Table Of Contents
What Are Balance Sheet Examples?
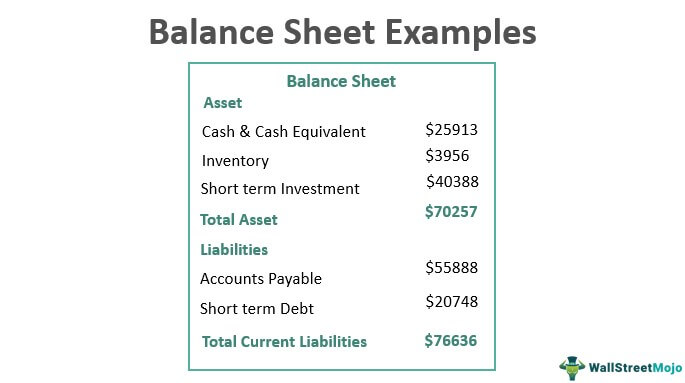
The following balance sheet example outlines the most common Balance Sheets of US, UK, and Indian GAAP. It is impossible to provide a complete set that addresses every variation in every situation since there are thousands of such Balance Sheets. Each Balance Sheet example states the topic, the relevant reasons, and additional comments as needed.
Based on the industrial and nationwide requirements, various rules prescribed by the International Accounting Standard Board (IASB) are formally termed International Financial Reporting Standard (IFRS). Based on their tradition and industrial specification, all nations adopt IFRS and modify it to draft their local Generally Accepted Accounting Principles(GAAP).
Table of contents
- What Are Balance Sheet Examples?
- A balance sheet is a statement having two sides, the asset and liability sides, that show the organization's financial situation as of any given date.
- The asset side represents the non-current assets and current assets. The liability side represents the owner’s capital and current and non-current liability.
- It is a base statement for all analysis and understanding of the company’s solvency.
- The balance sheet must be reliable, appropriately valued, have valid assumptions, and be prepared by trusted personnel so marketers can depend on them.
Balance Sheet Examples Explained
A balance sheet is a statement that shows the organization's financial position on any specified date with two sides, the asset and liability sides. The asset side of accounts balance sheet examples shows Non-current Assets and Current Assets. The liability side shows the Owner’s Capital and Current and Non-Current Liability.
Simple balance sheet examples are a summary of the assets and liabilities that help the stakeholders assess the financial health of the company, the solvency level and the liquidity position. Based on this statement the lenders take decision for providing funds and investors take investment decisions.
The balance sheet is the financial position statement that shows the company's oThe balance sheet is the financial position statement that shows the company's obligations and receivables. It is a base statement that is considered for all kinds of analysis and to determine the solvency of the company. All the experts rely on the balance sheet provided by the company. Hence the balance sheet needs to be reliable, correctly valued, with proper assumptions, and overall, must be prepared by the trusted personnel so that marketers can rely on the same. In this article, the various balance sheet examples for small business and big companies show us the items included in the document, how they are useful and how they can be interpreted and be useful to stakeholders.
Explanation of Balance Sheet in Video
Examples
Let us try to understand the concept of simple balance sheet examples with the help of some suitable examples.
Example#1 - Based on US GAAP
In the USA, US local GAAP is accepted for preparing financial statements. So let's understand the of accounts balance sheet examples in the USA with an example of two companies existing in the real world:
#1 - Walmart, Inc.

source: Walmart SEC Filings
- Current Assets - 59664,Property Plant & Equipment(PPE) net of Depreciation- 107,675,Lease receivables- 7,143, Goodwill – 59664,
- Property Plant & Equipment(PPE) net of Depreciation- 107,675,
- Lease receivables- 7,143,
- Goodwill – 18,242,
- Other assets- 11,798.
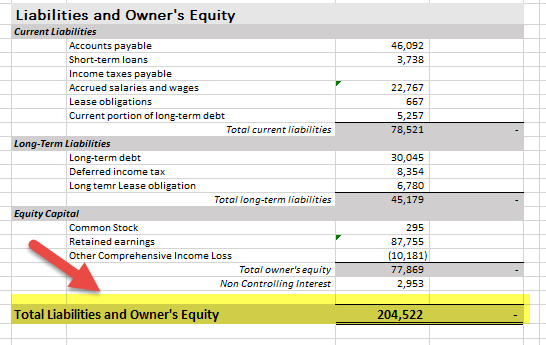
Equity Capital
- Share Capital – 295,
- Reserves-87,755,
- Other OCI Loss-(10,181),
- Non-Controlling Interest- 2,953
- Current Liabilities -78,521,
- Long term Debts- 30,045,
- Lease obligations-6780,
- Deferred Income tax & others-8,354
Along with the above data, comparable to last year for the same period is also needed to be disclosed;
#2 - Apple, Inc.
