Table Of Contents
Benchmarking Meaning
Benchmarking is comparing one's business processes and performance metrics to industry best practices or other companies that are considered leaders in the industry. The goal is to identify areas of improvement and establish a standard of excellence in the organization.
Competitive benchmarking provides a clear understanding of an organization's performance compared to competitors and the industry. This helps organizations set realistic operational targets and goals and identify improvement areas.
Key Takeaways
- Benchmarking analysis helps organizations identify improvement areas and adopt best practices for superior performance.
- In addition, it allows organizations to compare their performance against industry best practices and competitors, enabling them to identify ways to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage.
- It relies on collecting and analyzing data to make informed decisions about improving organizational performance.
Benchmarking In Business Explained
Benchmarking is a critical process for business organizations that enables them to evaluate their performance against industry best practices. By doing so, organizations can identify gaps and areas of improvement and develop strategies to achieve better results.
It also helps businesses identify and adopt best practices that lead to operational excellence and competitive advantage.
It can be internal or external. Internal benchmarking tools involve comparing performance metrics within different areas of the organization, while external benchmarking involves comparing performance metrics against competitors and other companies in the same industry. Both approaches provide valuable insights for organizations and help them to improve their processes and performance.
Another significant benefit is that it fosters a culture of continuous improvement within the organization. As a result, organizations can achieve operational excellence, enhance customer satisfaction, and increase profitability by continuously evaluating their performance and adopting best practices.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to it. For example, organizations may rely too heavily on it and overlook the unique needs and circumstances of their organization. Additionally, data can be challenging to obtain, and the comparison may only be partially fair due to differences in industry, size, or other factors.
In conclusion, a benchmarking process is a critical tool for business processes to evaluate their performance, identify areas of improvement, and adopt best practices to achieve operational excellence and competitive advantage. However, it is essential to approach it with a critical mindset, consider the unique needs and circumstances of the organization, and evaluate the data carefully to ensure that the comparison is fair and relevant.
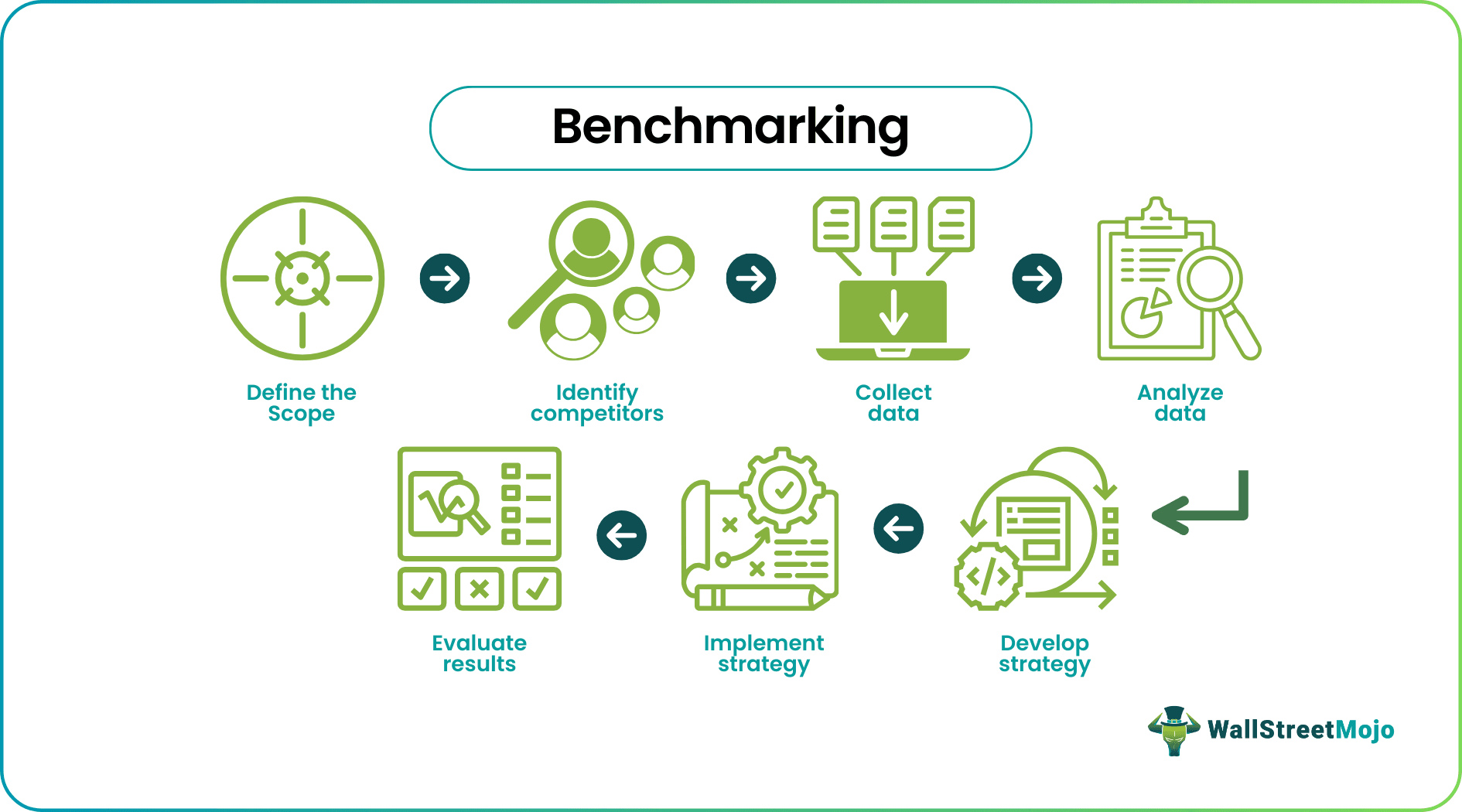
Process of Benchmarking
There are four primary steps to the process:
- Planning: In this step, the organization identifies what they want to benchmark, a specific process, product, or service. They also determine the partners, other companies, or organizations considered best in class for the same process, product, or service. The organization also determines the data collection methods and sets benchmarks for the comparison.
