Table Of Contents
Bailment Meaning
Bailment means transferring the possession to another person to fulfill some predetermined agreement that might require the bailee (person to whom possession is given) to do something or vice versa in exchange for some consideration that is not mandatorily required to exist.
In this arrangement, the bailor retains ownership of the property offered to the bailee but is not allowed to use it until the bailee uses it. It is different from a lease arrangement, where the lessors owns the property and allows the lessee to use it for a specific period at a specific cost. Moreover, lease is meant for real estate property, while bailment applies to all personal property.
How Does Bailment Work?
Bailment is an agreement that could be oral or written mutually agreed upon between the person giving possession and the person taking possession, which might involve consideration. The bailor transfers the possession to the bailee for any mutually agreed purpose.
The bailee fulfills the terms; in the end, the bailee transfers the possession of such bailed assets back to the bailor, and the bailor pays certain consideration if agreed upon. Generally, the bailor (owner of the asset) does not enjoy the right to use such bailed assets while they have bailee.
Let us say the person (trader) sometimes sells the shares without possessing the shares. I.e., I.e., short sell the shares to earn short term profits; thereupon, in this example, it could be seen that the seller sells the shares even without having ownership of the shares. In this transfer of the possession of goods, sometimes some liabilities are also transferred to the bailee depending upon the type of bailment. For example, when we park our car in the parking lot, it is the transfer of possession but not ownership, but in case there is some physical damage, then the person who has the person, i.e., bailee, will be responsible for the same.
A bailment agreement comes to an end only when the parties involved have achieved their purpose behind this arrangement and both of them agree to terminate it.
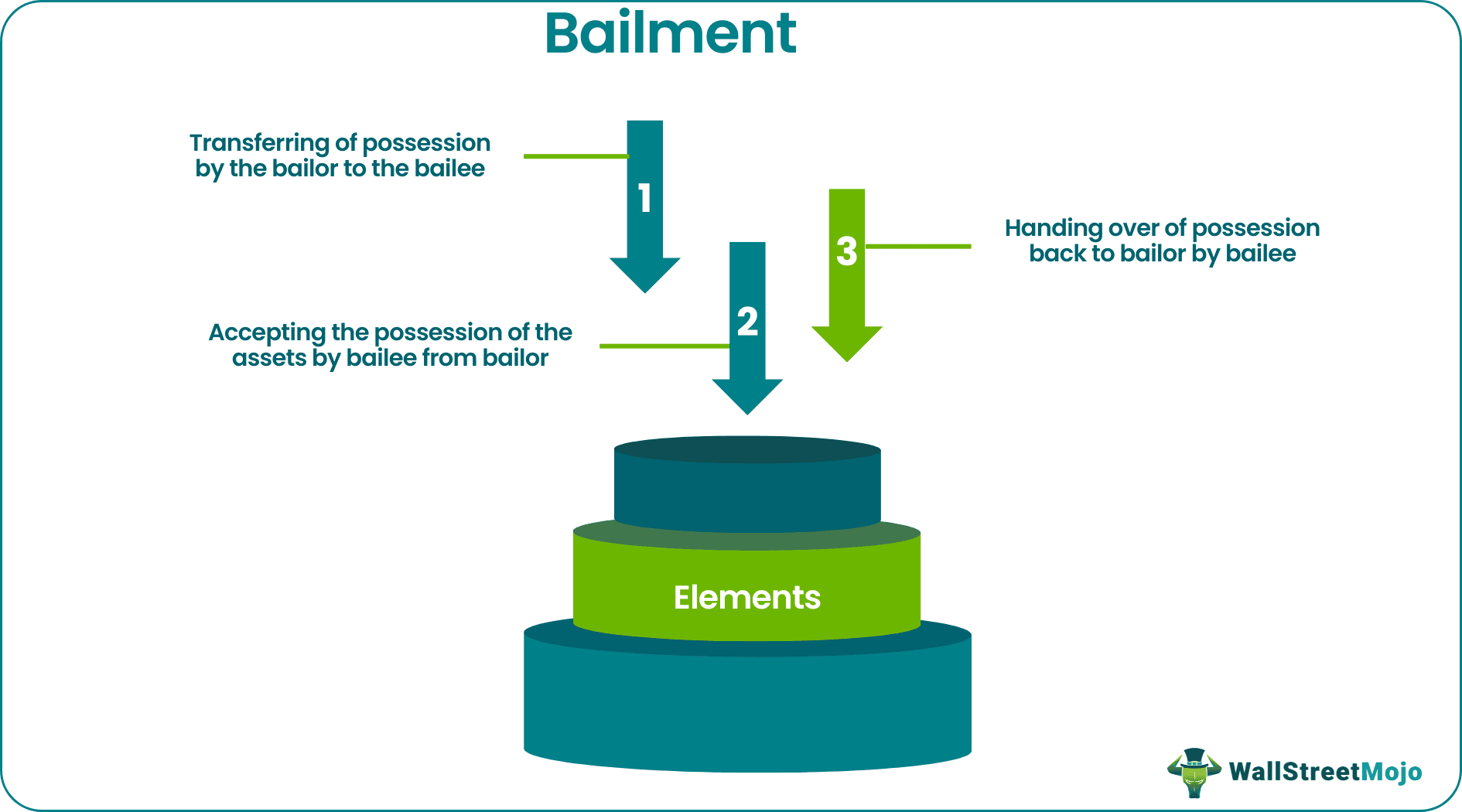
Elements
The unique components of the bailment process that make this bailor-bailee arrangement different from the lease arrangement are listed below. Let us have a look at them:
- Transferring of possession by the bailor to the bailee;
- Accepting the possession of the assets by bailee from bailor;
- Completion of such mutually agreed terms by both parties.
