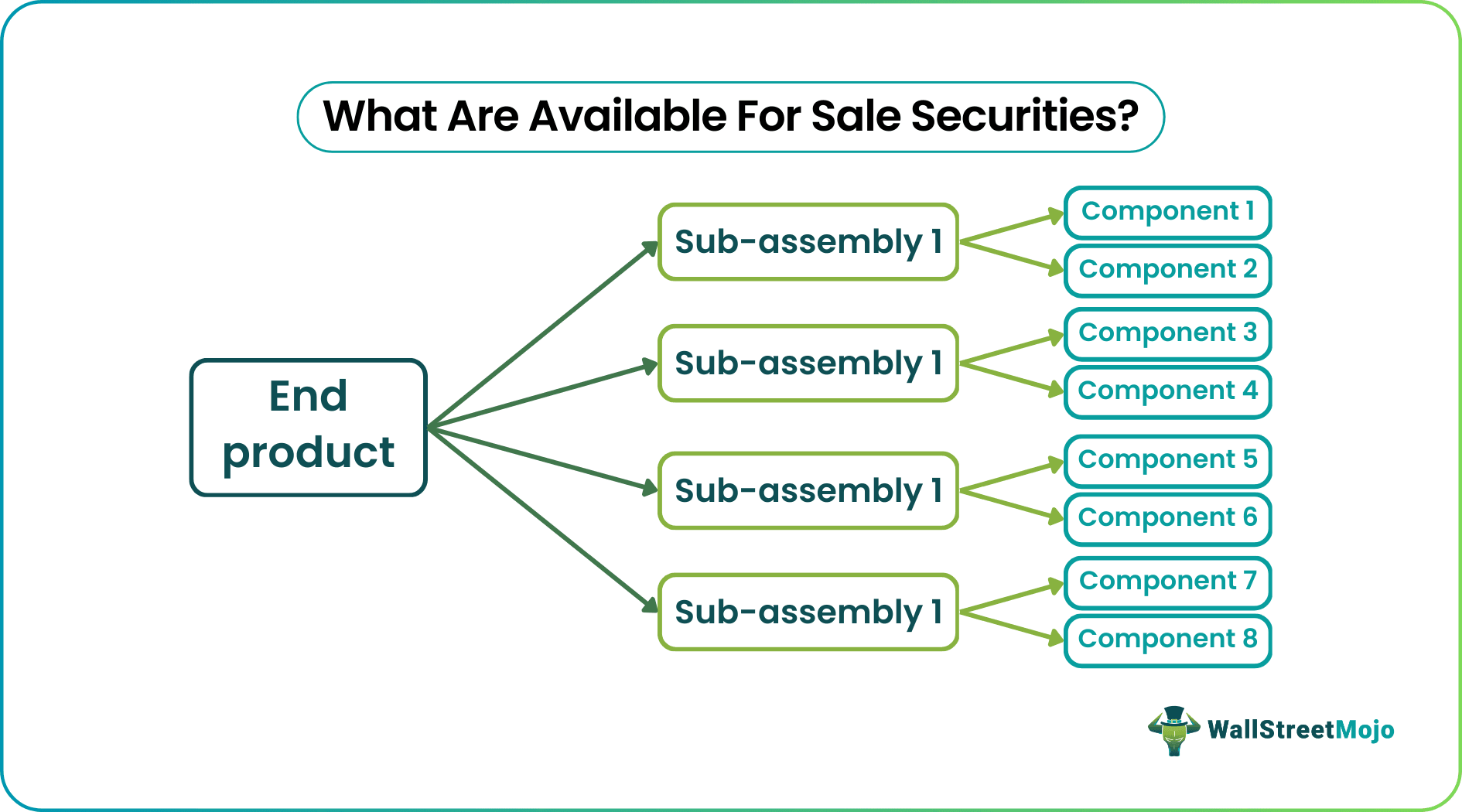
#2 - Multi-Level
Here the data is presented in a detailed tabular format with each column for Part Number, Part Name, Description, Quantity, Cost, additional specifications, etc.
Template
When it comes to preparing the bill of materials list, there are two factors that affect it – the business needs and the type of products to be manufactured. However, the template of the BOM is almost similar in all events.
There are two formats in which a bill of material can be displayed:
- 1. Explosion Format: It means to explode the end product into its component or parts (i.e., end to start)
- Implosion Format: It means to connect the individual parts to form an assembly at the highest level (i.e., Start to end).
Examples
Let us consider the following instances to understand the bill of materials definition and also see how to make it in Excel:
Example #1
A bill of material can be created in tabular or flow chart form. Creating a bill of the material requires knowledge of that sector. Detailed knowledge is not expected, but you should have a broad view of the product. As a basic example, we will consider the manufacture of bicycles. Let’s say there is a demand for 100 bicycles. The question is what parts/components/assemblies/subassemblies should be required. Well, there are so many types of bicycles. Deliberately, we consider "Mountain-bike" as complicated products so that BOM can be understood in a detailed manner.
Details of all significant parts of mountain-bike:

#1 - Basic BOM: (Flow Chart Format)
The flow chart format helps figure out how the manufacturing process would flow:

#2 - Detailed BOM: (Tabular Format)
The bill of materials sample below indicates how the list of items to be assembled can be shown in tabular form, which is simpler to understand:

Example #2
In August, US army officials called for industry inputs on the use of AI bill of materials. This call for inputs, however, aimed at encouraging entities to participate in the process and confirm where their AI algorithms emerged or began from. This came following the Pentagon’s attempt to support AI for quicker decision-making.
The motive of the US army officials behind including AI BOM in their settings is to reduce human risks in the battlefields that are highly influenced by advanced technology. This example shows how BOM finds relevance in every sector, including business and military setups.
Uses
These are the basic requirements of the manufacturing process. It only helps to compute the cost of purchases. After the BOM is confirmed, other costs, such as labor, manufacturing overheads, selling overheads, etc., are lined up further to identify the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- One cannot imagine a product without its BOM. It is the BOM that specifies all the components.
- Preparing a BOM is the most crucial aspect since anything not specified in the BOM will not be acquired.
- BOM helps identify the basic cost of components required to manufacture the end product.
- Once we have the cost of components, we can identify the assemblies we can get from a vendor instead of manufacturing them ourselves.
- It also helps to identify wasteful items that can be avoided.
- BOM helps in better decision-making whether to manufacture or buy it.
- It makes the manufacturing process a little cost-effective.
- BOM ensures that an overhaul all the components are considered.
Bill of Materials vs Bill of Quantities
BOM and Bill of Quantities (BOQ) sound similar, but they are two different concepts with different purposes to fulfil. Let us have a look at the difference between BOM and BOQ below:
- While BOQ is the list of materials along with their quantities and costs associated, BOM is the list of materials alone.
- BOQ is a concept that is more prominent in the construction industry, while BOM is the term that can be used in every sphere where finished products result out of the assembling of the raw materials, parts or components, etc.
- Bill of quantities provide clarity in terms of costs and materials in whatever quantity they are required. As a result, contractors get an idea on how much to bid for the project during the tendering process. On the contrary, BOM helps businesses in controlling the production/manufacturing process and estimating the cost of the finished products based on the list of items required to be assembled to finally develop them.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Bill of Materials (BOM). We explain the concept along with examples, template, types, vs bill of quantities (BOQ), and uses. You can learn more about it from the following articles –

