Table of Contents
What Is Adaptive Expectations?
Adaptive expectations are the theory that suggests that people, based on their past experiences, predict future outcomes and adjust their expectations to be ready to adapt to them. This is most common in people's daily lives, where they try to forecast an outcome because it has happened earlier.
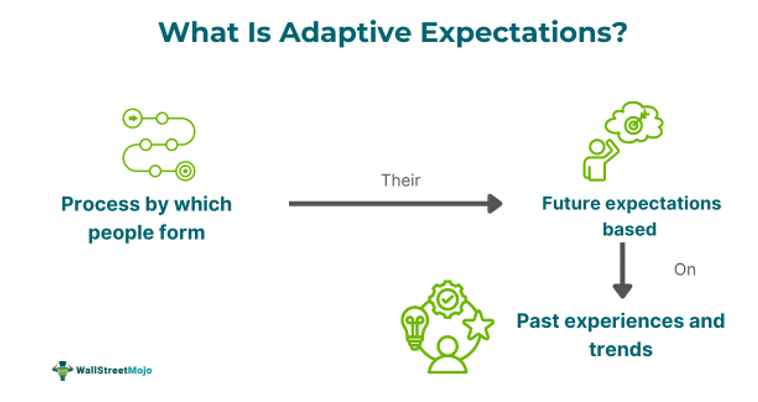
The theory may work in different scenarios for people in different fields of work or daily lives. Yet, it can also be termed a habit of people trying to see the foreseeable future based on past patterns, which may otherwise occur in a different outcome. The most common example is people predicting future inflation hikes based on last year's rise.
Key Takeaways
- Adaptive expectations are a hypothesis that people adjust their behavior for the future based on their past experiences or patterns.
- The opposite of adaptive expectations is rational expectations, which are said to be closely related to it yet are distinct.
- The adaptive expectations hypothesis has a formula and uses past data for future interpretations; hence, it is also called backward-thinking decision-making.
- The model applies in many areas, such as inflation rate determination, the housing market, and daily life.
Adaptive Expectations Explained
Adaptive expectations suggest that people gauge future prices based on the previous year's situation. The hypothesis primarily measures inflation in different financial markets and the economy. People expect a repetitive structure and adjust their behavior according to anticipated outcomes. This theory can have significant consequences, as market shifts may occur suddenly when people act on their beliefs, affecting demand and supply in the economy.
The model works reasonably well for judging small scenarios and making swift daily decisions. However, it has limitations when dealing with financial markets and determining aspects like inflation and economic strength. In contrast, many economists follow the rational expectations theory, which considers available data and uses critical thinking and logical decision-making. The adaptive expectations model is not suitable for predicting securities price movements in the stock market, as it can be hazardous and may lead to significant financial losses for investors. The most common application of the theory is to predict future inflation based on the previous year's inflation rate through a quantitative method.
Formula
Adaptive expectations involve using past data to predict future values, particularly in the context of inflation forecasting. The formula for adaptive expectations is:
= – 1 + )
Where:
- = next year’s expected inflation rate
- = current year’s expected inflation rate based on the previous year's expectation
- p = current year’s actual inflation rate
- α = adjustment coefficient between 0 and 1
This formula highlights how expectations are updated based on the difference between the actual inflation rate and the previously expected rate.
Examples
Here are two examples of adaptive expectations -
Example #1
Suppose there is a steady increase in inflation treated as a variable in the economy. According to the adaptive expectations theory, the expected inflation value will adjust based on the difference between actual and previously expected inflation rates. Assume a regular increase in the inflation value in an economy. Based on the hypothesis, consider:
- p = 0.4 (current year's actual inflation rate)
= 2 (previous year's expected inflation rate)
- Α = 0.5 (adjustment coefficient)
Using the adaptive expectations formula:
=
– 1 +
)
= 2+0.5(0.4−2)
= 2−0.8
= 1.2
This shows that the expected inflation rate for the next year will be 1.2% based on the current year's actual inflation rate of 0.4% and the previous year's expected inflation rate of 2%. Similarly, the following year's expected inflation rate will differ based on the updated actual and expected inflation rates.
Example #2
The US housing market is an example of an adaptive expectations model. Economists use various terms for this concept, such as biased expectations, learning from prices, and momentum trading. The idea is simple: people expect house prices to be higher in the future, making them less likely to sell now and more willing to buy now, even at current market prices. This expectation drives prices to rise even more rapidly.
The adaptive expectations theory influences the US housing market, where the prices people expect tomorrow affect the demand and supply today. It impacts both buyers and sellers; as prices go up, lenders also tend to project increasing prices and profits into the future. This behavior is often seen as the opposite of standard economic thinking, where higher prices are expected to reduce demand.
Limitations
Limitations of adaptive expectations are –
- Based solely on past data or patterns, which may not be relevant for future predictions.
- Susceptible to changes or impacts from new market aspects, particularly for inflation.
- Relies on assumptions rather than rational thinking.
- It is inaccurate and may not be applicable in every scenario or field.
Adaptive Expectations Vs. Rational Expectations
The critical differences between adaptive and rational expectations theory are –
- Adaptive expectations rely on past data or experiences, whereas rational expectations use all available information and patterns.
- Adaptive expectations are defined as backward-looking, while rational expectations are forward-looking.
- Adaptive expectations are based on assumptions and can be inaccurate, whereas the rational expectations hypothesis is based on analysis and is generally more accurate.
