Table Of Contents
Back Charge Meaning
A back charge refers to a bill presented to collect the outstanding payment from any previous period. If a customer has not paid the outstanding bill, the supplier will add the previous, pending amount and the current bill and send it to the customer.
Key Takeaways
- A back charge means presenting a bill for collecting any former pending payment. When a customer needs to pay an unpaid bill, the supplier may send it to the customer, adding the prior pending amount and the current bill.
- Suppliers, service providers, or any company involved in a transaction with other parties may impose a back charge. When a company represents a bill for supplied services or goods.
- The back charge is a payment that does not need authorization since it is an unpaid expense forgotten by a supplier to charge the customer.
Examples
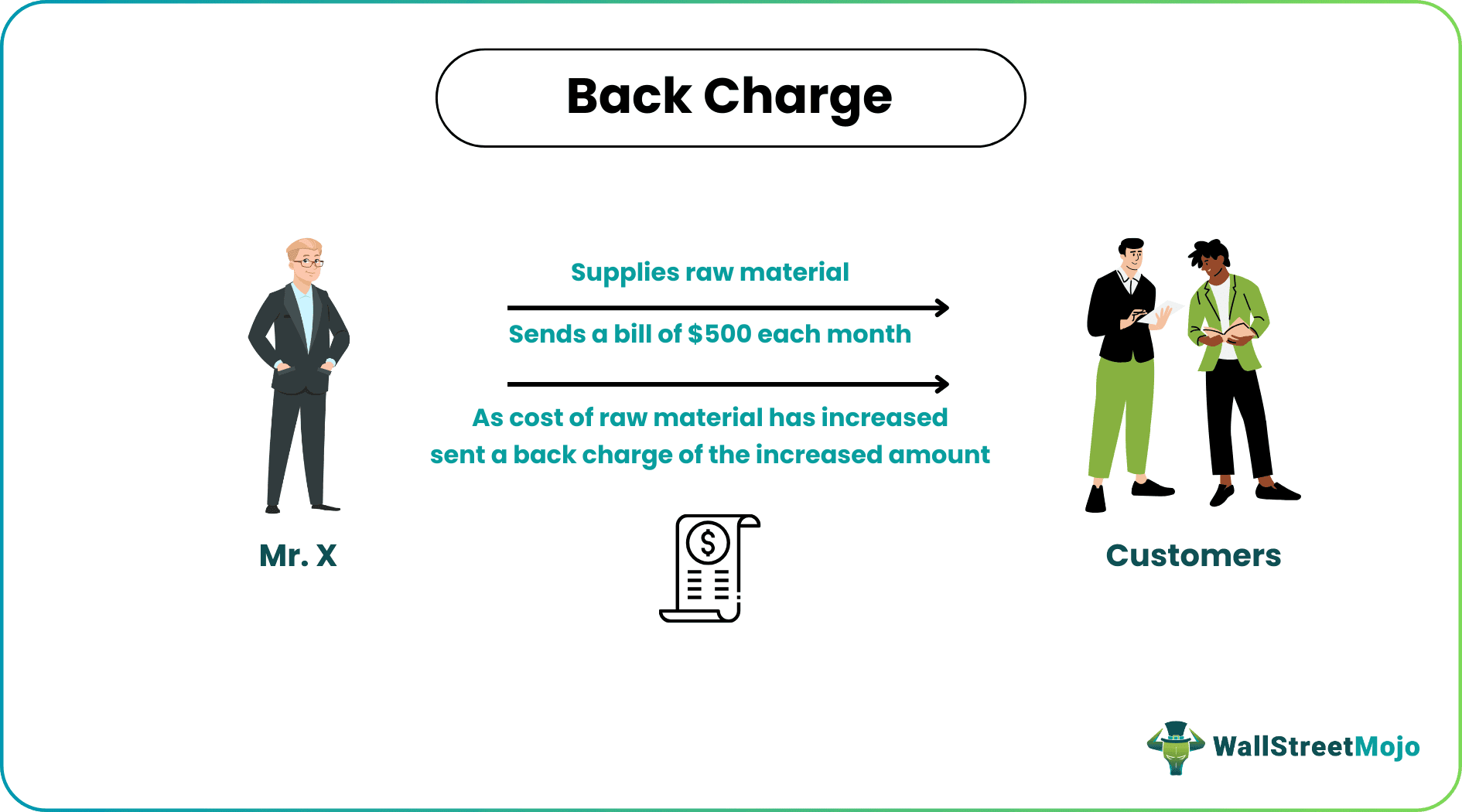
- Mr. X is a vendor who supplies raw materials to his customers. Each month Mr. X sends a bill of $500 to his customer. In March, Mr. X sent a similar bill of $500. After sending the bill, Mr. X realized that raw materials had increased. Next month, Mr. X sent a back charge of the increased amount along with the current month's bill. So this charge was due to an error caused by Mr. X. The charge will be an extra burden to the customer.
- Bank XYZ planned to increase the service fee of their credit cards from January. The bank didn’t inform the customers until February. So in February, back charges were sent to customers along with interest. It is common for credit card issuing banks as the interest is charged daily, and they try to delay the communication to the customers to charge interest on the charges.
Who Can take Back Charge?
A back charge can be taken by suppliers, service providers, or any company engaged in a transaction with other parties. Whenever a company produces a bill for services or goods supplied, they have the authority to produce such a charge in case of an error in billing or default in the payment received from the customers.
Back Charge vs. Change Order
The entire billing amount changes as the quantity changes and items change. The back charge doesn’t require any authorization as this is an outstanding expense that the supplier forgot to charge to the customer. On the other hand, the change order is a modification of the existing order and requires authorization. Say the customer ordered a particular arrangement, and due to some reason, if the supplier/customer is changing the order, then it will require authorization.
Advantages
- It allows suppliers to recover money if a wrong bill was sent to the customer. If the previous bill were less than the original revised bill, the supplier would lose. It also allows suppliers to recover money in case of mistakes in the billing process.
- If customers fail to make previous payments, then back charges give them another opportunity to clear dues and continue the transaction with the supplier. If there were no such mechanism, then a single default in bill payment would have ended the relationship between supplier and customer.
- These charges either increase your accounts payable, if you are a customer or, increase accounts receivable if you are a supplier. So this is important in accounting. The auditor needs the true picture of accounts receivable or payable to draw financial statements correctly.
