Table Of Contents
What Is Agency Problem?
The agency problem can be defined as a conflict when the agents entrusted with the responsibility of looking after the interests of the principals choose to use the power or authority for their benefits and in corporate finance. It is a conflict of interest between its management and stockholders.
It is a common problem in almost every organization, whether a church, club, company or government institution. A conflict of interest occurs when responsible people misuse their authority and power for personal benefits. However, it can be resolved if only the organizations are willing to fix it.
Key Takeaways
- The agency problem refers to the conflict when the agents are liable to look after the principals' interests selected for using the power or authority for their perquisite or corporate finance.
- The agency's problem is an interesting conflict between its management and stockholders.
- The agency problem types are stockholders vs management, stockholders vs creditors, and stockholders vs other stakeholders.
- Companies can tackle the agency issue by providing rewards for high performance, enforcing sanctions for poor performance
- and inappropriate behaviour, implementing stringent screening procedures, etc.
Agency Problems Explained
Agency problems are the mismatch of interests between the company’s management/ creditors/ other stakeholders (employees, customers, society, community, etc.) and its stockholders, which may sooner or later result in a conflict of interest. Therefore, companies must address the underlying problems to ensure that their regular profit business operations are not impacted. This problem can exist anywhere: a company, club, church, or government institution.
The three types of agency problems: stockholders vs. management, stockholders vs. bondholders, creditors, and other stakeholders like employees, customers, community groups, etc. Companies can resolve it with the help of measures like offering incentives for good performance and behavior and penalizing for poor performance and bad behavior, tough screening mechanisms, etc. Of course, it is almost impossible for companies to eliminate agency problems, but it can still minimize the same implications.
The problem may arise due to many reasons like change in goals, risk preferences and incentive structure, there may be a mismatch or lack of clarity in the flow of information, lack of consequences of action that is detrimental to the organization, lack of proper knowledge regarding the agent’s capabilities and intentions before assigning them the job, misalignment in the incentive structure. and compensation package of the agent leading to lack of satisfaction, etc.
However, principal agency problem is a very important concept in the corporate governance field as well as in economics and financial management. The concept brings into light the complex situations and challenges that commonly arise when many parties take decisions and also points out the importance of designing a mechanism that aligns the interest of all parties to achieve the best results.
