What Are The Benefits of An Investment Banking Course?
Table of Contents
What is Investment Banking?
Investment banking is a vital component of the finance industry that enables financial advice and facilitates capital-raising activities for corporations, governments, and institutions. Its importance in the financial world comes from its invaluable role in organizing the flow of capital between investors and issuers.
Thereby, they enable businesses to raise capital for expansion, acquisitions, and other strategic initiatives. Investment banks play a crucial role in underwriting securities, including initial public offerings (IPOs), debt offerings, and secondary market offerings, helping companies access capital markets and raise funds from investors.
Investment banks are also instrumental in providing strategic insights to corporates and other clients on mergers and acquisitions (M&A) transactions. These services help them identify potential targets or buyers, negotiate deal terms, and structure transactions to maximize value.
Additionally, investment banks engage in trading activities, including proprietary trading and market-making, to provide liquidity to the market and facilitate efficient price discovery. Areas of expertise within investment banking include corporate finance, capital markets, mergers and acquisitions, restructuring, and financial advisory services.
Investment bankers require a diverse skill set, including financial analysis, valuation techniques, negotiation skills, and market knowledge. These skills help them to advise clients and execute transactions effectively. Regulatory compliance, risk management, and ethical considerations are also critical factors in investment banking, given the industry's complex and highly regulated nature.
Key Takeaways
- An investment banking course provides a comprehensive understanding of investment banking, which involves advising corporations, governments, and institutions on financial transactions, mergers and acquisitions, and capital-raising activities.
- Gain specialized knowledge and skills in financial analysis, valuation techniques, and deal structuring. These skills are essential for roles in investment banking and related fields.
- Increase job prospects and career opportunities in investment banking firms, corporate finance departments, private equity, hedge funds, and other financial institutions.
- Acquire hands-on experience through case studies, projects, and simulations, preparing individuals for the demands of real-world financial transactions.
Functions of Investment Banks
Investment banks and bankers are the most in-demand segment of the financial market. Their functions are diverse to ensure all the needs of their clients are fulfilled. Let us understand a few of their most common functions through the points below.
- Underwriting Securities Offerings: Investment banks assist companies in issuing securities such as stocks and bonds by underwriting the offerings, pricing them, and facilitating their sale to investors to raise capital.
- Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) Advisory: Investment banks advise clients on M&A transactions, helping them identify potential targets or buyers, negotiate deal terms, and structure transactions to maximize value.
- Capital Markets Activities: Investment banks operate in the capital markets, facilitating the buying and selling of securities on behalf of institutional investors and providing liquidity to the market.
- Trading and Sales: Investment banks engage in proprietary trading activities, where they trade financial instruments such as stocks, bonds, currencies, and derivatives on their behalf to generate profits. They also have sales teams that market these financial products to institutional clients.
- Financial Advisory Services: Investment banks provide strategic advice to clients on various matters, including corporate restructuring, divestitures, and capital raising strategies. They help clients optimize their capital structure, enhance shareholder value, and navigate complex financial situations.
- Research: Investment banks produce research reports and analyses on companies, industries, and market trends to help investors make informed investment decisions. This research is disseminated to clients and used to inform investment strategies and decisions.
Types of Investment Banks
The different types of investment banks form a segment within a segment of finance. They cater to companies or other clients at different scales and provide a variety of services. The most common types are:
- Bulge Bracket Banks: These are the largest and most prominent investment banks, often with a global presence and offering a wide range of services across various sectors. Examples include Goldman Sachs, JPMorgan Chase, and Morgan Stanley.
- Middle Market Banks: These banks focus on mid-sized companies and transactions, providing investment banking services tailored to their needs. They typically have regional or industry-specific expertise and may offer services such as M&A advisory, capital raising, and restructuring. Examples include Piper Sandler and Houlihan Lokey.
- Boutique Banks: Boutique investment banks are smaller firms that have expertise in particular industries or types of transactions. They often offer personalized service, deep industry knowledge, and senior-level attention to clients. Boutique banks may focus on niche markets or sectors such as healthcare, technology, or real estate. Examples include Evercore and Lazard.
- Regional Banks: These banks operate in specific regions or countries, catering to local businesses and clients. They provide a range of investment banking services tailored to the needs of their regional market. Examples include Raymond James and KeyBanc Capital Markets.
Role of an Investment Banker
An investment banker is a professional with a deep understanding of investment options, asset classes, and financial data. They provide different types of assistance to their clients. A few of the most common ones are:
- Financial Advice: Investment bankers provide strategic financial advice to clients, including corporations, governments, and institutions, on various matters such as mergers and acquisitions, capital raising, and restructuring.
- Deal Execution: Investment bankers play a central role in executing transactions, including mergers, acquisitions, initial public offerings (IPOs), and debt offerings. They coordinate due diligence, negotiate deal terms, and enable the transaction proceedings from start to finish.
- Client Relationship Management: Investment bankers build and maintain relationships with clients. They also provide personalized service and address their financial needs and objectives. They act as trusted advisors, offering insights and guidance to ensure clients achieve their strategic and financial goals.
- Market Analysis and Research: Investment bankers conduct market analysis and research to identify opportunities, assess market trends, and evaluate the potential impact on clients' businesses and investments. They provide clients with valuable insights and recommendations based on their expertise and analysis.
- Risk Management: Investment bankers assess and manage risks associated with transactions, including financial, regulatory, and reputational risks. They curate strategies to alleviate risks and ensure that transactions are executed effectively and in compliance with regulatory requirements.
