Table of Contents
Actuary Definition
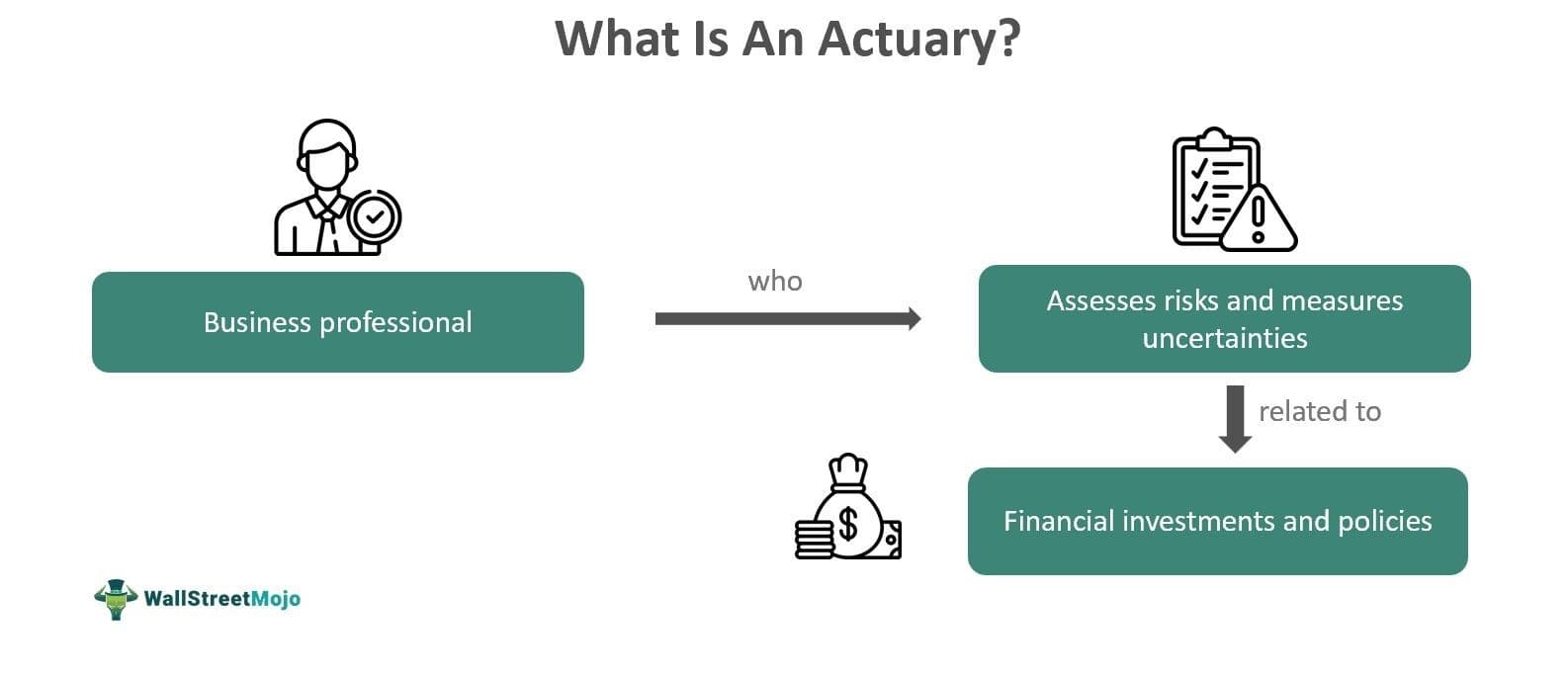
An Actuary is a business professional specializing in risk management and assessment of uncertainties associated with financial investments that one makes. They use financial theories, mathematical tools, and statistics to predict risks, design innovative ideas to deal with them and reduce their impacts to a minimum for an entity.
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link.
They also help organizations plan for future risks and safeguard them from expected as well as unexpected losses. They aid firms in their growth and help them make investments for profits, mitigating risks to the utmost possible extent. Financial entities, including insurance firms, employ actuaries to utilize their skills in determining how much to invest or allow an individual or entity and where to stop.
Key Takeaways
- An actuary is a business professional who analyzes the financial risks associated with a financial investment and its impact on a business, be it insurance or any other financial institution.
- They are responsible for various tasks, including developing and testing theories about the organization's risk issues, analyzing trends
- To become a certified actuary, one has to pass many exams and get enough exposure to the financial industry to sharpen their existing mathematical, statistical, and analytical skills time and again.
