Table Of Contents
What is Annuity Due?
Annuity Due can be defined as those payments which are required to be made at the start of each annuity period instead of the end of the period. The payments are generally fixed and there are two values for an annuity, one would be future value, and another would be present value.
Key Takeaways
- Annuity due is an annuity in which the payments or cash flows are made at the beginning of each period, as opposed to the end.
- Annuity due calculations involve adjusting the formulas used for regular annuities to account for the difference in timing. This adjustment is typically made by multiplying the familiar annuity formula by (1 + r), where r is the interest rate.
- Annuity-due payments can be found using mathematical formulas, financial calculators, or spreadsheet software. The present value of an annuity is due can also be calculated by discounting the future cash flows to their current value.
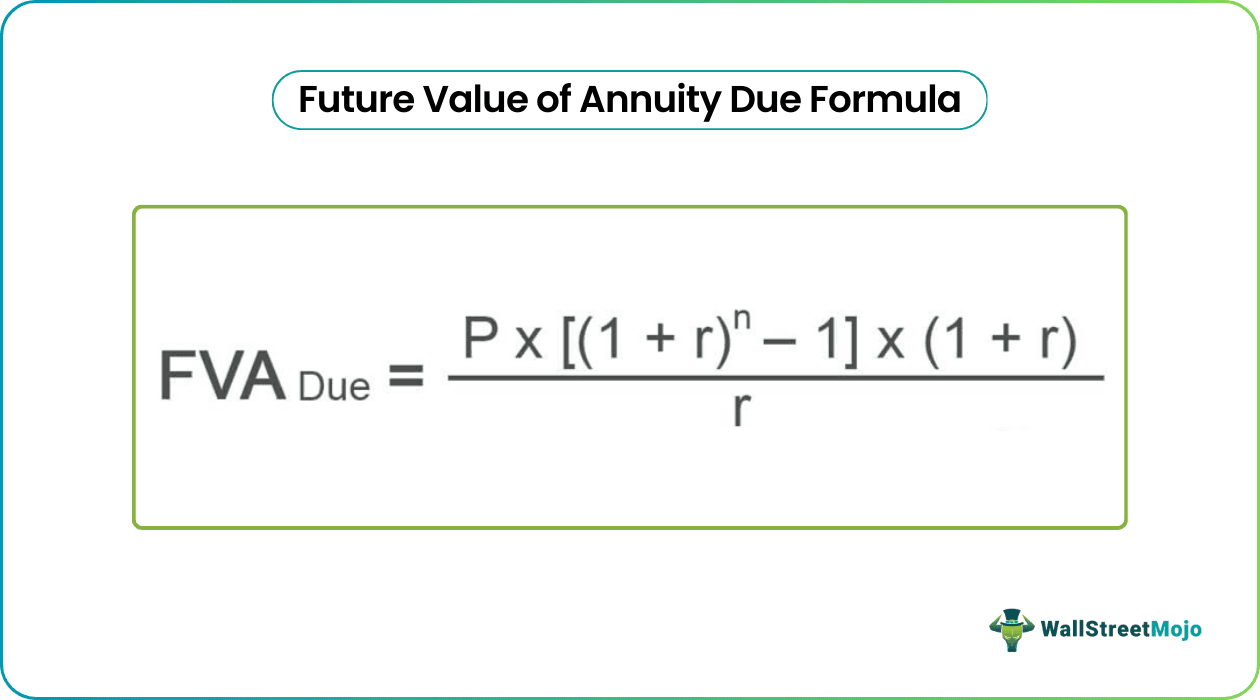
Annuity Due Formula
The below formulae can be used depending upon what is short for, whether the present value or the future value.
Present Value of Annuity Due = P + P
and
Future Value of Annuity Due = (1+r) x P
Where,
- P is the Periodic Payment
- r is the interest rate for that period
- n will be a frequency in that period
Examples
You can download this Annuity Due Formula Excel Template here – Annuity Due Formula Excel Template
Example #1
Stephan has deposited $1,000 at the start of the year and plans to invest the same every year until five years. The interest rate earned will be 5%. You are required to do the calculation of the future value of an annuity due.
Solution:
Here we are being asked to do the calculation of the future value of an annuity due using the below information
- Periodic Payment (P): 1000
- Number of period (n): 5
- Rate of Interest (r): 5.00%
For calculation of the future value of an annuity, we can use the above formula:

Future Value of Annuity Due = (1+5.00%) x 1000
Future value of an annuity due will be -

Future value of an annuity=$ 5,801.91
Therefore, the future value of the annual deposit of $1,000 will be $5,801.91
Example #2
Mr. William wants to purchase a house after a couple of years. His target house value is $3,000,000. He decides to invest in a product where he can deposit yearly $600,000 starting at the beginning of each year until year 10. He wants to know what is the present value of the annuity investment that he is doing. This would enable him to know what the true cost of the property in today’s term is. You are required to do the calculation of the present value of the annuity due that Mr. William is planning to make. Assume that the rate earned on investment will be 12%.
Solution:
Here, Mr. William is making an annual investment of $60,000 to achieve the goal of purchasing the property, which values around $3,000,000.
- Periodic Payment (P): $600,000
- Number of period (n): 10
- Rate of Interest (r): 12%
- Frequency of Interest: 1
We are given the principal amount, the frequency of investing, and the rate of interest, and therefore we can use the below formula to calculate the same.

Present Value of Annuity Due = 60,000 + 60,000

It appears that by investing $600,000 yearly in the product, Mr. William would be easily able to purchase the house, which is what he is planning for.
Example #3
Company X is a highly capital-intensive invested company. It imports most of the machinery from foreign countries as it is cheaper than buying from the local market. The company plans to set aside an amount of $118,909 semi-annually starting now. As per the recent market trends, the average revenue earned on the investment is 8%. The company expects to fund the machinery after 15 years, where they expect the value of the machinery to be $7,890,112. The company wants to know what the future value of the investment shall be, and will they be able to fund it, or they would require funds in the form of a loan.
You are required to calculate the future value of the annuity investment done by the company and compute the amount of loan if the company requires it?
Solution:
In this example, the company is trying to keep aside funds for replacing the machinery and avoid any Ad Hoc fund requirement in the form of costly borrowing.
- Investment amount per period (P): $118,909
- Number of period (n): 15
- Rate of Interest (r): 8%
- Frequency of Interest: 2
The frequency here is semi-annually. The payment every period gave is $118,909, and the period will be 15*2, which is 30 years. The rate of interest will be 8/2, which is 4%

Future Value of Annuity Due = (1+0.04) x 118,909 [{(1+0.04)30-1}/0.04

The value of the machinery is $7,890,112, and the return from the investment amount is $6,935,764.02, and therefore, the company will be required to borrow a loan, which shall be a difference of these which is equal to $954,347.98.
Relevance and Use of Annuity Due formula
An annuity due will require payments to be made at the start of the period, contrary to the end of every period of an annuity. An individual who is legally entitled to payments represents it as an asset. On the flip side, the individual required to pay the annuity, which is due, shall have a legal debt liability that requires timely payments.
Because a series of annuity due payments represents several cash inflows or outflows that shall occur in the future, the recipient or the payer of the funds would like to compute the wholesome value of the annuity while accounting for the time value of money. This can be accomplished by using the present value of an annuity due.