- Payment of consideration, if any.
- Handing over of possession back to bailor by bailee;
Features
The concept of bailment is often confused with other similar contractual procedures, like lease arrangements. Therefore, it is important to check some of the characteristics that help recognize and identify the bailor-bailee relationship uniquely.
Listed below are some of the features to have a look at:
- The first basic requirement is the agreement, which may be written or verbal, and should be clear from any ambiguity.
- The possession of goods or assets must have been transferred from one person to another, i.e., from bailor to bailee. It will need to be returned to the bailor after the expiration of the bailment agreement.
- They should be for some predetermined purpose; for instance, we may give our car to the service center to be serviced.
- The existence of consideration depends upon its type, i.e., the monetary presence of consideration is not mandatory.
Types
The bailor-bailee relationship exists in a couple of forms, which one must know about before involving in any such contract. The kinds of bailment arrangement that are most commonly found are as follows:
#1 - Gratuitous
This type does not include any consideration; in other words, the bailment with no consideration is gratuitous. They may either be for the benefits of bailee or bailor or maybe for both, for instance, parking the car at your friend’s house due to lack of space, giving the car to your friend for use, etc.
#2 - Non-Gratuitous
Similarly, those bailments in which the bailee gives some consideration to the bailor are non-gratuitous. They are generally entered into for the sake of earning, for instance, hiring a motor vehicle from some hiring agency on the agreement of payment of hiring charges.
Examples
Let us consider the following instances to understand what is bailment and also check some daily incidents where this arrangement finds relevance:
- Where one person is handing over the keys of their car to the car valet service provider;
- When one person parks his car at his friends or some known house.
- Situation when we give our car to our friend to use;
- When we deposit our shoes at the shoe center while visiting any temple, monuments, etc.
- The most common example is availing locker services from banks, i.e., banks are the bailee, and the person keeping his belongings in such lockers is the bailor. They both agreed upon some consideration, i.e., bailor uses the locker, and in turn, bailee charges the consideration for providing such services.
Difference Between Bailment and Pledge
Bailment and pledge are two types of arrangements that are dominant in the financial market. However, they differ in multiple aspects. Let us have a look at few of the differences between them:
- Bailment involves the transfer of assets or property from one party (bailor) to another party (bailee), while pledge is the transfer of asset to act as a security or collateral to back a debt.
- In the former arrangement, two parties are involved – a bailor and a bailee. On the contrary, a pledge contract has three parties involved – pledgor, pledgee, and debtor.
- The bailor-bailee arrangement is done to use a property for some specific purpose, while the pledge arrangement is done to secure a debt or loan.
- The risk factor shifts to bailee in a bailment, while the same remains with the pledgor in the pledge contract.
Difference between Bailment and Consignment
Bailment and consignment also share a set of differences being similar to each other so far as the exchange of property in two different forms are involved. Listed below are the differences to have a look at:
- Under bailment, the transferor of assets is called the bailor. The receiver is called bailee; conversely, in consignment, the transferor is called the consignor, and the receiver is called the consignee.
- Under bailment, the ultimate possession and ownership rest with the bailor. On the other hand, under consignment, the consignor can sell out such assets that are handed over to the consignee under consignment.
- Bailment does not give any right to transfer the ownership to the bailee, but under consignment, the consignor may have to transfer the ownership rights if the consignor sold the consigned assets.
- The assets transferred under bailment are for a temporary purpose. However, in the case of consignment, the assets might have converted into permanent possession of the consignee if the assets are sold.
