Table Of Contents
What Is Asset Misappropriation?
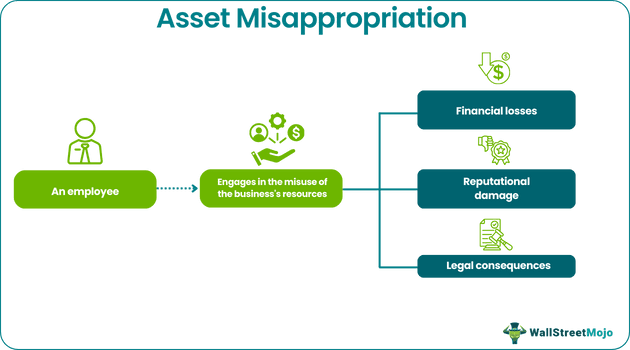
Asset misappropriation refers to unlawful activities that involve an organization’s employees taking advantage of their position to commit financial crimes. The theft or misuse of a company’s resources can damage its reputation and lead to significant losses besides regulatory and legal consequences. Hence, avoiding it is imperative.
Misappropriation of assets is one of the most common types of fraud in a workplace. The extent of the losses depends on what strategy the business uses to prevent it and how fast it can identify the fraud. Asset misappropriation is of different types, for example, skimming fraud, employment fraud, lapping, direct theft of money and goods, etc.
Key Takeaways
- Asset misappropriation refers to the unauthorized or fraudulent activities carried out by a company’s employee that involve misutilization of the organization’s resources or assets for personal gain or benefit.
- There are different types of asset misappropriation. A few examples are employment fraud, lapping, and billing schemes.
- Some popular asset misappropriation red flags include evasive employee behavior, unauthorized or unusual financial transactions, and sudden changes in an employee’s lifestyle.
- Organizations can consider rotating duties of employees belonging to the accounts department to prevent misappropriation of assets. Moreover, they can consider carrying out random audits to avoid illegal activities.
Asset Misappropriation Explained
Asset misappropriation refers to the most popular form of occupational fraud that involves employees misusing the business’s resources through inflated expenditure reports, fraudulent billing, etc. It is a noteworthy concern for businesses of different sizes; they must take measures to avoid it. Or else it might lead to regulatory or legal consequences, damaged reputation, and financial losses. Usually, people committing such fraud are a part of the top-level management. For example, they could be senior managers or directors because they have more control over the business’s assets.
Furthermore, in most cases, they decide how to utilize such assets. Note that assets may include machinery, office equipment, cash, vehicle, or anything that employees can utilize at work or take home with them without anyone knowing.
Generally, the reasons behind the unlawful activities are as follows:
#1 - Opportunity
Misappropriation happens when employees are trusted with assets they misuse. Hence, the opportunity requires employees to be in specific positions that allow them to manage assets. Note that weak internal controls may offer an opportunity as the employees are aware that the possibility of them getting caught is low.
#2 - Rationalization
Since fraud is unethical, people must rationalize their actions to eliminate the guilt related to committing a crime. They have to convince themselves no other way exists to fix the problem. Also, people might excuse it as taking funds that the organization will not miss since they make a substantial amount of money.
#3 - Motivation
Any employee who engages in fraud is often under some form of non-financial or financial pressure. A person may think that they cannot share their issues with their supervisors as it won’t lead to any solution. Hence, they look for other ways to fix their issues, even if that translates to going against ethical beliefs.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Types
Let us look at the different types of asset misappropriation.
- Skimming: It involves telling funds before the accounting team records them in the organization’s accounting system. Organizations often find it challenging to detect skimming when the employee who diverts the funds records the transactions.
- Direct Theft Of Money And Goods: This can cover a wide range of illicit or unlawful activities, for example, pocking funds in sales transactions and stealing physical goods, for example, assets, such as equipment and office supplies.
- Lapping: This deceptive practice involves employees covering their theft by utilizing funds from a different source. Generally, in this case, an employee diverts cash from a client to balance out the receivable from the first client.
- Employment Fraud: This type of fraud involves manipulating payroll or creating ghost employees to make personal gains.
- Intellectual Property Theft: As the name suggests, it means the theft of a business’s intellectual property, for example, proprietary information, trade secrets, or patents. Such fraud can take place if employees share confidential details with any competitor or utilize those details to commence a competing business.
- Billing Schemes: A billing scheme involves individuals manipulating existing invoices or creating fraudulent invoices in an attempt to steal funds from an organization. Such a scheme can also include inflating a legitimate invoice’s amount and keeping the difference.
How To Detect?
The following asset misappropriation red flags can help one detect the different types of illegal activities discussed above.
- Incomplete Or Missing Documentation: This may include missing invoices, receipts, or any other financial records.
- Sudden Lifestyle Alterations: A sudden change inthe lifestyle of an employee can be a tell-tale signal of asset misappropriation.
- Employee Behavior: If any employee becomes defensive or evasive when questioned regarding the organization’s financial transactions, it could indicate that they are hiding some kind of fraudulent activity
- Unexplained Transactions: Such transactions can include unauthorized or unusual expenses, like unexplained cash withdrawals, unusual spending patterns, or unauthorized expenses.
Other signs of employees misusing an organization’s funds are as follows:
- Unusually high frequency of replacements or repairs
- A high number of failures or tests
- Unbranded packaging
- Insufficient information in product packaging
- Inadequate warranty information
- Frequent inventory shortages
- Frequent reports or complaints regarding a specific employee
- Too many write-offs in the organization’s accounts receivables
Examples
Let us look at a few asset misappropriation examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose David was an employee of ABC Company, an online apparel and clothing store. He was working in the accounts department. When collecting payments from customers, he inflated the invoice amount without authorization and diverted the additional funds to a separate account outside the organization for personal gain.
That said, his manager identified the asset misappropriation because of two red flags — a great deal of defensiveness in David’s behavior when questioned regarding invoicing and a sudden upgrade in his lifestyle within a short period. Once David’s manager had doubts regarding David’s ethics, the former reported the latter to the top-level management. After a thorough investigation, the allegations were found to be true.
Example #2
In October 2023, the South China Morning Post reported that a person who was previously employed by ASML Holding faced accusations relating to asset misappropriation. The accused stole trade secrets from their former employer and later joined Huawei. ASML stated that the misappropriation of data associated with its proprietary technology violated certain export controls. Per a Bloomberg report, the theft targeted a chip machine repository, which included information regarding an advanced machinery of ASML.
The Veldhoven-based company informed the authorities regarding the breach and executed specific remedial measures in reply. Also, the organization stated that it would not have any material effect on the organization.
How To Prevent?
Let us look at some tips to prevent the misappropriation of assets.
- Carry out thorough background checks at the time of hiring any employee.
- Rotate duties of employees working in the accounts department.
- Do not pay any commission before the delivery of goods and services.
- Execute an ethics hotline that encourages employees to report any wrongdoing anonymously.
- Conduct undisclosed and random audits on every company account.
- Scrutinize business bank accounts from time to time.
- Do not give an employee access to different employees.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Generally, misappropriation involving cash is more straightforward to spot for businesses when compared to non-cash misappropriation.
Corruption includes bribery, conflicts of interest, financial extortion, and illegal gratifications. On the other hand, misappropriation of assets includes skimming, lapping, direct theft of money and goods, intellectual property theft, etc.
Among the various assets utilized by businesses, cash is the most susceptible to theft. That said, one must remember that inventory can be subject to theft as well.
There are different types of non-cash misappropriation of assets, for example, unauthorized transfer of assets and misuse of proprietary information for personal gain. As the name suggests, in the case of non-cash asset misappropriation, cash is not involved directly.

