Table Of Contents
Advantages and Limitations
The primary advantage of premium bond amortization is that it is a tax deduction in the current tax year. Suppose the interest paid on the bond is taxable. In that case, the premium paid on the bond can be amortized, or in other words, a part of the premium can be utilized towards reducing the amount of taxable income. Also, it leads to reducing the cost basis of the taxable bond for premium amortized in each period.
However, in the case of tax-exempt bonds, the amortized premium is not deductible while determining the taxable income. But the bond premium has to be amortized for each period, and a reduction of cost basis in the bond is necessary each year.
Conclusion
For a Bond investor, the premium paid for a bond represents part of the cost basis for tax purposes. Therefore, premium amortized yearly can be used to adjust or reduce tax liability created by interest income generated from such bonds.
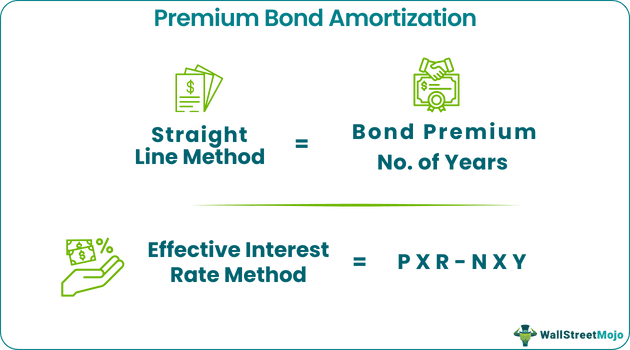
Calculating Bond Premium amortized can be done by any of the two methods mentioned above, depending on the type of bond. Both bond amortization methods give the same final results. However, the difference arises in the pace of interest expenses. The Straight Line method of amortizationgives the same interest expenses in each period.
An effective Interest rate method of amortization, on the other hand, gives decreasing interest expenses over time for premium bonds. In simple words, expenses decrease with a decrease in book value under the Effective Interest rate method. This logic seems practical, but the straight-line method is easier to calculate. If the primary consideration is to defer current income, the Effective Interest rate method should be chosen to amortize the premium on bonds. The Straight Method is preferable when the premium amount is very less or insignificant.