Table Of Contents
Anchoring Bias Definition
Anchoring bias is a cognitive bias that explains the human tendency to base a decision on a particular piece of data or anchor. The anchor acts as a reference point while making a decision when there is no other reliable way of finding the exact answer. This bias prohibits a person from making an informed and rational decision.
The concept finds utility in behavioral finance. Traders mostly fall into the trap of anchoring bias in stock and securities trading. Anchoring bias comes into play due to emotional decision-making. Most of the time, the historical data set acts as an anchor that pushes an individual towards this bias. The first instance of information always influences decisions for subsequent events or objects.
Key Takeaways
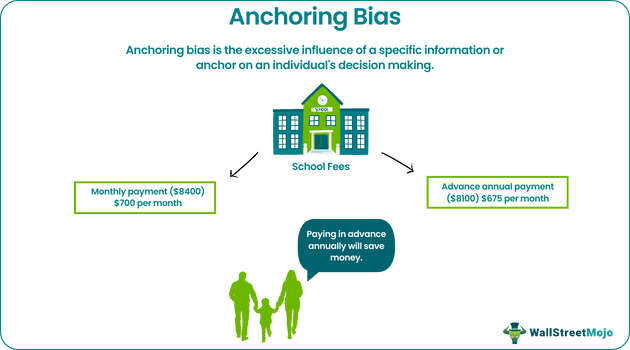
- Anchoring bias is the excessive influence of a specific information or anchor on an individual’s decision-making.
- It may result in irrational decisions and substantial losses.
- In behavioral finance, it explains the fixation of buyers towards a particular price that influences their buying decisions.
- In stock trading, investors keep an anchor price of a security in mind and take a position in the market without finding its intrinsic or real value.
- The only way to overcome the bias is by being a logical, rational, and analytical thinker and using extensive research on quality, price, and history before making any decision.
Anchoring Bias Explained
Anchoring bias is a human inclination to depend on certain information, usually the first, for decision making. This initial information or anchor references all subsequent negotiations. Note that the anchor can be any information that may or may not be related to the decision.
Psychologists Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman first propounded the theory of Anchoring bias in their book Judgment under Uncertainty: Heuristics and Biases. Anchoring bias is the most common and necessary evil in everyone’s life that escapes notice when making any buying decision.
Whenever people go to buy a product, they already have some idea of the product price or research the same. But at times, there is no clear way of knowing the exact price of the product. That’s when people get swayed by the anchor.
Either people come up with a reference or anchor, or someone else provides them with it. It sets their expectations of the product price and creates prejudice in the mind that a particular item is the best one available at the lowest price.
Suppose a person walks into a showroom with a budget of $1000 to buy an item of antique furniture. The person finds a unique piece of furniture whose value is hard to determine. The salesperson mentions its rate as $1500 and offers to give a discount on it. It creates the impression that any deal below $1500 is reasonable.
Thus, discounted price acted as an anchor based on which the person gets inclined to buy the furniture. Here the sales personnel provided the anchor, which influenced the person to buy beyond the budget without giving two thoughts about the actual worth of the furniture.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Examples in Finance
Although anchoring bias is mainly related to psychology. But it finds wide application in the finance world. Many securities traders make a wrong investment under the influence of Anchoring bias, as explained in the following anchoring bias examples.
Examples #1
Let’s assume investor A decides to buy the shares of Amazon after looking at its splendid performance in the stock market in the year 2021. In July 2021, Amazon stock reached the pinnacle of $3,731. This price acted as a mental anchor for his decisions.

Source: Yahoo finance
So, on January 26, 2022, he bought the 1000 shares of Amazon at $2,777. He waited for the stock prices to go up. As expected, within a month, the stock prices rose and reached $3,308. However, since his mental anchor was set at $3,700, he didn’t sell the stock and waited for the price to touch the anchor. Unfortunately, the Amazon stock prices took a deep dive.
Thus, due to anchoring bias, A couldn’t sell the stock at any value below the anchor price. This resulted in a substantial loss for A.
Example #2
Let us assume that the stock market grew by 90% in 2021, closing at 15,200 points. It had closed at 8,000 points in 2020. Hence, investor X looks into the above information and makes his trading decisions based on the market's exponential growth
However, trader X never realized that the stock market had only gained a miniscule 20% in 2020. Had X known the 2020 situation of the markets, the trader would not have relied only on 2021 performance.
Thus, the trading decisions of X were skewed by anchoring bias where the stock market performance of 2021 served as the anchor. As a result, X suffered huge losses.
Video Explanation - Anchoring Bias
How To Avoid?
The anchoring bias is an inbuilt cognitive function of the human brain. Every person falls for it to make quick decisions. It is entirely based on the emotional thinking brain.
Hence, to overcome the bias of anchoring:
- Remove high emotional quotient from decision making
- Analyze the rationale in all the decisions of life and stick to it
- Conduct thorough research before making any decision
- Develop an objective mentality in every circumstance
- Promote critical and logical thinking
All these traits must be transformed into daily thinking habits to overcome the anchoring bias in any aspect of life.
In securities trading, all the above behavioral traits must be led by extensive research about the past and present performance of financial instruments. Investors must examine these data critically and use technical and fundamental analysis tools to ascertain the true value of a security before making a trading decision. This helps avoid anchoring bias which is an integral part of speculative trading.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is the weakness of the human mind which clouds an individual’s decision-making ability and restricts it to a specific anchor or information. The anchor is then utilized to make the decisions without any rational and logical thinking.
When instant decisions have to be made, anchoring bias helps people make a reasonable judgment. Moreover, sellers can exploit the anchoring bias of the buyers and provide an anchor price. This encourages buyers to strike a deal at a price close to the anchor price.
The only way to minimize Anchoring bias is to be more pragmatic in approach, be cautious of the seller's trap, be more vigilant of emotional interference, and have a logical and analytical approach in all the decision-making process.

