Table Of Contents
Arbitration Meaning
Arbitration, in technical terms, is a procedure where the parties can solve their disputes without the court's intervention. The main purpose of the arbitration clause is that it allows the parties to resolve their disputes with the help of a third party.
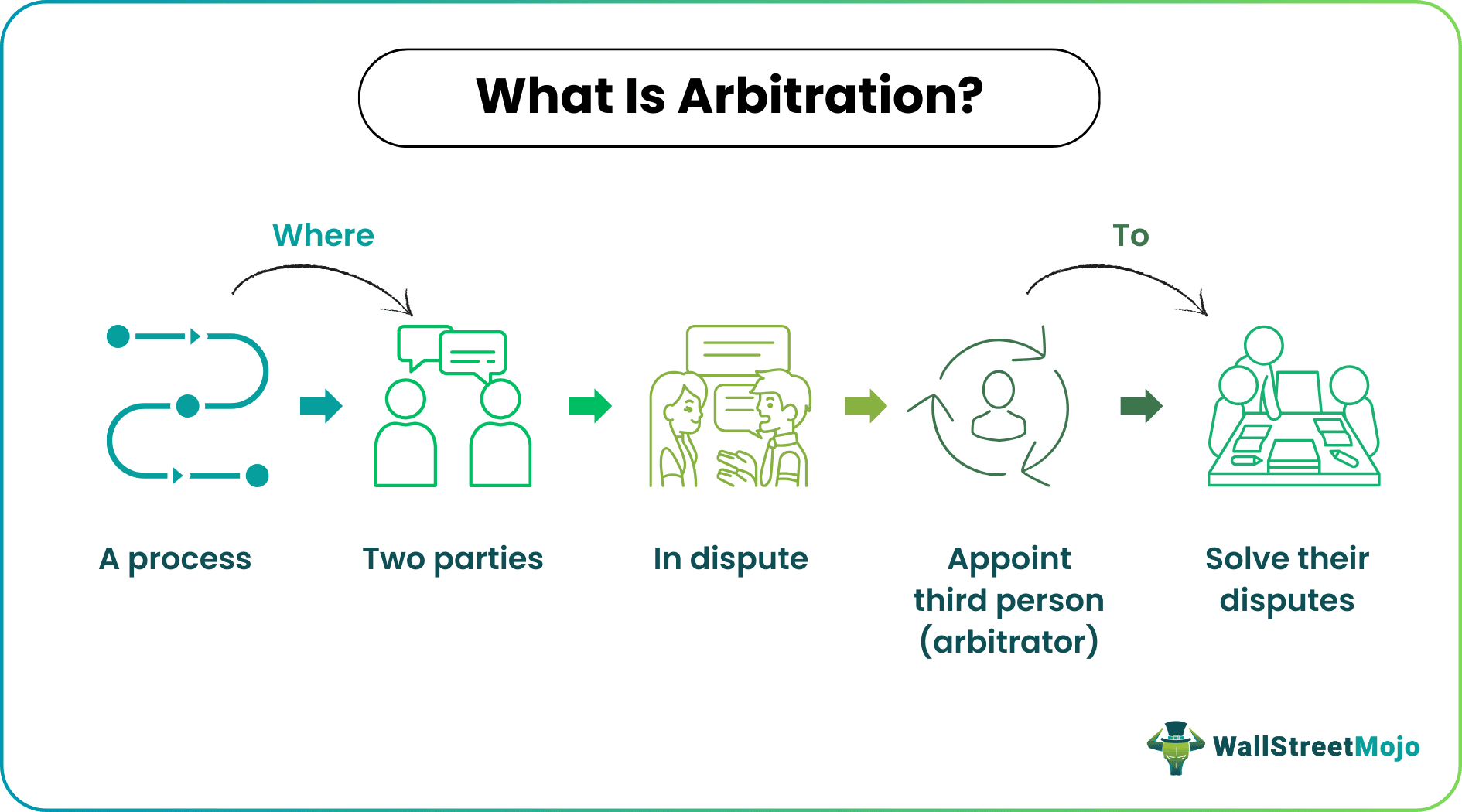
The arbitration agreement is popular in the stock market, business, and other property deals. It acts as a neutral decision-maker in disputes. As a result, these are confidential. Also, it is faster and more convenient to execute. However, once an arbitrator makes a decision, it cannot be denied by other parties.
