Table Of Contents
Backorder Meaning
Backorder is defined as an order received for good or service but cannot be fulfilled and can be due to various reasons such as the non-availability of the ordered product, the stock is still in the production phase, or the order being placed with the manufacturer and delivery is still pending, etc. It indicates the company's backlog, i.e., it needs to increase its supply & produce more.
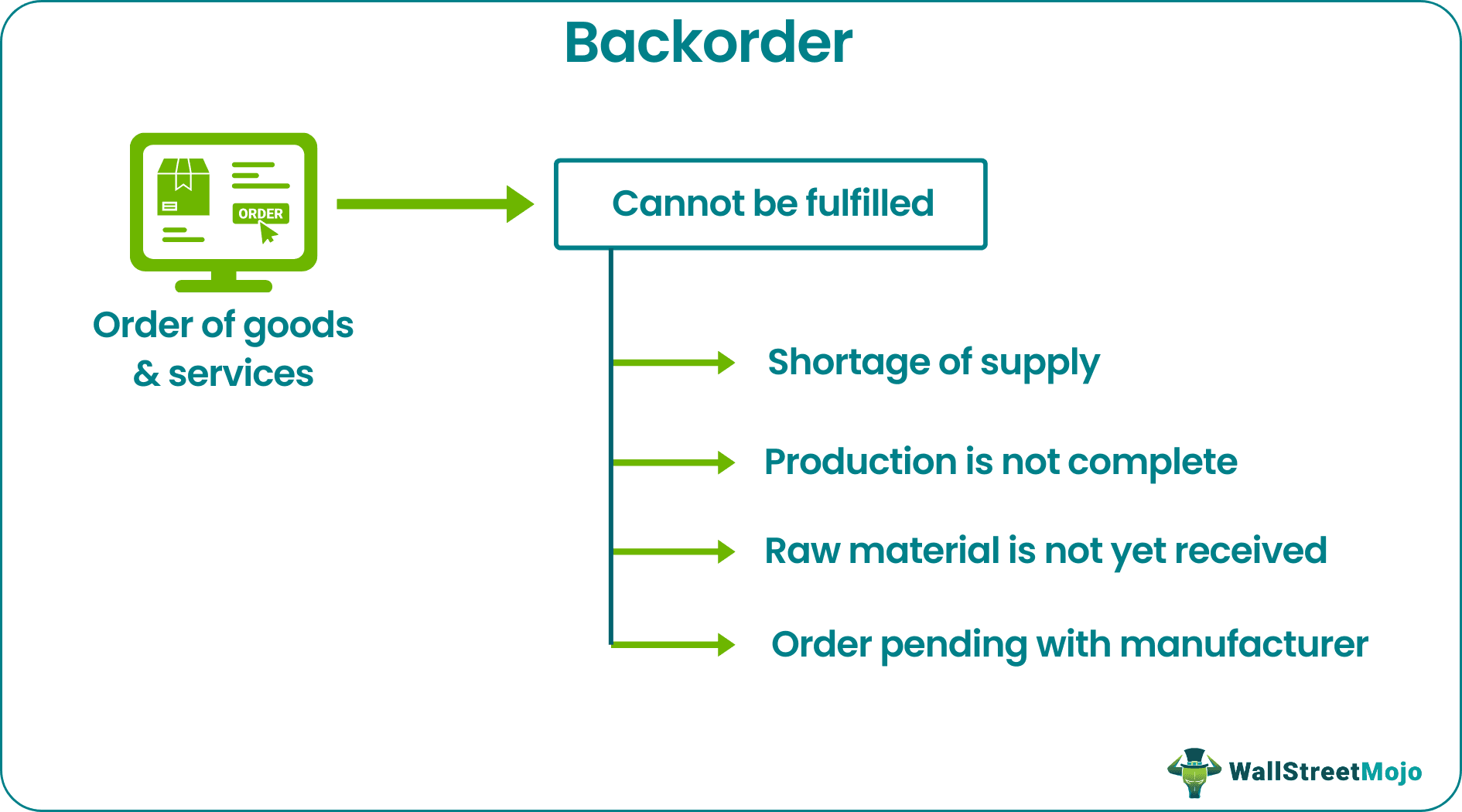
It indicates the company’s backlog, i.e., it needs to increase its supply & produce more. Good customer relation, monitoring inventory levels and proper demand estimation helps handle and minimize such situations. Sometimes it helps in cross-selling related goods or services.
Key Takeaways
- Backorders occur when an order cannot be fulfilled due to reasons like product unavailability or ongoing production. This necessitates the company to increase its supply to meet demand and avoid potential lost sales.
- When a product is on backorder, the company must inform customers and provide an estimated delivery time.
- Customers can either wait or cancel their order, and their decision should be respected, even if there are potential sales with return options.
- Efficiently managing backorders can lead to reduced inventory costs and increased staff productivity.
Backorder Explained
Backorder is a type of order in which the company cannot deliver the goods and services that the customers have ordered on time. The customer has already placed the order but there may be a shortage of the products, or they are unavailable for now. In such cases, the company has to assure the buyer that their order will be fulfilled as soon as the goods become available.