Types
Every organization has its own set of long-term and short-term goals and objectives that it wishes to achieve in a predetermined period. In this context, one must also note that the management's plans may not necessarily align with the stockholders, leading to principal agency problem.
The management of an organization may have goals that are most likely derived to maximize their benefits. On the other hand, an organization's stockholders are most likely interested in their wealth maximization. This contrast between the goals and objectives of the management and stockholders of an organization may often become a basis for agency problems. Precisely speaking, there are three types which are discussed below: -
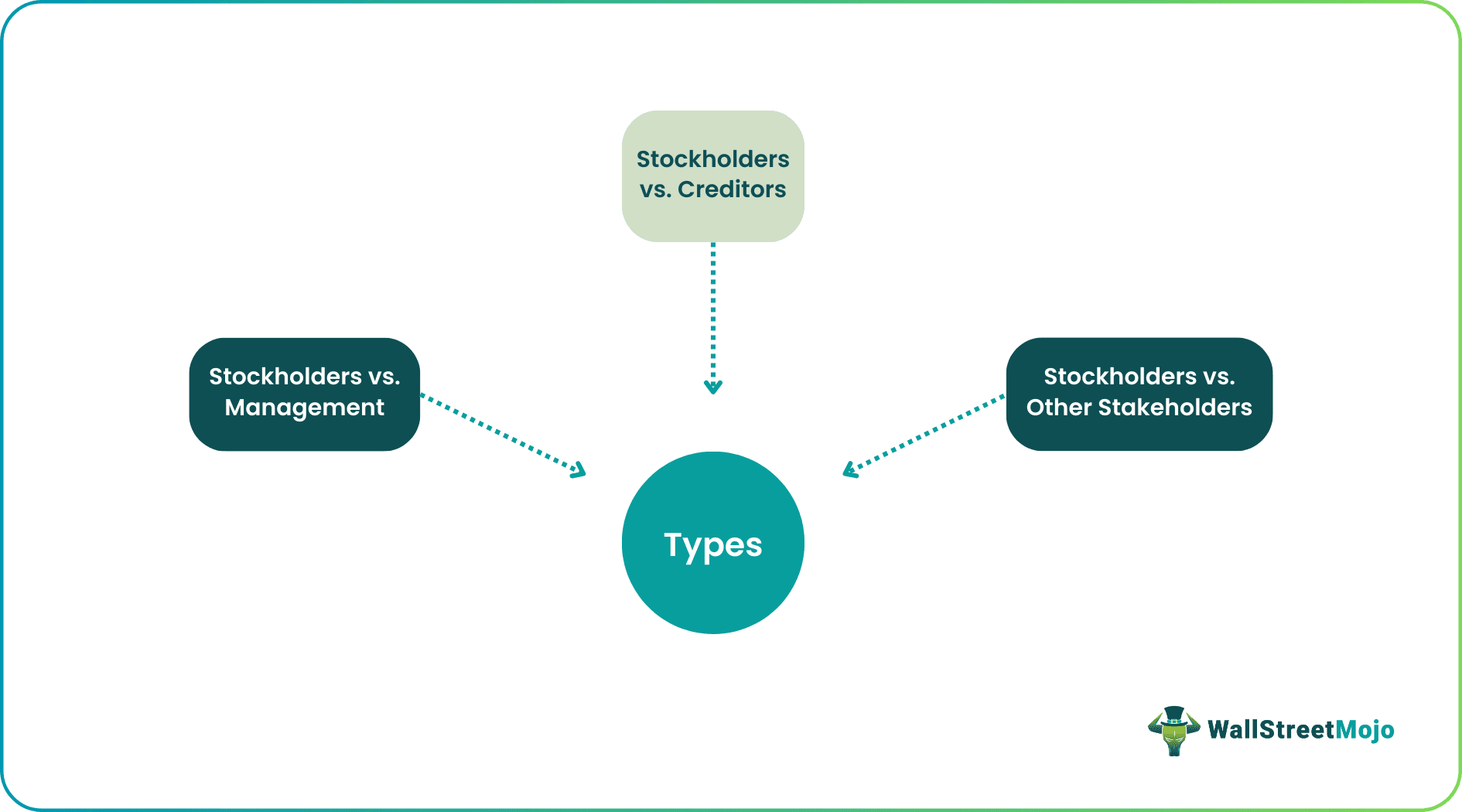
- Stockholders vs. Management – Large companies may have many equity holders. It is always crucial for an organization to separate management from ownership since there is no reason to form a management part. Segregating rights from management has endless advantages as it does not affect regular business operations. The company will hire professionals to manage the key functions of the same. But hiring outsiders may become troublesome for stakeholders. The managers hired may make unjust decisions and misuse the shareholders’ money, which can be a reason for the conflict of interests between the two and agency problems.
- Stockholders vs. Creditors – The stockholders might pick up risky projects to make more profits. This increased risk might elevate the required ROR on the company’s debt. Hence, the overall value of the pending debts might fall. If the project sinks, the bondholders will supposedly have to participate in losses, resulting in agency problems with the stockholders and the creditors.
- Stockholders vs. Other Stakeholders – The stakeholders of a company may have a conflict of interests with other stakeholders like customers, employees, society, and communities. For example, the employees might be asking for a hike in their salaries which, if rejected by the stakeholders, there is a probability of agency problems occurring.
Example
Let us understand the concept of agency problem in corporate governance with the help of a suitable example.
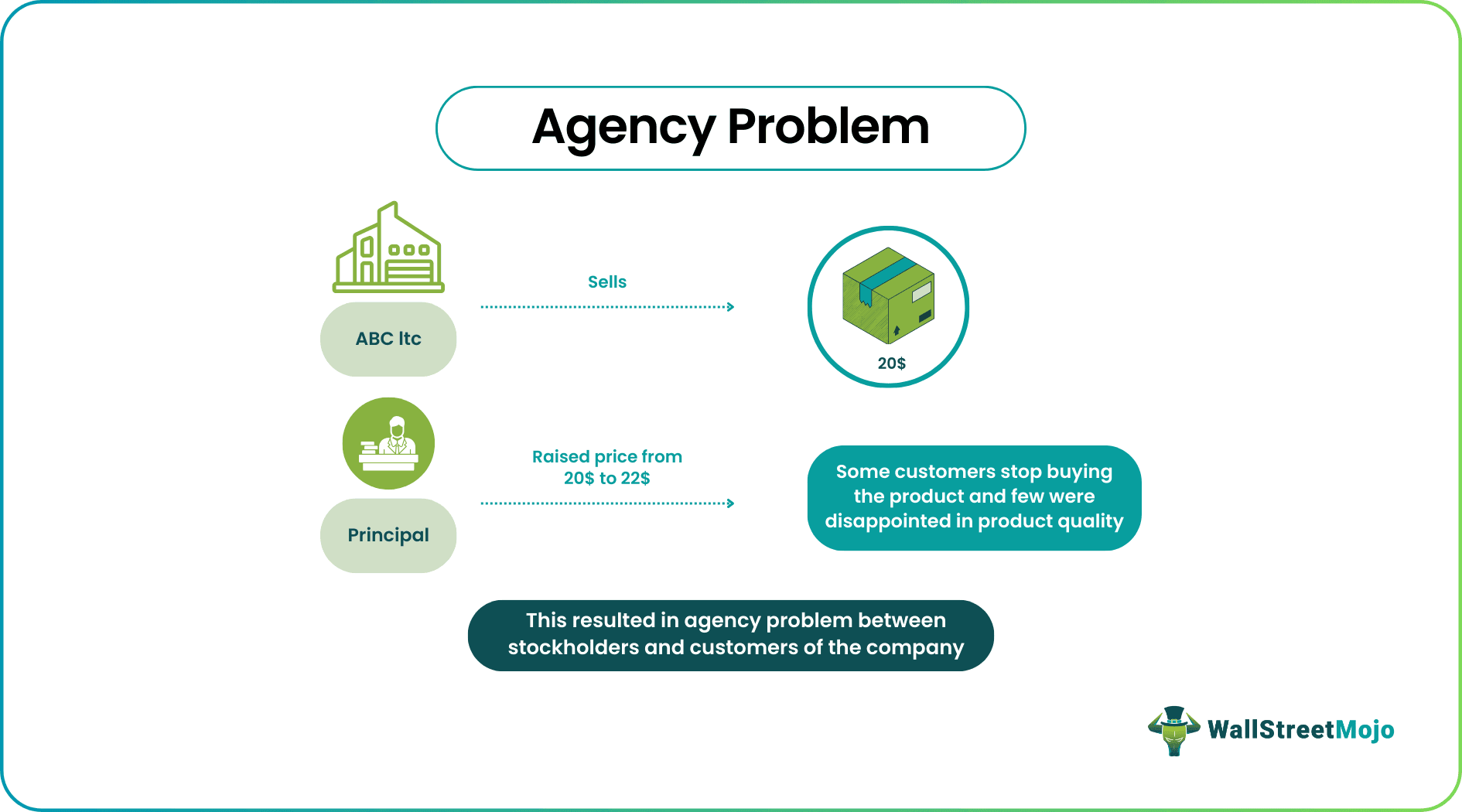
ABC Ltd. sells gel toothpaste for $20. The company's stockholders raised the selling price of the toothpaste from $20 to $22 to maximize their wealth. This sudden unnecessary rise in the cost of toothpaste disappointed the customers and boycotted the product sold by the company. Few customers who bought the product realized a fall in the quality and were utterly disappointed. It resulted in agency problems between the stockholders and the loyal and regular customers of the company.
Causes
