Table Of Contents
What Is Advance Payment Guarantee?
An advance payment guarantee mitigates a buyer’s prepayment risk. If the seller breaches the contract, the buyer receives a refund. In that case, the agreement is considered null and void. It is also referred to as an advance payment bond.
This document is common in construction, import, export, heavy equipment purchases, bulk orders, and domestic transactions. Without the advance payment bond, the buyer faces prepayment risks. If the seller defaults, the buyer incurs heavy losses.
Key Takeaways
- An advance payment guarantee acts as collateral and protects the buyer’s prepayment. If the seller defaults, the buyer recovers the prepayment amount. It is also called an advance payment bond.
- Sellers and contractors require prepayment for working capital, procuring raw materials, and paying wages. Without prepayment, a seller or a contractor cannot complete large orders.
- The client receives a refund if a seller or contractor breaches contractual terms. Once the refund is received, the client returns the original contract with a letter of release.
How Does Advance Payment Guarantee Work?
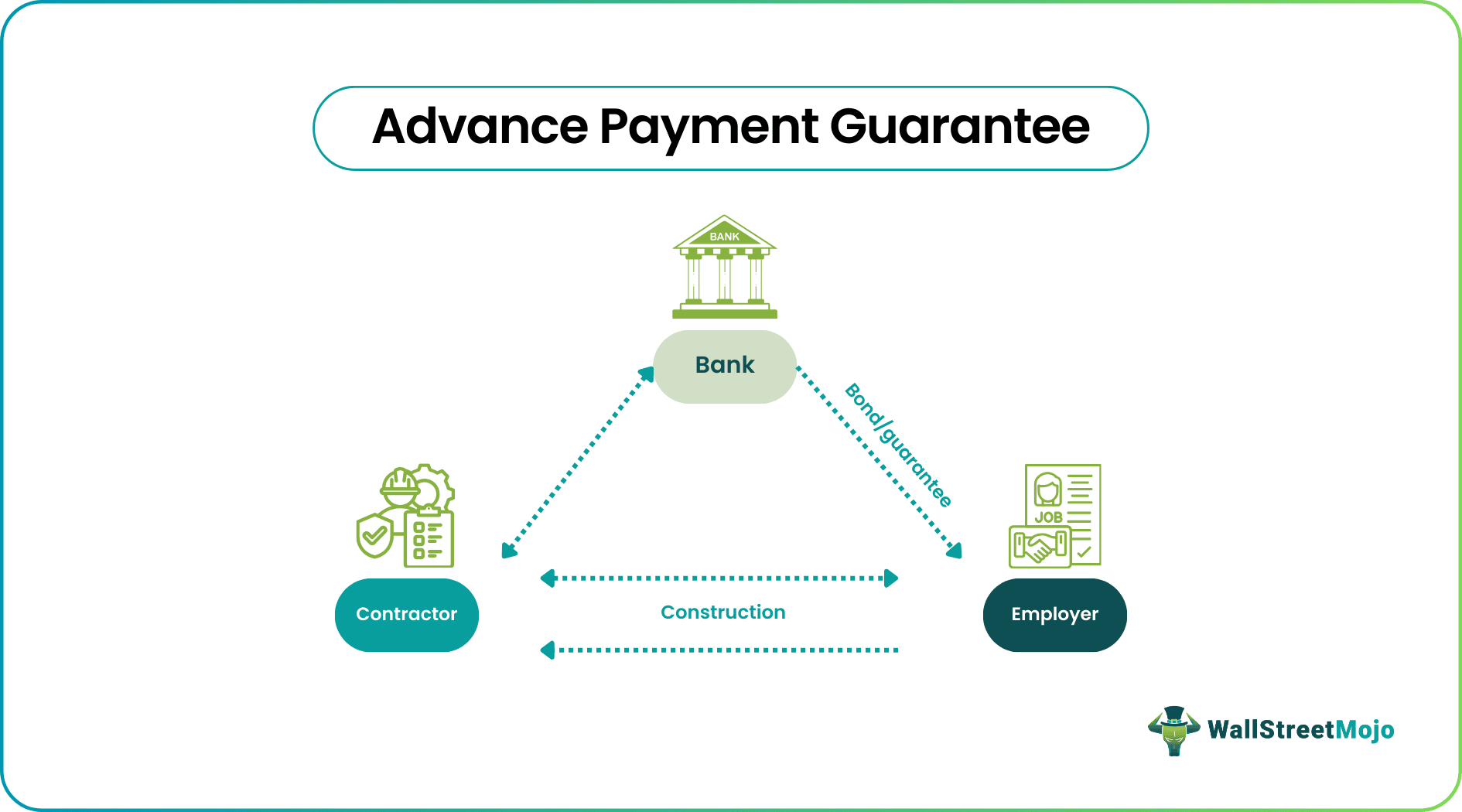
An advanced payment guarantee is issued by a contractor and given to the client. It is also called an advance payment bond. If a client hires a contractor for construction, the client pays an amount in advance. But here, the client bears the risk of non-completion of the task. To mitigate this risk, an advance payment bond is used.
