Although ABCP and commercial papers share much in common, they have distinct features. So, let us look at the differences between them:
Table Of Contents
Asset-backed commercial papers, or ABCP, are short-term financial securities backed by assets, issued for 90 to 270 days. Hence, if the underlying assets fail to generate sufficient cash flow, there is a risk of default on the ABCP. The primary purpose of ABCP is to fulfill the company's capital requirement (or other borrowers).
These ABCPs intend to fill the debt gap of short-term money rules. Usually, the cycle for these money market vehicles remains between three to 9 months. Likewise, the payback period also stands at less than 30 days. However, asset-backed commercial paper issuers might not adhere to the standards leading to higher risk.
Key Takeaways
Asset-backed commercial papers are money market securities issued by large companies for less than a year. The maturity date for the ABCP is 270 days at maximum. Plus, its issuance is either on an interest or discount basis. In addition, they are set up by sponsoring financial institutions.
Therefore, the process of ABCP is similar to the commercial paper. However, it involves some extra elements and procedures. Let us look at them:
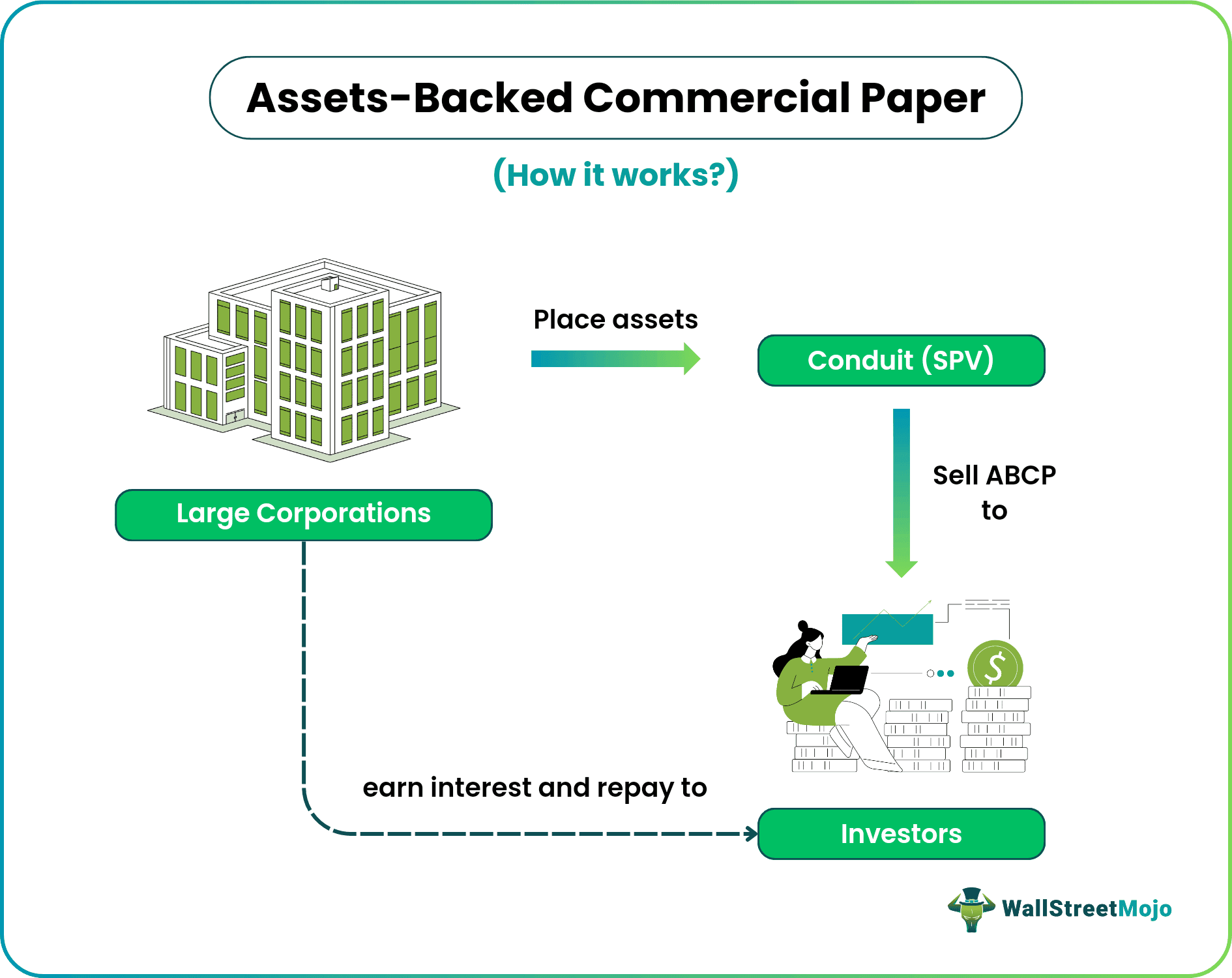
Usually, asset-backed commercial paper issuers give debt with lower credit risk. Hence, this risk is backed by collateral that includes the corporation's assets. The firm needing the money will issue an ABCP and sell it in the secondary market. However, they must first set up an SPV. The issuers who provide this facility are conduit or special purpose vehicles (SPV). Thus, the primary purpose of SPV is to own the sellers' assets. These assets could be notes like trade receivables with a short-term recovery period.
Let us look at the history from the rise to the asset-backed commercial paper in detail:
The structure of asset-backed commercial paper issuers involves two sellers, namely a single seller and a multi-seller program. Let us look at them:
As per this structure, there is a single seller who then buys assets from just one person. Plus, there is only one collateral kept within the SPV. Thus, there is no diversification, plus it involves higher risk.
Here, there are more sellers involved. Thus, there are various assets placed within the conduit. As a result, there is lower credit risk and higher liquidity.
Let us look at the examples of asset-backed commercial paper to comprehend the concept better:
