Table Of Contents
What Is The Annual Report?
An annual report is a document published by the company for its various stakeholders, internal and external, to describe its performance, financial information, and disclosures related to its operations. These reports have become legal and regulatory requirements over the years. For example, US companies have been mandated to publish such reports by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) since the early 1930s.
Components of Annual Reports
Across global markets, Annual reports have different formats and components; this happens due to statutory requirements in different economies. Following are some of the components in general:
- Director's message to shareholders
- Information on corporate governance
- Financial highlights
- Management discussion and analysis
- Shareholding pattern, management/board of directors’ information
- Detailed and audited financial statements
- Statement of financial position
- Income statement
- Statement of Cashflows
- Statement of Changes in Equity
- Notes to financial statements
- Usage of accounting policies and changes, if any
- Other information or disclosure.

Annual Report Format
It usually starts with the director's message to shareholders. This message intends to brief them about the key performance points of the current year. It also acknowledges the growth prospects relative to its industry landscape to mostly get shareholders' attention to the company's potential for excellence.
These reports also give an account of corporate activities and legal highlights. In addition, the MD&A section emphasizes management commentary on the business.
Then comes the most important section – financial statements and associated notes. Financial statements give financial details of the current year and the past year; this makes year-on-year comparisons easier for a shareholder. In addition, the notes to financial statements describe the technical anomalies and assumptions taken in preparing the financial statements.
The later sections of this accounting report present changes in accounting policies, financial disclosure, capital projects, and other information relevant to shareholders.
Note: In the United States, these reports can also be presented in a format known as the 10-K. However, there are many differences between these two documents. An annual report is more graphical and interactive to its shareholders.
Example

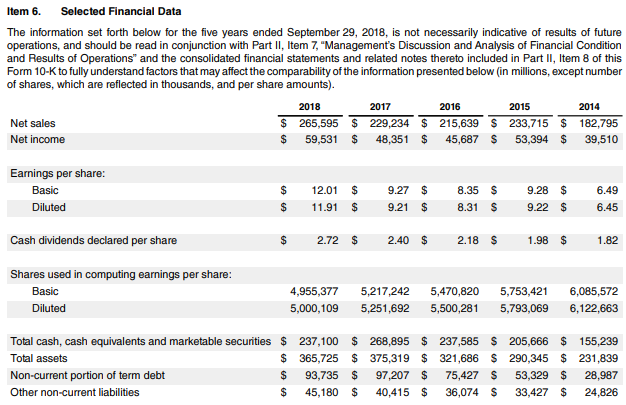
Source: https://s2.q4cdn.com
How To Read an Annual Report?
There are no specific guidelines to read annual reports. However, these are some general tips on how to make the most out of it –
- It starts with the director's note. It outlines the highlights of the current year and recent past and a brief on prospects and strategies.
- It gives a section on management discussion and analysis. This section helps the stakeholder know what the management thinks about company performance and prospects. It also gives a view of the industry and economy in which the business operates.
- Financial Statements are perhaps the most important section. It is crucial to know the structure of the subject business by reading the information on shareholding patterns; this helps define if the report is a consolidated or standalone publication.
- Notes to financial statements are an unavoidable reading as this section backs up the data contained in the three financial statements. To analyze financial statements and carry out forecast methodologies, notes to financial statements are significant.
Below is an illustration of how Amazon Annual Report describes its competition landscape:

Source: https://ir.aboutamazon.com
Benefits
- Annual reports are intended to provide information and disclosure on business prospects and financial performance, its stakeholders, which include investors, creditors, auditors, government officials, etc. Moreover, they serve the employees, suppliers, customers, etc.
- Institutional and individual investors use them to analyze and forecast financial statements to evaluate the company's prospects.
- These reports are, in essence, standardization practices for companies to report their business performance. Such standardization helps government authorities in taxation and audit purposes.
Limitations
- Annual reports are comprehensive but are not always fulfilling in terms of completeness. They are used with other SEC filings, corporate press releases, management notes, proxy statements, etc.
- These are sometimes released to attract investors and supply-chain parties. The prospective expenditures and income are projected in a way that makes the business appealing.
- They are based on historical performance. Hence, the estimation of future performance is not always best measured.
Important Points to note
- Annual reports contain financial information for the past several years. However, these financial data are subject to changes in the future. Changes in accounting policies can lead to prospective as well as retrospective applications. The users should consider this and perform their analysis accordingly.
- Besides these reports, companies also release quarterly reports. It is good to refer to both kinds of reports to gather relevant information.
- While using these reports to analyze and forecast financial statements, the best practice is to use data from the most recent years. For instance, data for FY2016 should be taken from the Annual report 2016-17; this is because companies keep on revising data with changes in accounting policies regarding the retrospective approach.
Below is an excerpt from the Annual Report of Airbus company highlighting the Changes in Accounting Policies and disclosures:
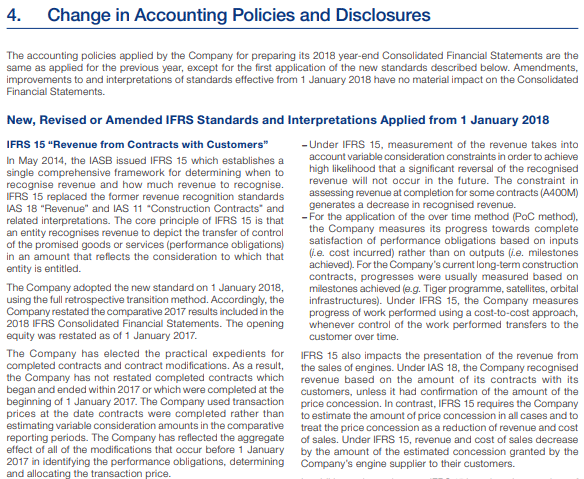
Source: https://www.airbus.com
Conclusion
An annual report is helpful for its stakeholders in understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the business. This document is prepared for different purposes and serves different users. In preparing this document, companies must follow accounting standards and depict business to its investors and creditors as clearly as possible.
Independent teams of auditors verify this report, and credibility depends on the report's accuracy. These reports are published and released online and made available in hard print to stakeholders.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to what is an annual report. Here we discuss components, examples, and how we read an annual report and its benefits and limitations. You can learn more about financing from the following articles –