This might occur due to sudden rise in demand, supply chain related problem, delay in manufacturing or shipping, non-availability of raw materials, etc. for this purpose, it is extremely important for companies to maintain a healthy relationship with the customers and suppliers so that during such crisis the backorder management can be done without much problem and without losing the existing customer base.
It is important to keep the customers informed about any change or delay in supply of orders so that there is no sudden loss of sales. Good and clear communication helps in maintaining the faith and trust so that the clients can also get time to plan their next step accordingly.
This situation sometimes gives rise to opportunities for cross-sales, where companies try to sell some other alternate product or service as a replacement for the one the clients originally ordered. Again, however, transparent communication is the key to handling it.
Backorder Process
- Backorders are the orders placed by customers that cannot be fulfilled due to the non-availability of products in stock. It indicates that the company needs to hurry up its operations to remain competitive.
- If backorder management is well done, backorders can benefit the company at large as it reduces the inventory carrying cost and enhances the efficiency of operational staff. If the customers are ready to wait for the product, it is a sign for the company that customers have faith in the product, and the company needs to keep the faith.
- Every company needs to properly communicate to the customers that the order for the product is received and the time limit for delivery of the product.
- It is upon the customer to wait or cancel the order depending upon the type and goodwill of the product and the need of the customer.
Example
It shows how well the company manages the backorder quantity and customers & how effectively it communicates to retain its customers. The examples of backorder are as follows:
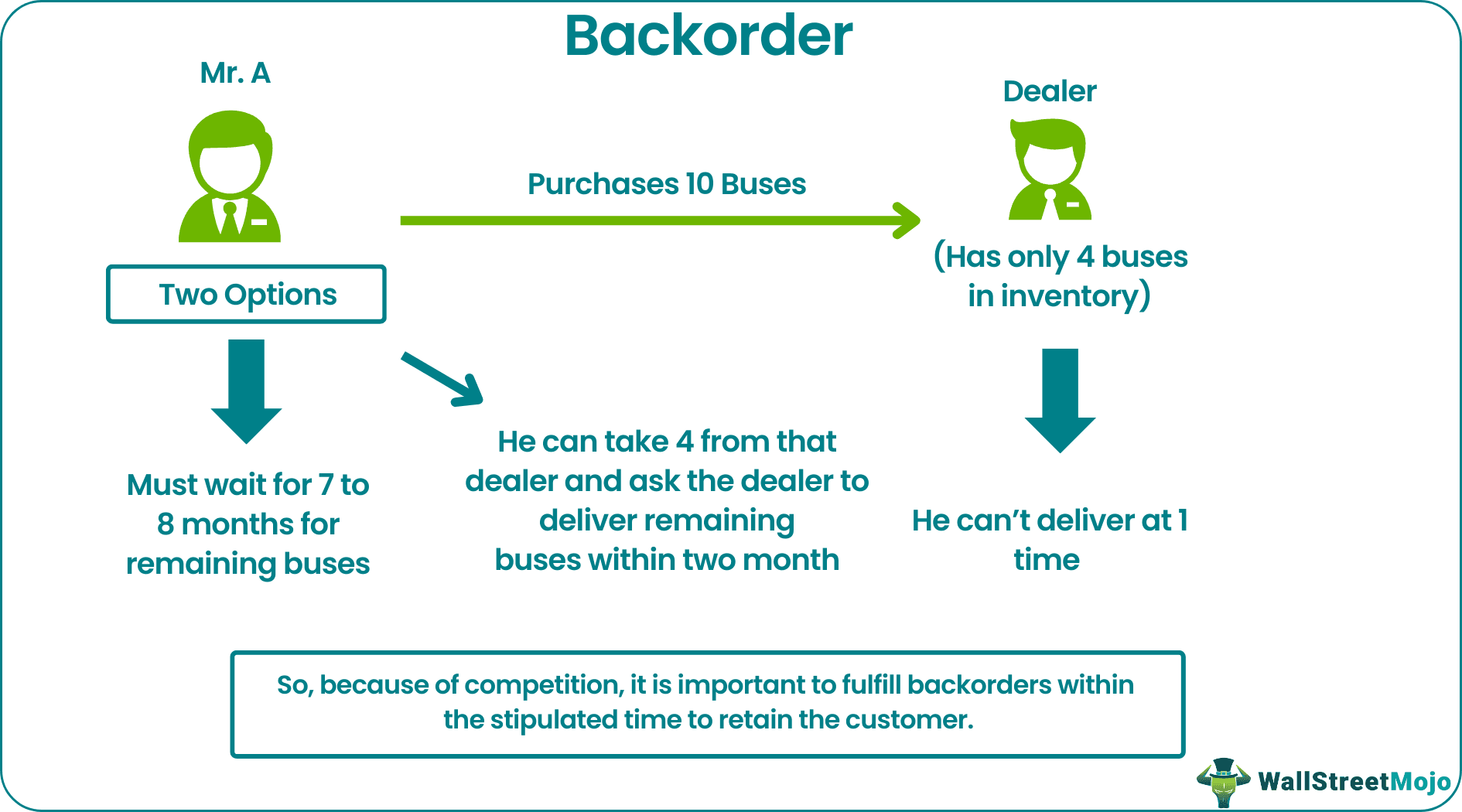
- Mr. A purchases ten buses from the dealer, but the dealer only has four buses in inventory, which he can deliver, and for the remaining six buses, Mr. A has to wait for 7 to 8 months as it takes the dealer 7 to 8 months to get it from the supplier.