Table of contents
- Arbitration Meaning
- Arbitration is an alternative available to court proceedings (like litigation) where the parties can resolve their disputes in the presence of a neutral third person.
- The procedure for arbitration differs from the court tribunals. Here, arbitrators conduct a hearing, and after evaluating the matter, the panel takes the final award (decision).
- It is easy, comfortable, and convenient to conduct. However, there are many minor fees included. Also, the arbitrator's decision is final and cannot change.
- FINRA is the major institution to solve disputes between investors and brokers.
How Does Arbitration Work?
Arbitration is an alternative to litigation that allows parties to resolve their disputes in the presence of arbitrators (neutral parties). It is a form of alternative dispute resolution. Here, arbitrators listen to their arguments, understand the case, and likewise give a decision. In short, they settle the dispute without needing a court proceeding.
In most cases, investors and brokers or broking firms go for an arbitration agreement. And institutions like FINRA (Financial Industry Regulatory Authority) regulate them. The arbitration process usually allows them to arbitrate any dispute with the broker. So, if the investor is in any dispute with the broker, they can appeal to FINRA for it. They must submit the Statement of Claim and Submission Agreement.
It contains the disputed matter, the amount of money involved, and the consent of parties to name FINRA as an administrator. Also, they must pay arbitration fees, including initial filing, brokerage firm fees, injunctive claims, hearing sessions, adjournment, etc. Thus, FINRA will appoint two or more (usually three) persons who act as arbitrators on their behalf.
Arbitrators are either financial experts from the industry or partially biased toward a party. They then review the matter and make a final decision (also known as "award") within 30 days. However, the number of arbitrators depends on the case value. For example, if the claim is up to $100,000, there is one arbitrator. Likewise, for more than $100,000, there are three persons appointed.
However, the decision does not follow any legal precedent or state or federal laws. Thus, both parties can only accept the arbitrator's decision on statutory grounds.
A broker cannot compel an investor to arbitrage if an agreement lacks an arbitration clause. However, FINRA permits a customer to use arbitrage at its request. Likewise, if any parties oppose the panel award, it leads to a violation or breach of the arbitration act. However, the resolution can take almost 16 months if the arbitration goes for a hearing.
Types
Let us look at the types of Arbitration to understand the concept better:
#1 - Institutional Arbitration
Here, an institute acts as an arbitrator who tries to resolve disputes between parties. It is used mostly by investors and broking firms. These institutions might be on either a national or international level. Also, they stay within the federal arbitration act for conducting the proceedings. For example, the American Arbitration Association and FINRA are some institutions conducting arbitrage.
#2 - Ad Hoc Arbitration
It is used more by the parties who need help to afford the institutional arbitrators. According to ad hoc arbitration, parties appoint an arbitrator who acts as neutral to resolve their disagreement. They have the freedom to conduct it the way they want. Therefore, it is easier to perform.
#3 - International Arbitration
Parties go for this Arbitration when disputes are between two parties living in different countries. As a result, conducting an arbitrage becomes difficult. Therefore, an international institution conducts it following the arbitration process and regulations. For example, the International Court of Arbitration is an international arbitrator operating in 45 nations.
#4 - Domestic Arbitration
When parties live in the same city and choose arbitrage, it is known as domestic arbitration. So, if the parties reside in New York, arbitrage of their dispute occurs domestically.
#5 - Emergency Arbitration
If either party fears losing their assets, the arbitrator can fasten the process in such an emergency case. As a result, the former can request the arbitrator for such interim urgent relief.
Examples
Let us look at the examples of arbitration to understand and comprehend the concept better:
Example #1
Suppose a sale agreement bonds between Enid and Robert. While the former is an investor, and the latter is the broker working on the small scale level. According to the deal, if Enid bought 1000 shares, Robert would charge $2 per transaction as brokerage. However, as Enid wished to do so, Robert denied proceeding. As a result, the former approached FINRA for a third person to solve the dispute. The FINRA appointed an arbitrator to review the matter, conduct a hearing, and give an award. Ultimately, the arbitrator asked Robert to proceed with the transaction and that the decision was final.
