Table of Contents
Affect Heuristic Meaning
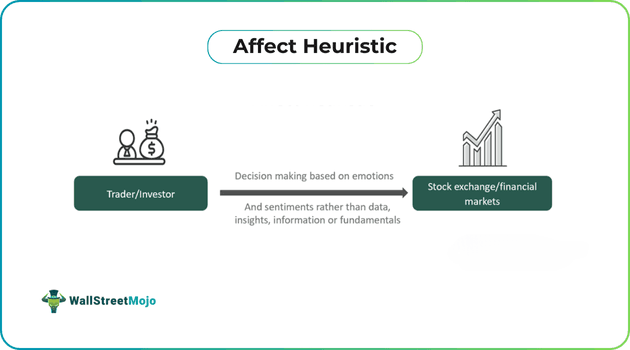
Affect heuristic refers to decision-making psychology in which people tend to make swift decisions based on their current emotions and scenarios, taking a shortcut. Such decisions are based on sentiments and are not backed by any supporting concrete evidence or reasonability.
Several psychological factors influence every decision-making. Emotions do impact a clear thought process, and therefore, any decision made with affect heuristic may come out as a good decision or may come out as a bad decision as they are purely made in haste under the umbrella of current emotion.
Key Takeaways
- The affect heuristic is the decision-making process based on an individual’s current emotional state and feelings.
- It was introduced by Paul Slovic, an American psychology professor, in the year 2000 in a paper published by him reflecting experimental findings on emotional influence.
- Affect heuristic bias is common in financial markets and daily life activities, where people tend to give more weightage to their emotions and sentiments than to data.
- It is risky and may bring financial harm or monetary losses; therefore is encouraged to replace it with logic, data, insights and information.
Affect Heuristic in Finance Explained
Affect heuristic defines a scenario of decision-making psychology where people are driven by their emotions and sentiments rather than data, information, logic or rationality. Such decisions are considered shortcuts or quick but lack statistics, data, insights, or information. The term was introduced by Paul Slovic, an American psychology professor, in 2000 through his research papers on emotional influence in decision-making processes.
The affect heuristic definition states that a person with a positive mindset is more likely to evaluate any situation with high benefits and low risks. Conversely, when an individual possesses a negative emotional state, they are inclined to give more prominence to high risks and low benefits. It is always important to acknowledge the affect heuristic and try to overcome it more, particularly in finance and monetary decisions, because decisions made through emotions have a higher degree of risk, eventually resulting in a loss.
There are many affect heuristic examples in daily life that can be observed easily, where people make decisions based on their emotional state of mind. Such a decision can be correct and work out perfectly, but the key aspect is that emotions play an important role in decision-making. At the same time, they must be avoided. When it comes to financial decisions, the affect heuristic is largely criticized, and people are encouraged not to mix their emotions while making any decisions regarding investing, finances and money.Affect heuristic defines a scenario of decision-making psychology where people are driven by their emotions and sentiments rather than data, information, logic or rationality. Such decisions are considered shortcuts or quick but lack statistics, data, insights, or information. The term was introduced by Paul Slovic, an American psychology professor, in 2000 through his research papers on emotional influence in decision-making processes.
The affect heuristic definition states that a person with a positive mindset is more likely to evaluate any situation with high benefits and low risks. Conversely, when an individual possesses a negative emotional state, they are inclined to give more prominence to high risks and low benefits. It is always important to acknowledge the affect heuristic and try to overcome it more, particularly in finance and monetary decisions, because decisions made through emotions have a higher degree of risk, eventually resulting in a loss.
There are many affect heuristic examples in daily life that can be observed easily, where people make decisions based on their emotional state of mind. Such a decision can be correct and work out perfectly, but the key aspect is that emotions play an important role in decision-making. At the same time, they must be avoided. When it comes to financial decisions, the affect heuristic is largely criticized, and people are encouraged not to mix their emotions while making any decisions regarding investing, finances and money.
Examples
Below are two examples of affect heuristic bias -
Example #1
Suppose Gerrard is a new investor; he is still trying to understand many fundamentals, is quite impatient, and mostly works his way through quick decisions. Recently, he came across a private bank stock that had a bullish run for the last three days. Gerrard wants to make the most of this opportunity and, therefore, invests a lump sum amount of money in it.
Gerrard here did not read anything about the private bank stock, didn’t mind checking its fundamentals, neither followed any news nor took any advice from others, and acted upon his emotions. Now, it is equally possible that Gerrard made a good short-term profit from it, but it is also possible that he may have invested without any data or knowledge, and later, the stock declined in price, bringing a loss to him. It is a simple effect heuristic example; such actions are often criticized, especially in the stock market and should always be avoided.
Example #2
Another good example is the use of affect heuristic psychology in marketing; when advertising and branding their products, many brands tend to link it with an emotional connection associated with the customer base. Companies market their products in a certain way because they know that people connect with their products on an emotional level.
Clothes, creams, bags, watches, gadgets and many more are sold with the idea that wearing them or owning them makes people feel important, fancy and powerful. Companies, especially global brands, know that customers have an affect heuristic and make buying decisions based on their emotions. Hence, they tend to use this to make a sale or profit.
Pros & Cons
The pros of the affect heuristic are -
- Helps people make quick decisions and reach conclusions swiftly, therefore saving time.
- In certain scenarios, emotions do play a significant role and make people believe in something that is most unlikely to happen but happens anyway against data and logic.
- People with affect heuristics do not require data and information to make a decision.
The cons of the affect heuristic are -
- People rely on emotions and sentiments rather than data or concrete information.
- Because the decisions are not based on logic and insights, they involve a higher degree of risk and are prone to error.
- Decisions under the influence of affect heuristic are often considered suboptimal.
Affect Heuristic Vs Availability Heuristic
The key differences between the affect heuristic and availability heuristic are -
- The affect heuristic is based on emotions, but the availability heuristic is based on quick and available information.
- Affect heuristic is often credited with gut feeling and beliefs. In contrast, the availability heuristic is defined as the overestimation of events based on available information.
- Paul Slovic published about the affect heuristic in 2000. In comparison, the availability heuristic was introduced by Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky in 1973.
- Investing in a stock based on emotions is an affect heuristic, but investing in a particular stock based on the first available data and knowledge that comes to mind refers to the availability heuristic.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.