- So Mr. A has two options either he can purchase four buses on the spot and for remaining he can wait for 7 to 8 months, or if Mr. A needs all ten on an urgent basis, he can take four from that dealer and ask the dealer to deliver within two months if possible and if it is not possible then cancel the order for remaining six buses which he will buy from another dealer. So, because of competition, it is important to fulfill backorder level within the stipulated time to retain the customer.
Accounting
The backorder quantity needs special accounting as the order received. Still, the product is not sold, and the company has to inform the customers about the status of the product ordered and the expected delivery time. After receiving information on whether to wait or cancel the order, it is upon the customer. The backorders can be treated as a sale on a return basis as it involves the chances of cancellation of the order. The accounting treatment is as follows:
- Record the sale as backorder sale and if the company has ordered a supplier for backorder products, record it as backorder purchases. If the manufacturing is in the process, it comes under inventory as a work in progress. If the order is canceled, the company's sales wouldn't be affected as it doesn't record backordered sales as complete sales. Once the order is fulfilled, transfer the backorder sale to a sales account, and if the order is canceled and goods arrive, transfer the backorder sales to the inventory account.
Advantages
If the problem of backorder is effectively and efficiently managed, it can lead to a number of advantages as given below:
- Reduces the Inventory Storage Cost – The backorders, if effectively fulfilled within a short period, the customers can wait, and its benefits as a cost advantage to the company. It reduces inventory storage costs.
- Enhances Customer Relationship – The backorders enhance the customer relationship if they are properly communicated to the customers. Waiting by the customer for products shows the customer's faith in the product and the company.
- Determines the Demand for Product – Backorders help determine the demand for the product in the market. It is an indication of high demand and that the company needs to increase the manufacturing or purchase to fulfill the demand.
- Helps to Stay in Competition – If the company fulfills backorders within a reasonable time, it can stay in the market for longer and can face competition.
- Determines the Capabilities of the Company and Enhances Efficiency – Backorder indicates that the company has underestimated the demand for its products. Fulfilling it within a reasonable time enhances staff efficiency as the process gets faster to fulfill the order at the earliest.
- If treated efficiently, backorder level make the business run faster and satisfy the customers.
Disadvantages
However, along with its advantages, the situation has has a number of disadvantages as follows:
- Cancellation of Orders – Due to backorders, the customer might cancel the order as he might not be able to wait due to the urgent need of the product, and hence the business of the company can be transferred to the competitor.
- Adverse Impression on Customers and Reduces Goodwill – If the product continuously remains in backorder, it creates the wrong impression in customers' minds. Eventually, it reduces the faith and goodwill of the company.
- Indication of Improper Management by Company – If backorders take a long time to complete, it indicates improper management by the company. It needs to improve to sustain itself in the market.
- Can Enhance the Cost – In the hurry of fulfilling the backorder demands, it can increase the cost as the supplier may sell the material at a higher rate due to high and urgent demand.
Backorder Vs Out Of Stock
The above situations are an indication that the goods ordered are not available immediately for delivery. But the differences between the two of them are as follows:
- In case of the former, the products are not available at present but backorder inventory are expected to be available in the near future, but fo the latter, the products are not expected to be available in the future also.
- In the case of the former, orders are taken but in case of the latter, the company does not accept any order.
- As soon as the goods are available, they will be sent to the customers, but this will not happen for the latter.
- Backorder inventory means the customer will get the same product or service but at a later date. If the goods are out of stock, customers must buy an alternate product or a substitute or switch sellers to get what they want.
- In case of the former, there is less chance of the company losing its customers but for the latter, there is a huge possibility of loss of customers.
Thus, both the situations may arise in a business but the business should devise methods and efficient support systems to minimize them so that the operation can run smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Backorders can occur for various reasons, including sudden spikes in demand, supply chain disruptions, delays in production or transportation, inaccurate forecasting, or inventory management challenges. In such situations, the demand for a product exceeds the available stock, leading to customers having to wait for the item to be restocked before it can be fulfilled.
Backorders are not guaranteed, as they depend on the product's availability from the supplier or manufacturer. Sometimes, the backordered item may become unavailable, leading to potential order cancellations or substitutions.
Backorder and backlog are related concepts, but there is a distinction. Backorder refers to customer orders that cannot be immediately fulfilled due to product unavailability. Backlog, on the other hand, includes all pending work, orders, or tasks, which can encompass backorders along with other pending activities within a business.