- Analysis: This step involves collecting and analyzing partner data and comparing it to the organization's data. The data can be managed through surveys, interviews, or site visits and should be relevant and reliable. The analysis helps to identify gaps and areas of improvement for the organization.
- Integration: In this step, the organization identifies the best practices they can adopt from the partners. They evaluate the feasibility of integrating these best practices into their processes and develop an action plan to implement the changes.
- Action: This step involves implementing the changes identified in the integration step and monitoring the results. The organization should evaluate the effectiveness of the changes and make any necessary adjustments.
Types
Its primary types include -
- Internal Benchmarking: This involves comparing the performance of different departments or processes within the same organization. The objective is to identify best practices and improve the organization's performance. Internal benchmarking can be a simple and effective way to improve efficiency and productivity, and it does not require external data.
- Competitive Benchmarking: This involves comparing the organization's performance against its competitors in the industry. The objective is to identify areas where the organization lags behind its competitors and implement strategies to improve its competitive position. It requires external data, and obtaining accurate data from competitors can be challenging.
- Strategic Benchmarking: This involves comparing the organization's performance against the best-in-class companies in the industry, regardless of whether they are direct competitors. The objective is to identify and implement strategies for superior performance and competitive advantage. It requires external data and is often more complex than the other two types of benchmarking.
Examples
Let us understand it in the following ways.
Example #1
Suppose a small software development company wants to improve its product development process. The company could conduct internal benchmarking by comparing the performance of its different teams and identifying best practices that could be shared across the organization. The company could also show competitive benchmarking by comparing its development process to its competitors in the industry to identify areas where it can improve.
Example #2
Walmart announced that it would benchmark the sustainability practices of its suppliers. Walmart is the world's largest retailer, committed to reducing its carbon footprint and promoting sustainable practices in its supply chain. To achieve this goal, Walmart plans to assess its suppliers' sustainability practices and benchmark them against industry best practices.
The objective is to identify areas where suppliers can improve their sustainability practices and work with them to implement changes. This is an example of strategic benchmarking, where the organization compares its performance against the best-in-class companies in the industry to achieve superior performance and competitive advantage.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Some of the essential pros and cons are discussed below.
Advantages
- Improved performance: It helps organizations identify areas where they need to improve and adopt best practices to help them achieve superior performance.
- Competitive advantage: It allows organizations to compare their performance against industry best practices and competitors, enabling them to identify ways to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage.
- Increased customer satisfaction can help organizations improve their products and services, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Culture of continuous improvement: It fosters a culture of constant improvement within the organization by encouraging ongoing evaluation and adoption of best practices.
Disadvantages
- Data collection can be complex: Obtaining accurate data can be challenging, particularly when comparing against competitors.
- Unfair comparison: Organizations may not compare apples to apples, as the data may not consider factors such as company size, location, and resources.
- Over-reliance: Organizations may become overly reliant on it and overlook their organization's unique needs and circumstances.
- Resistance to change may uncover areas where changes are needed, but some employees may resist change, leading to implementation challenges.
Benchmarking vs Competitive Analysis
Benchmarking and competitive analysis are two different approaches used by organizations to evaluate their performance and improve their competitiveness. Here are some critical differences between benchmarking and competitive analysis:
- Definition: Benchmarking systematically compares an organization's performance against best practices in the industry or within the organization. Competitive analysis is a process of evaluating an organization's competitors to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
- Focus: Benchmarking identifies areas of improvement for the organization by comparing its processes, products, and services to industry best practices. The competitive analysis focuses on understanding the competitive landscape and identifying strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
- Data: Benchmarking requires collecting data from various sources, such as industry reports, surveys, and site visits. Competitive analysis requires collecting data on competitors' products, pricing, marketing strategies, and customer feedback.
- Scope: Benchmarking can be internal, competitive, or strategic, depending on the organization's goals. The competitive analysis focuses exclusively on the competition.
- Implementation: Benchmarking involves developing an action plan to implement best practices identified through comparison. The competitive analysis involves developing strategies to gain a competitive advantage.
- Usefulness: Benchmarking helps identify areas of improvement and best practices to adopt. Competitive analysis helps develop strategies to outperform the competition.