Example #2
According to a statistical report by FINRA, in 2022, there were 2,423 new arbitration cases registered with them. Out of them, 64% were consumer related. However, in 2020, there were almost 3,615 new cases. And the number drops by 11% compared to 2021 (2711 cases).
Advantages And Disadvantages
Arbitration is an essential element of an agreement for investors, brokers, and business deals. However, it does have some pros and cons to the concept. Let us look at them:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Less expensive compared to court proceedings. | No further appeal as the arbitrator's decision is final. |
| High confidentiality by the arbitrators | There is no right of discovery for parties |
| No legal or exclusionary rules of evidence are applicable. | Although less expensive, there might be many charges discovered. |
| No intervention from the court | Lack of transparency in the process |
| Less penal damages compared to ligation. | Standards or processes used by arbitrators sometimes need to be clarified to the parties. |
| Easy and convenient to exercise. | |
| Fair decision made by the arbitrator | |
| Faster resolution of disputes between parties |
Difference Between Arbitration And Mediation
Although arbitration and mediation involve a third party, they have different roles in both contexts. Let us look at the differences between them:
| Basis | Arbitration | Mediation |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A type of dispute resolution where parties resolve without the need of court with the help of an arbitrator. | Mediation involves a mediator who helps to resolve the dispute between two parties. |
| Purpose | To settle a legal matter in the presence of a third party (the arbitrator). | To clear up all misunderstandings that arose during the conflict between the parties. |
| Process | It is conducted formally. | It happens informally. |
| Third-party | FINRA appoints three arbitrators. | Only one mediator acts between them. |
| Occurs between | Investors, brokers, broking firms, business partners, and others. | Anyone |
| Final decision | The arbitrator's decision is final and cannot be appealed. | Here, the mediator can only suggest solutions. However, the outcome lies with the parties. |
Difference Between Arbitration And Conciliation
Although arbitration and conciliation are types of alternative dispute resolution, they have distinct differences between them. Let us look at them:
| Basis | Arbitration | Conciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It is an alternative to litigation to resolve disputes between parties with the help of a third person (the arbitrator). | Conciliation involves an independent person that helps in resolving a conflict between parties. |
| Purpose | To resolve conflicts without the intervention of the court. | To peacefully settle the disputes between the parties. |
| Decision-making power | Arbitrator has the power to make the final decision on the matter. | The conciliator cannot enforce their decision. |
| Availability of the third person | It can be used today as well as in the future. | The conciliator is only available for current disputes and not future ones. |
Arbitration vs Negotiation
Although arbitration and negotiation are methods to resolve disputes, they have major differences. Let us look at them:
| Basis | Arbitration | Negotiation |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It refers to a procedure where parties can resolve conflicts following the third-person (arbitrator) decision. | Negotiation is an initiative either party takes to resolve their dispute or disagreement. |
| Purpose | To resolve disputes with the help of a third person. | To settle the conflict without approaching court or any third person. |
| Procedure | There is a proper procedure followed like hearings, conferences, and others. | Parties do not need any procedure. They can perform with any set objectives in their mind. |
| Cost/Fees | Different fees include filing, hearing, administrative, and other fees. | Compared to the former process, the cost involved is minimal. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
According to FINRA, many minimal fees are included in the arbitrage process. However, they are less compared to litigation. For example, the arbitration fees range from $50 to $2300 depending on the claim value between $0.01 to $5,000,000. However, for non-monetary claims, the filing fee is $1600.
Yes, non-binding arbitration is mostly used in the United States and Canada. In addition, it is also followed in Europe.
Yes, the arbitrage clause remains to survive despite the main contract expiration. However, it can be violated if the parties refuse to accept the arbitrator's decision.
It can be voluntary or mandatory, depending on the agreement's terms. Formerly, the parties themselves decide voluntarily to resolve their dispute through arbitration. In contrast, mandatory arbitration requires them to appoint an arbitrator per their deal.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Arbitration and its meaning. We compare it with mediation and conciliation, its types, examples, advantages, and disadvantages. You may also find some useful articles here -