Career Paths after Investment Banking
The benefit of enrolling yourself in a detailed and reputed investment banking course is that you shall enjoy the luxury of choices in the world of finance and business. A handful of the most common career paths after investment banking are:
- Private Equity: Many investment bankers transition to roles in private equity firms, where they focus on investing in and managing private companies. This career path offers opportunities to participate in deal sourcing, due diligence, and portfolio management.
- Hedge Funds: Some investment bankers move to roles in hedge funds, where they manage investment portfolios and engage in trading strategies to generate returns for investors. This career path allows for exposure to a variety of asset classes and financial markets.
- Corporate Finance: Investment bankers may pursue opportunities in corporate finance departments of corporations, where they focus on financial planning, capital budgeting, and strategic financial decision-making. This career path offers opportunities to work directly within companies and contribute to their growth and financial success.
- Venture Capital: Another common career path for investment bankers is venture capital, where they focus on investing in early-stage and growth-stage companies. This role involves evaluating investment opportunities, conducting due diligence, and providing strategic guidance to portfolio companies.
- Entrepreneurship: Some investment bankers choose to pursue entrepreneurship and start their businesses or join early-stage startups. This career path offers opportunities to apply financial and strategic skills to build and grow innovative companies
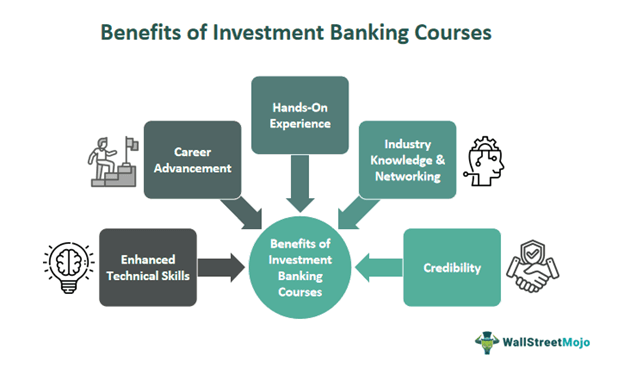
Benefits of Investment Banking Course
The benefits of taking up a detail-oriented investment banking course are second to none. They not only equip you with immense knowledge but also help you secure better roles. Let us understand how by understanding the benefits of such courses.
- An investment banking course provides in-depth knowledge of the financial services industry. It includes the knowledge of capital markets, mergers and acquisitions, and corporate finance, preparing individuals for roles in investment banking and related fields.
- Investment banking courses typically cover financial modeling, valuation techniques, and other technical skills. These skills are essential for analyzing companies, structuring transactions, and executing deals effectively.
- Taking an investment banking course allows individuals to network with industry professionals, including instructors, guest speakers, and fellow students, providing valuable connections and potential career opportunities.
- Completing an investment banking course enhances individuals' qualifications and credibility, making them more competitive candidates for entry-level and mid-level positions in investment banking firms, corporate finance departments, and related fields.
- Many investment banking courses include hands-on projects, case studies, and simulations that provide practical experience in analyzing real-world financial transactions. These experiences prepare individuals for the challenges and demands of working in investment banking.
How to Become an Investment Banker?
If you have read this blog so far, one question is sure to have popped up in your mind – "How do people end up doing such fancy-sound jobs?". Let's put this doubt to rest through the explanation below that covers the textbook route to commence an investment banking career.
- Educational Background: Obtain a bachelor's degree in finance, economics, accounting, or a related field. Some investment bankers also pursue advanced degrees such as an MBA or master's in finance.
- Gain Relevant Experience: Seek internships or entry-level positions in finance-related roles, such as investment banking analyst programs, corporate finance, or financial advisory roles.
- Develop Technical Skills: Acquire proficiency in financial modeling, valuation techniques, and Excel. Take courses or certifications to enhance technical skills relevant to investment banking.
- Networking: construct a solid network by attending events relevant to the industry. Additionally, candidates can join finance-related clubs or organizations, and connecting with professionals through platforms like LinkedIn.
- Apply for Positions: Research and apply for entry-level positions in investment banking firms, such as analyst programs or internship opportunities.
- Prepare for Interviews: Practice interview questions and case studies commonly used in investment banking interviews. Showcase knowledge of financial markets, analytical abilities, and problem-solving skills.
- Continuous Learning and Development: Stay updated on industry trends, regulations, and market developments. Consider pursuing additional certifications or advanced degrees to enhance career prospects and skills.
Future of Investment Banking
The world of finance and business has been growing at an incredible pace. There is absolutely no doubt that investment banking shall grow to newer heights at regular intervals. Let us understand how this growth shall be achieved within this dynamic industry.
- Technological Advancements: Investment banking is expected to undergo significant technological transformation, with the increasing use of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation. These advancements shall be used to streamline processes, enhance efficiency, and improve decision-making.
- Globalization: Investment banking is becoming increasingly globalized, with firms expanding into new markets and serving clients across borders. This trend is expected to continue, driven by the globalization of capital markets, cross-border M&A activity, and demand for investment banking services in emerging economies.
- Regulatory Environment: Investment banking will continue to operate in a highly regulated environment, with increasing scrutiny from regulators and governments worldwide. Firms will need to navigate evolving regulatory requirements and compliance standards to ensure business continuity and mitigate risks.
- Shift in Client Preferences: Clients' preferences and expectations are evolving, with increasing demand for personalized advice, innovative solutions, and transparency in fees and services. Investment banks will need to adapt their offerings and client engagement strategies to meet changing client needs and preferences.
- Emerging Trends: Emerging trends such as sustainable finance, impact investing, and digital assets are expected to shape the future of investment banking. This creates new opportunities and challenges for firms to capitalize on emerging markets and meet evolving client demands.

