Table of Contents
What Is The Basel Committee On Banking Supervision (BCBS)?
The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) is a committee of banking supervisors that sets global standards for bank supervision. The committee is composed of country central banks and banking regulatory authorities. The standards aim to regulate and supervise banks and regulators to enhance financial stability.
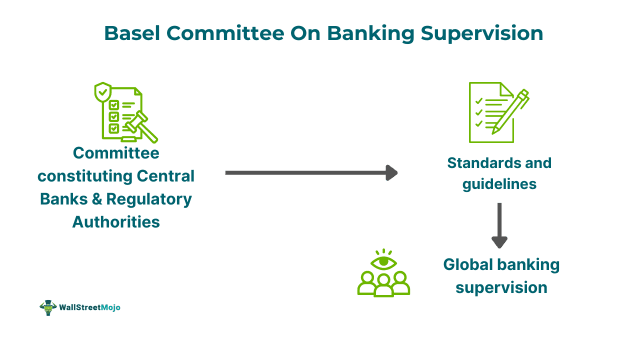
The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision principles is a set of standards that provide a framework for supervisors and banks to function. Based on these principles, governments, supervisors, and regulators adopt and frame their regulations. They cover areas such as business model sustainability, operational resilience, and climate-related financial risks.
Key Takeaways
- The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision is a standard-setting body of banking regulations that are to be implemented across the globe. It consists of members from 28 jurisdictions.
- The committee works with the aim of developing and promoting standards and guidelines to build a resilient, stable global banking system.
- The commodities available for trade in the futures market include agricultural products, energy, and metals. \These are exercised three days before their expiry, after which they become futures contracts.
Basel Committee On Banking Supervision Explained
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision is a committee of regulators and central banks that sets global standards for bank functioning. It aims to strengthen existing banking regulations and practices worldwide to enhance the stability of financial systems.
The internal structure of the BCBS comprises the committee, groups, virtual network working groups, task forces, the chair, and the secretariat. The committee is the decision-making body and ensures the achievement of mandates. The groups, task forces, and networking groups all manage the functioning of the BCBS. The chairs direct the committee's work in accordance with the mandate. The secretariat is a provision of the BIS or the bank for international settlements to support the works of BCBS constituents.
The BCBS is not a supranational authority and does not have legal force to its standards. It seeks to achieve the mandates through member commitments.
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision members include organizations with direct banking supervisory authority apart from central banks. After the committee's consultation, the BCBS chair may also invite organizations to become observers. Membership and observer status will be reviewed periodically.
The committee makes its recommendations to a group of governors and the heads of supervision for changes amongst its members. The secretariat publishes the members and observer list on its website. The member's commitment spans the promotion of financial stability, enhanced bank regulations, and supervision and development of such standards. It also covers the implementation of BCBS standards within domestic jurisdictions and promotes global stability. Participating in BCBS reviews is also included in their functions.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
History
The BCBS was established in 1974 and was initially named the Committee on Banking Regulations and Supervisory Practices. A group of ten nations established it to improve financial stability after a series of disturbances in banking markets and the international currency. The committee headquarters are located at the BIS in Basel, hence the name. The first meeting of the committee was in 1975(February). Since then, regular meetings have been held three to four times a year.
From the first 28 jurisdictions at the beginning, the membership has increased to 45 institutions. The first paper issued for supervisory standards was called Concordat. This set the principles for sharing responsibilities of supervision for banks, their foreign branches, joint ventures, and even subsidiaries between parent and host authorities. In 1990, a supplement to the 1983 Concordat was issued to enhance the cross-border flow of information. In 1992, a few of the reformulated concepts were issued as minimal criteria for the supervision of international banking groups and cross-border businesses.
In 1996, the Basel Committee released a report on cross-border banking supervision and involved supervisors from non-G10 jurisdictions and offshore centers. The report proposed solutions to overcome obstacles and establish healthy relationships between home and host countries. The 1996 G7 finance minister report highlighted the need for supervision of financial marketplaces and emerging market economies. These standards of accords in capital adequacies have also been established since the inception. They are popularly known as Basel I, Basel II, and Basel III.
Role/Activities
Given below are the roles and activities that the BCBS undertakes to achieve its mandates:
- Exchanges information on banking industry developments and the financial markets to identify prevailing or upcoming risks for the global financial system. Sharing of supervisory issues, methods or approaches to promote a common understanding and cross-border cooperation.
- Establish global standards, guidelines, and sound practices for the regulation of banks.
- Address regulatory gaps and monitor them to implement standards.
- Coordination and cooperation with financial sector standard-setting authorities, international bodies and related authorities.
Importance
The points that highlight the importance of BCBS are given below.
- BCBS members set global standards for regulation and supervision to maintain consistency worldwide.
- The standards help in identifying and mitigating risks.
- Facilitates cross-border information sharing and cooperation among members.
- Provides an opportunity for equal participation of authorities.
- Addresses regulatory concerns and gaps.
- Established maximum capital and liquidity standards for banks to withstand shocks.
- The set standards enhance the capacity of existing regulations.
- Contributes to a transparent and accountable global financial system.
- The standards set aim to strengthen the economy.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

