The differences between both the concepts are given as follows:
Table Of Contents
What is back running?
Back running is a trading strategy in which a transaction is executed shortly after another event that offers a profitable opportunity. It is an arbitrage method of Strategic engagement between strategic traders and institutional investors using order anticipation approaches based on previous order flows.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link.
It is a method by which traders undertake trading of high-value transactions soon after another. Backrunners take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity created by the previous transaction's price impact. Traders may utilize this strategy to acquire an unfair advantage in the market over other traders by leveraging sensitive information for personal gain.
Key Takeaways
- Backrunning is a trading strategy where a transaction is executed shortly after another event that offers a profitable opportunity.
- This unethical behavior can result in market manipulation and unfair advantages. It exploits bonding curves in DeFi transactions, where users buy tokens on decentralized exchanges, assuming the recently bought currency is less valuable.
- It can lead to missed profits and network congestion. The method is widely regarded as unethical and prohibited in many jurisdictions due to its potential to undermine market integrity.
Back running in trading explained
Backrunning is observing deals made by other market participants and subsequently performing similar trades. The trades are done to make a profit from the imbalances created as a result of previous transactions. This unethical behavior is frequently carried out secretly to avoid detection and can result in market manipulation and unfair advantages.
The strategy takes advantage of disparities caused by bonding curves in DeFi transactions. When a user buys tokens on a decentralized exchange, it is assumed that the recently bought currency is valuable compared to the currency sold and, hence, less valuable. Backrunners capitalize on this by arbitraging between exchanges, purchasing the devalued or sold token at a reduced price and selling it elsewhere at a premium due to the value disparity. The profit for the back runner is the premium amount minus transaction fees.
Backrunning is a type of MEV (Maximal Extractable Value) that can lead traders to miss out on potential profits. The approach offers services to networks by maintaining stable token prices across exchanges. However, it has flaws. The major concern with backrunning is the risk of network congestion from a surge in arbitrage transactions. It involves numerous transactions with slightly higher fees, leading to congestion. Although intended to stabilize prices, backrunners' strategy can overwhelm the network with excessive activity.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Examples
Let us look into few examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1 (Hypothetical)
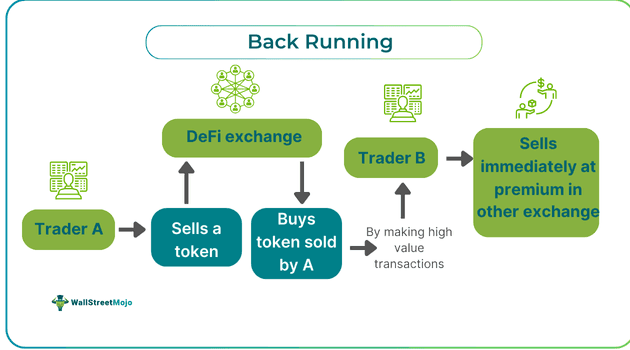
Let's consider a hypothetical scenario involving two traders, Trader A and Trader B, to illustrate the concept of backrunning in decentralized exchanges (DEXs).
Trader A purchases a token on a decentralized exchange, causing a shift in the bonding curve, making the token more valuable. Unbeknownst to Trader A, Trader B is engaging in backrunning and monitoring the DEX transactions. Recognizing the market imbalance caused by Trader A's trade, Trader B seizes the opportunity for arbitrage. Trader B swiftly buys the token that Trader A sold from the market at a significantly lower price. With the acquired tokens in hand, Trader B then proceeds to sell them on another DEX where the token is valued higher. After accounting for transaction fees, the difference between the token's purchase price and the sale price becomes Trader B's profit. This example illustrates the concept of back-running in decentralized exchanges, where Trader B exploits the temporary imbalance in token values to profit from the price discrepancy. However, backrunning is often considered unethical due to its unfair advantage and potential to disrupt market integrity. Engaging in such practices in real-world trading can have legal and regulatory implications.
Example #2 - Real-life example
In recent updates concerning the Ethereum blockchain, the utilization of approximately 500 billion gas by backrunning bots has come to light, as per analysis from Dune Analytics. This equates to roughly 45,000 full blocks. The revelation has prompted concerns within the cryptocurrency community about the implications of extensive bot activity on network congestion and transaction fees.
Importance
given below are a few points that show why understanding the concept is important :
#1 - Gaining Unfair Advantage:
The strategy grants traders an unjust advantage by utilizing non-public information regarding other market participants' orders.
#2 - Ethical and Legal Concerns:
The strategy is widely regarded as unethical and is prohibited in numerous jurisdictions due to the unjust advantage it provides and its potential to undermine market integrity.
#3 - Preserving Market Integrity:
The strategy compromises the integrity of financial markets as it enables traders to profit unfairly at the expense of others. Understanding the scenario helps in making better investment decisions.
#4 - Regulatory Scrutiny:
Regulatory bodies closely monitor trading activities to identify and penalize instances of the method, aiming to uphold market fairness.
#5 - Preserving Investor Confidence:
Instances of back running have the potential to erode investor confidence in the equitable and transparent nature of financial markets, leading to reduced investor participation. Authorities can better monitor the market with the inferences of situations.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Importance
Back running vs. front running
| Basis | Back running | Front running |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Definition | Back running entails executing trades after obtaining information about other traders' orders. | Front running involves executing trades prior to a known forthcoming order. |
| 2. Timing | Back running takes place subsequent to the initiation of an order by another trader. | Front running involves executing trades ahead of the anticipated execution of the known order. |
| 3. Order of Execution | Back running involves entering trades following the order of other market participants | Front running entails executing trades before the known order is executed. |