Suppose Killis Ltd. is a credit financing company that provides loans to businesses. They have, in total, $100 million worth of collateral from home loans. However, the firm wishes to earn interest on these assets. Therefore, they intend to place these assets in an SPV. Killis Ltd then issues ABCP to the respective investors.
The collateralized assets of home loans backed this short-term security. Throughout the period, they earn interest and principal payments on it. Later, the firm went into bankruptcy. Still, the firm was able to repay the investors.
In this case, the SPV acted as a separate entity. Thus, there was no default repayment available.
For 2023, market analysts for the asset-backed commercial paper sector in the United States have a neutral outlook.
According to a recent update from Fitch Ratings, the ABCP sector would experience declining asset performance in 2023 due to its significant exposure to vehicle loans and leases, corporate and commercial loans, and trade receivables. However, due to the continuous credit quality, assigned scores on ABCP investments have endured.
According to Federal Reserve figures published on Monday, there was $1.1 trillion in outstanding asset-backed commercial paper. Due to a boom in issuance that started in August, unsettled commercial paper was up 9% for the year back in September.
Fitch analysts stated in the outlook that "volumes in ABCP were mostly unchanged in 2022, a pattern that we expect to continue in the near term."
Hence, in 2023, ABCP is anticipated to benefit from transaction-savvy administrators and liquidity support, particularly given the expected softening of underlying assets.
Besides, Fitch anticipates choppy inflows during the first three months of the year, but that institution-quality money-market mutual funds may still see a 0.08% gain in total assets.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages
Disadvantages
Although ABCP and commercial papers share much in common, they have distinct features. So, let us look at the differences between them:
| Aspect | Asset-Backed Commercial Paper | Commercial Paper |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Meaning | It refers to commercial papers issued for at least 90 days to a maximum of 270 days. | Commercial papers are debt instruments large corporations issue irrespective of the time frame. |
| 2. Purpose | To earn interest on the assets withheld in the SPV. | It acts like a promissory note to meet short-term obligations. |
| 3. Collateralized | Here, the ABCPs are backed by assets. | Any asset does not hold these papers. |
| 4. Credit Rating | There is no specific credit rating required. | A high-credit rating firm must issue commercial papers. |
| 5. Origin | 1900s | 1800s |