Table Of Contents
What Is Bank Reconciliation?
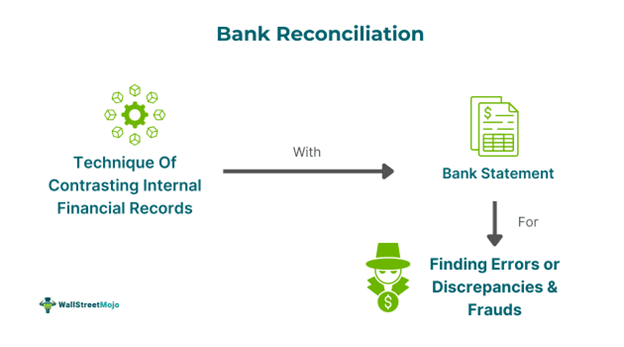
Bank reconciliation is the process of matching transaction entries in accounting records with those in bank statements using specialized tools. This method helps businesses clearly understand cash availability, conduct accurate reporting, find errors and omissions, and expedite financial closeouts.
It has to be done periodically to authenticate that all transactions, such as deposits, withdrawals, and checks, are documented accurately in the dual system. It encourages businesses to comply with various mandatory accounting standards and keep their records ready for official inquiries or audits.
Key Takeaways
- Bank reconciliation represents a process of comparing bank statements and accounting books, providing a detailed view of cash availability, accurate reporting, identifying errors, and expediting finance close.
- It consists of internal, external and aggregate reconciliations.
- The process involves comparing company records with bank statements and adjusting for deposits in transit, notes receivable, and NSF checks. Ensure the adjusted bank balance matches the company's records.
- Its challenges include incorrect financial statements and discrepancies from manual entry errors. Other issues are complications from delayed transactions, non-recording of unexpected charges, and difficulties in including income from unknown sources.
Bank Reconciliation Explained
Bank reconciliation is the procedure of contrasting a company's internal financial records with its bank statement pdf to excel to determine inaccuracies. In this manner, firms ensure the accurate documentation of their transactions and conserve the integrity of financial data. It has implications like preventing fraud and theft by revealing discrepancies indicating unlawful transactions.
Additionally, it helps in adherence to accounting standards, which is crucial to financial integrity and auditing. With the advent of bank reconciliation templates and software, the process has become automated, streamlining many tasks. This method is widely used by businesses to ensure financial safety. In the broader financial sector, transparency and trust in financial reporting are created. Businesses can manage cash flow effectively, which leads to successful investment decisions and strategic planning.
Types
Businesses often face challenges in choosing the right type of reconciliation for their needs. The following list clarifies the different types:
- Internal Reconciliation: Such a type of reconciliation helps in entry comparison amongst various departments working in the same organization or company.
- External Reconciliation: It aids in reconciling accounts between different entities, such as a bank and a business, or between separate companies.
- Aggregate Reconciliation: It sets a single class of documents or records against which verification of combined multiple accounts takes place. This helps authenticate financial statement accuracy and enables adherence to regulations.
Process Flow
Bank reconciliation can be efficiently conducted by following these steps:
Step # 1: First, compare the deposits and issued checks in the company’s records with those listed in the bank statements. This will help identify any deposits in transit or uncleared checks.
Step # 2: Add any deposit in transit into the balance of the bank statement.
Step # 3: Determine the balance of the adjusted bank cash after deducting outstanding checks.
Step # 4: Next, adjust the company’s closing cash balance by adding the amounts of notes receivable and earned interest.
Step 5: Subtract NSF checks, penalties, and bank service fees from the company's cash balance.
Step # 6: Finally, ensure that the adjusted bank balance matches the company’s adjusted balance.
Examples
Let us use a few examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
Let us assume that Art Supplies Limited of Old York City has been conducting its monthly reconciliation for June. The company’s financial report exhibits $60000 cash. However, the cash listed in its bank statement is $50000. As a result, a massive search exercise for the missing entry was carried out, and they found that $11000 for payment of their 10 large canvas orders had been in transit. Upon further investigation, the company also discovered that the bank had charged $1000 as fees for bank services related to wire transfers.
Hence, Art Supplies Limited adds $11000 to the bank statement balance, taking the balance to $61000. After that, the company subtracts the $1000 charged as bank fees from the financial statements, which leads to a balance of $50000. Hence, the company successfully reconciled the bank statement to $50000.
Example #2
An online article published on 10 May 2024 discusses Validata's expansion of its partnership with Temenos to enhance bank reconciliation. Validata has integrated itself with Temenos core banking to provide various services. Tementos supports ISO 2022 standards throughout different payment structures to give next-generation solutions concerning cash and nostro reconciliation to EMIs and banks. Furthermore, the ConnectIQ platform uses machine learning and AI to automate end-to-end and ongoing reconciliation.
The platform can also enhance reconciliation procedures, aiding trade matching and intersystem reconciliations. According to executives of Temenos and Validata, their collaboration has ensured transparency, speed, and accuracy in the reconciliation of payment systems and modern banking. As a result, efficiency has increased, while operational costs have decreased considerably.
Benefits
Its importance and benefits for businesses are as follows:
- Helps make the financial records up-to-date and accurate.
- Creates awareness of a firm's financial situation and manages cash flows.
- Identifies early suspicious transactions, risks, and miscalculations, improving error and fraud detection.
- Ensures accurate payment processing to and from suppliers. Customers and employees.
- Maintains positive trading relationships.
- Provides up-to-date and organized, simplifying financial reporting and tax filing.
- Reduces work overload during peak tax seasons.
- It increases and tightens internal controls through distinct checks and balances placed in proper places.
- It also facilitates accurate reconciliation, management and tracking of accounts payables and receivables.
Challenges
It has its own set of challenges for business, as listed below:
- Incorrect financial statements can result from errors in data processing done using manual entry.
- Discrepancies between bank statements and company records can happen due to bank delays like month or end-of-day transactions.
- Reconciliation can become complicated due to non-recording or non-receipt of unexpected bank charges until the bank has issued a statement.
- Before reconciliation, it might be difficult to accurately include the income from unknown sources such as investments and interest.