There can be various causes of agency problem in corporate governance. These causes differ from the position of an individual in the company. However, the root cause of these problems is the same in all mismatch or conflict of interests cases. When the agenda of the stockholder clashes with the other groups, the agency problem will occur. In the case of employees, the reason would be the failure of stockholders to meet employees’ expectations concerning salary, incentives, working hours, etc.
In the case of customers, the cause would be the failure of stockholders to meet customers’ expectations like the sale of poor-quality goods, poor supply, high pricing, etc. In the case of management, the causes of agency problem theory could be the misalignment of goals, separation of ownership and control, etc.
Solutions
The companies can resolve the agency problem in finance between the stockholders and the company’s management by offering stock packages or commissions for the decisions taken by the administration and their outcomes on the shareholders. In addition, the companies can try to resolve these problems that can exist between its stockholders and management/ creditors/ other stakeholders (employees, customers, society, community, etc.) through taking instituting measures like tough screening mechanisms, offering incentives for good performance, and behavior and likewise penalizing for poor performance and bad behavior, and so on. However, an organization cannot completely heal from agency problems since the associated costs outweigh the total outcomes sooner or later.
Agency Problem Vs Agency Cost
The above are two related concepts that are very often used in the context of establishing relationships between the principal and agent. Even though they are very closely related, there are some differences between them as follows:
- The former refers to the conflict of interest that arise between the agent and principal but the latter direct and indirect expenses that the principal incurs.
- The agency problem in finance arises during delegation of authority and decision-making power to the agent, while the latter arises when the principal tries to mitigate or control the former.
- The former is a problem that arises due to creation of separate ownership between the principal and agent whereas the latter arises when the principal tries to monitor, control and take action and provide better incentives the agent.
- The agency problem theory deals with a broader and more complicated issue which faces many challenges, whereas the latter deals with costs related to monitoring, bonding or implementation and residual cost.
- The goal of the organizations are to ultimately reduce the agency cost and bring it under control so that in the process there is a reduction in the agency problem.
However, both require equal effort, planning and strategy designing so that the organizational challenges are reduced and the interest of both principal and agent is aligned to achieve the best and optimum result.