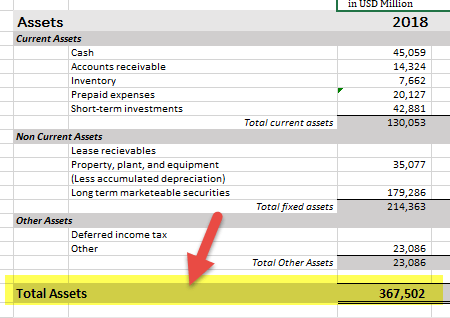
source: Apple SEC Filings
- Current Assets- 130053,
- Property Plant & Equipment(PPE) net of Depreciation- 35,077,
- Long term marketable securities – 179,286,
- Goodwill-, Other assets- 23,086.
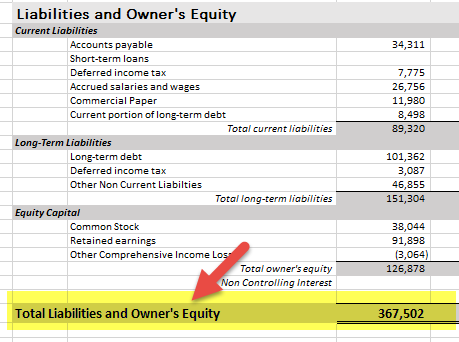
Equity Capital
- Share Capital- 38044,
- Reserves- 91,898,
- Other OCI Loss-(3,064),
- Non-Controlling Interest- Nil
Long Term Liabilities
- Current Liabilities-89320,
- Long term Debts - 10,1362,
- Lease obligations-46855,
- Deferred Income tax Liability & others-3087
Along with the above data, comparable to last year for the same period is also needed to be disclosed;
Major financials are prepared under the US GAAP and in the format published by SEC for their annual filing in the USA. The main aim behind the standardization of such a process is the comparability and proper disclosure of the facts for investors.
One should note that one must prepare a comparison for last year under the said accounting policies, assumptions, methods, and approaches in which financials of current years are prepared which is applicable for various balance sheet examples for small business and big companies.
Example#2 - Based On UK GAAP
Firms in the United Kingdom are compulsorily required to prepare financials as per the local UK and Irish GAAP. Also, based on the development at the global level, UK and Irish GAAP are blended into the IFRS for the global reporting perspectives.
Let’s understand the same by viewing the liabilities and assets on balance sheet examples of some existing companies:
#1 - Vodafone Group PLC
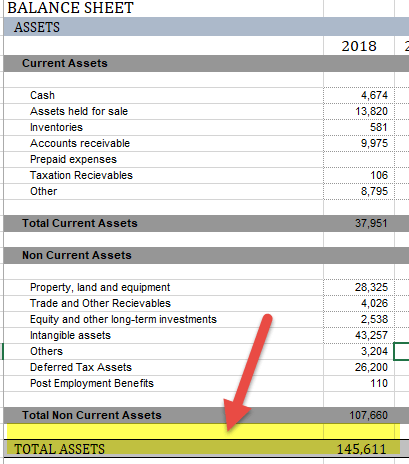
source: Vodafone Annual Report
- Current Assets- 37,951,
- Property Plant & Equipment(PPE) net of Depreciation- 28,325,
- Investments– 5,742,
- Deferred Tax Assets - 26,200,
- Goodwill- 43,257,
- Other assets-4,136

Equity Capital
- Share Capital- 154,993,
- Treasury Shares – (8,463),
- Accumulated losses- (106,695),
- Other OCI Loss- 27,805,
- Non-Controlling Interest- 967
Long Term Liabilities
- Current Liabilities-28,025,
- Long term Debts-37,980
Along with the above data, comparable to last year for the same period is also needed to be disclosed;
#2 - BP PLC

source: BP Annual Report
- Current Assets-74,968,
- Property Plant & Equipment(PPE) net of Depreciation- 129,471,
- Investments– 24,985,
- Deferred Tax Assets- 4,469,
- Intangibles – 29,906,
- Other assets- 12,716.