- Actuary help predict future risks and impacts on firms, whereas underwriters categorize customers as per the insurance bucket, and financial analyst presents an overall picture of the existing fund.
Actuary Explained
An actuary is a financial professional who performs risk evaluations and develops methods for controlling the impact of financial risks. They solve problems using their strategic thinking and help predict and measure the risks associated with future events. Their skills allow them to forecast the financial impact of a decision or future event on a business or entity. Many government bodies and business firms employ actuaries to aid them in building low-risk models and planning accordingly for the future.
They are quite creative, enthusiastic, and able to adapt easily to the situation. They analyze the risk and help entities succeed in the ventures they invest. Unlike accountants, they focus on analyzing future risks. They use their mathematical skills based on the financial records presented to them and examine the probability of whether a firm's finances look secure or are at risk. Plus, they also help financial entities predict the cost of impending claims of customers and the total load of paying pensions to the pensioners.
Their main work involves calculating the total liability and losses faced by businesses on account of the following:
- Onsite injury to workers or visitors
- A security breach of data can lead to losses
- Bad investment by a company may badly hurt its finances
- Claim arising out of accident or death of the insured
Actuaries are found in different sectors, and the nature and meaning of actuary can easily be interpreted by how they are called in different sectors:
- Insurance actuaries
- Real estate insurance actuaries
- Injury or casualty actuaries
- Pension and savings actuaries
- Enterprise risk management actuaries
Role And Responsibilities
Based on the sectors in which they operate, their roles and responsibilities vary. Some of them have been listed below:
- Develop and test the theory on the company's risk factors
- Gather data and analyze patterns
- Calculate the prediction of events happening and their impacts
- Examine prevalent and rare risk factors within various industries
- Be aware of the corporate regulations to assess their impact on output
- Develop ideas for risk management strategies in the financial realm
- Use risk assessment theories and market trends to support these predictions
- Create graphs and tables to help shareholders and management of the company understand complicated statistics and concepts
- Fill out and update risk registers for every project
How To Become?
To become an actuary, one must fulfill the following criteria:
- Have a degree in accounting, mathematics, finance, statistics, or economics.
- Love for probability, statistics, mathematics, and calculus.
- Working knowledge of economics, finance, and accounting.
- Able to work in spreadsheets, data programs, and statistics analysis.
- Pass the two prelim exams of actuarial exams, namely – Exam P & Exam FM from the Society of Actuaries
- Take up an internship under a senior actuary or a team of actuaries
- After the internship, get entry-level actuary jobs.
- Later, get an associate-ship, namely - Associate of the Society of Actuaries (ASA) and Associate of the Casualty Actuarial Society (ACAS), after passing five exams.
- Go for a fellowship comprising ten actuary exams to pass to become a certified actuary.
- Finally, after passing all the exams, one can either become a Fellow of the Society of Actuaries (FSA) or a Fellow of the Casualty Actuarial Society (FCAS).
Salary
In the United States, the average actuary salary is $113,990 in 2022. The salary for the highest-paid and the lowest-paid actuaries ranges from $84,800 to $155,670. New York, Charlotte, Fort Wayne, Springfield, and Hartford are the cities that pay the best to actuaries, given their mathematical and statistical skills help organizations analyze the risk facts and invest accordingly into schemes and business plans.
Actuary vs Underwriter vs Financial Analyst
Though the three terms might appear to be similar in terms of their roles in studying the risk factors, they differ widely. Let us have a look at some of the differences between them below:
| Actuary | Underwriter | Financial Analyst |
| They are the ones who study the future risk and impact of future events. | An underwriter is responsible for categorizing a customer into an appropriate insurance bucket. | They develop an overall picture of prevailing investments or funds. |
| They assess and manage risk for and on behalf of a firm. | They assess the risk associated with lending money to another party for and on behalf of their firm. | They work as per the client's daily needs. |
| They create various categories for analyzing the risk. | They use these risk categories to adjust potential customers. | They have interacted with clients and fulfilled their clients' financial goals. |
| They determine only general risks. | They determine the specific risk of an individual or firm. | They monitor the securities market to know the financial trends. |
| They have a variety of sectors where they work. | They get limited to the insurance sector only. | They analyze financial data. |
| An actuary may not become an underwriter. | An underwriter can become an actuary. | They consult businesses and clients to assess financial needs and investment options. |
| They tend to forecast risks and manage them only. | They get to decide the extent of insurance an applicant can get. | They also recommend strategies to sustain the financial status of companies. |