The contractor receives an advance, and in return, the contractor sends an advance payment bond to the client. If the contractor fails to complete the task, the client can recover the prepayment using the document (advance payment bond). Also, the contractor uses the prepayment amount to purchase raw materials, rent machinery, and pay workers.
A bank or financial institution backs these documents to assure that the employer will receive a refund in case of a contract breach. Such agreements are commonly witnessed in business transactions, domestic trade, and construction projects. The document also comes in handy if there is a dispute. The client will be able to recover the prepayment.
Before venturing further, let us first understand how an advance payment works. Advance payment is a payment made by a buyer to the seller before the actual scheduled time of receiving the goods and services. It protects the seller from the risk of non-payment. More importantly, if the seller manufactures goods, they need capital to procure raw materials.

Prepayments protect sellers and contractors from unforeseen losses. But it is a bad deal for buyers—it poses a risk. This is where an advance payment bond comes in. It mitigates buyer’s losses if there is a contract breach.
Thus, this document is similar to insurance—it protects buyers and clients. If the construction contractor fails to complete the construction, they must refund the prepayment (to the client). Similarly, if a seller cannot deliver goods on time, they have to refund the prepayment (to the buyer). In such scenarios, the buyer considers the deal void.
A bank undertakes the responsibility for contractual obligations and deliverance. Such agreements are seen in big projects. For large-scale projects, contractors cannot handle the working capital without financial assistance from the employer.
A contract breach is when a contractor declines, reneges, repudiates, or retracts the contract. In such scenarios, the client receives a refund. Once the refund is received, the client returns the original contract with a letter of release.
Advanced payment bonds may be issued flatly without any financial review. For example, a $10,000 guarantee document costs between $100 to $140. Usually, the prepayment ranges between 5% to 20% of the total order.
Examples
Now, let us look at advanced payment guarantee examples.
Example #1
Justin deals in heavy machinery; he manufactures equipment. Leah is a client who requires customized machinery for her factory.
Leah and Justin enter into a contract; Justin agrees to deliver the machines within a month. The total order costs $9000. Leah disburses $2700 as a prepayment. An advance payment bond outlines the agreement. If Justin fails to deliver within the stipulated time, the whole agreement will be declared null and void. In that case, Leah will receive a refund ($2700).
Example #2
Emily wants to build a new home; she finds a construction company. Emily and the contractor mutually agree to various details. The construction company asks for an advance, and Emily agrees. An advance payment bond binds the agreement.
According to the contract terms, the construction is supposed to take a maximum of three months.
After three months, Emily visits the construction site. She realizes that only half of the work is done. Emily is dissatisfied and asks for a refund. She returns the contract as soon as she receives the refund. Along with the original contract, Emily submits a letter of release. This document is a formal declaration that the agreement is null and void.
Template
Following is an advance payment guarantee template:


Usually, an advance payment bond contains clauses discussed between parties—the start and end date of the project and other information. It also contains information about the exact amount exchanged between the parties.
The document establishes the employer (client) and the principal (contractor). It mentions the name of each party and their address. The intermediary bank is also mentioned.
Advance Payment Guarantee vs Performance Bond
Now let us look at the advance payment guarantee vs performance bond comparison to distinguish between the two.
- Advance payment bond agreements are used to recover advance payments. In contrast, performance bonds ensure contractual obligations. Breach of contract is mitigated using financial guarantees.
- When there is a contract breach, the damage extends beyond the prepayment. Yet, the advance payment bond only recovers the advance. In contrast, performance bonds ensure compensation for the damages—additional losses caused by the contract breach (failure to complete a task).
- If a manufacturer fails to produce agreed-upon goods, the buyer can recover the prepayment using an advance payment guarantee. Performance bonds go a step further. If the manufacturer fails to complete the order, the manufacturer is liable to pay the cost of the complete order.