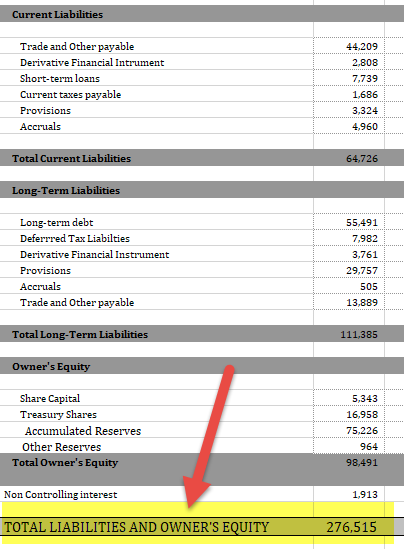
Equity Capital
- Share Capital- 5,343,
- Share Premium Account- 12,147
- Capital Redemption Reserve- 1,426,
- Merger Reserve-27,206
- Treasury Shares – -16,958,
- Non-Controlling Interest- 1,913
Long Term Liabilities
- Current Liabilities-64,726,
- Non-Current Liabilities-11,385,
Along with the above data, comparable to last year for the same period also needs to be disclosed.
In the UK, financial statements must be submitted to the Financial Conduct Authority annually in XBRL format. Chartered accountants of ICAEW must audit and certify it and then submit the same.
Example #3 - Based On Indian GAAP
In India, financials are to be presented by considering Indian GAAP and acceptable IFRS in line with the global reporting framework. Until 2019, IFRS 15 (Revenue from Contracts with Customers) and IFRS 9 (Financial Instruments) are fully implemented. In this line, other IFRS will also be implemented with specific carve out as per the Indian scenario.
Schedule 3 of the Companies Act 2013 provides the the liabilities and assets on balance sheet examples format, under which all the Indian companies are needed to prepare their financial statements annually and quarterly.
Let's understand the said format by taking a real example from the existing company:
#1 - Reliance
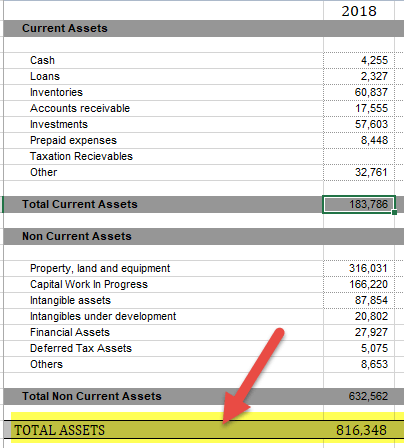
source: Reliance Annual Report
- Current Assets-183,786,
- Property Plant & Equipment(PPE) net of Depreciation- 316,031,
- Capital Work in Progress– 166,220,
- Deferred Tax Assets- 5,075,
- Intangibles – 87,854,
- Other assets- 57,382
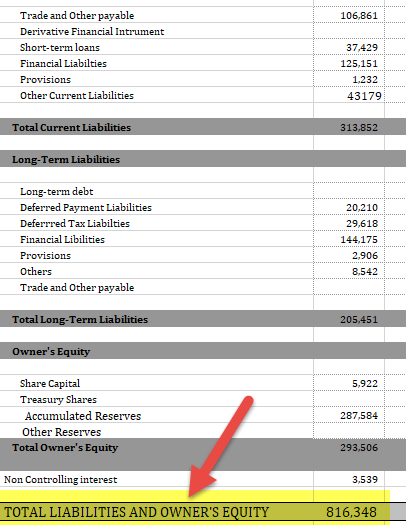
Equity Capital
- Share Capital- 5,922,
- Other Reserves- 287,584,
- Non-Controlling Interest- 3,539
Long Term Liabilities
- Current Liabilities- 313,852,
- Non-Current Liabilities- 205,451.
The above data comparable to last year for the same period also needs to be disclosed.
In India, complete financial statements consist of the Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash flow statement, Changes in Equity, and Statement of Other Comprehensive Income. Financial statements must be submitted to the Ministry of Corporate Affairs annually in September.
Thus the above examples give a clear idea about the various types of financial transaction that are a part of the balance sheet. They show how they to identify them and use them. The format as per the US GAAP, the UK GAAP and the Indian GAAP shows how the different accounting standards help in differentiating the formats as per the rules applicable in the specific countries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A company's management borrowing money to pay accumulated losses rather than providing more shares by equity funding may lead the company's balance sheet to display negative shareholders' equity.
On a balance sheet, expenses are shown more indirectly, where the retained earnings line item in the equity section of the balance sheet may reduce by the same amount as the expense.
The company investors use a company's balance sheet to know the company's net worth as part of the investment summary.
A balance sheet must always be balanced. The "balance sheet" refers to the fact that assets will always remain equal to liabilities and shareholders' equity.
Recommended Articles
It is a Guide to Balance Sheet Examples. Here we provide practical Balance Sheet Examples of companies following US GAAP, UK GAAP, and Indian GAAP. You can learn more about Accounting from the following articles –

