Let us understand the difference between activity-based costing v/s activity-based management.
Table Of Contents
What Is Activity Based Management (ABM)?
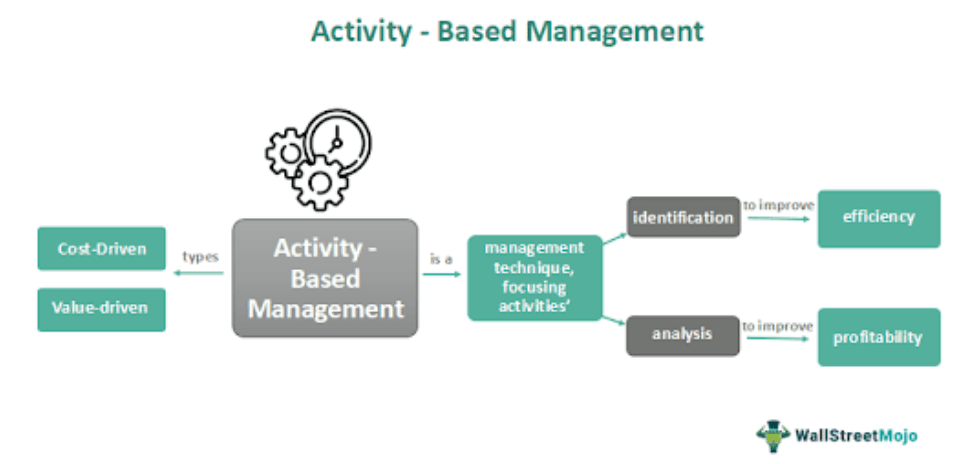
Activity-Based Management (ABM) is a management technique that analyses an organization's activities to identify areas where improvements can be made in efficiency and profitability. It purpose includes breaking down the organization's activities into smaller components and analyzing them to determine their contribution to the overall cost of its products or services.
It is crucial as it helps organizations understand their cost structure better and make informed decisions about resource allocation. The process may involve eliminating unnecessary activities, redesigning processes, or reallocating resources to more valuable activities. ABM is commonly used in manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries but can be applied to any organization that wants to improve its operations.
Key Takeaways
- Activity-based management (ABM) involves identifying and analyzing the various activities within a business process or system and then determining the value of each activity in terms of its contribution to the result.
- ABM helps businesses to identify non-value-adding activities, such as unnecessary steps or wasted resources, and eliminate or streamline them.
- By focusing on and optimizing the most valuable activities, ABM can improve productivity, reduce costs, and increase profitability.
- ABM requires significant data collection and analysis and collaboration between different departments and stakeholders within a business.
Activity Based Management Explained
Activity-based management (ABM) is a management approach that focuses on identifying and analyzing the activities performed by an organization to improve efficiency and profitability. In addition, ABM emphasizes the importance of understanding the costs of individual activities and how they contribute to the overall cost of the organization's products or services.
ABM involves breaking down the organization's activities into smaller, more manageable components and then analyzing them to identify areas where improvements can be made. This may involve eliminating unnecessary activities, redesigning processes, or reallocating resources to more valuable activities.
By implementing ABM, organizations can better understand their cost structure and make more informed decisions about allocating resources. This can lead to increased efficiency, improved profitability, and better customer satisfaction. ABM is commonly used in manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries but can be applied to any organization that wants to improve its operations.
Types
There are two main types of Activity-Based Management (ABM):
#1 - Cost-Driven ABM
This type of ABM focuses on reducing costs associated with activities by eliminating or optimizing non-value-added activities. The goal of cost-driven ABM is to reduce costs without compromising the quality of the product or service.
#2 - Value-Driven ABM
This type of ABM focuses on increasing the value of activities by improving the quality of products or services or adding new features or benefits. The goal of value-driven ABM is to increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, which can lead to increased sales and profits.
Both types of ABM are designed to improve an organization's overall efficiency and profitability. Organizations can choose to implement one or both types of ABM depending on their goals and objectives.
Techniques
There are several techniques used in Activity-Based Management (ABM) to identify and analyze activities and to make decisions about how to improve efficiency and profitability. Some of these techniques include:
#1 - Activity Analysis
This involves breaking down the organization's activities into smaller components and analyzing them to determine their cost and value.
#2 - Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
This technique assigns costs to activities based on their consumption of resources, providing a more accurate picture of the cost of producing products or providing services.
#3 - Process Mapping
This technique involves visualizing a process to identify areas where improvements can be made, such as eliminating bottlenecks or reducing cycle time.
#4 - Benchmarking
This involves comparing an organization's performance to its competitors or industry standards to identify areas where improvements can be made.
#5 - Value Stream Mapping
This technique involves mapping a product or service's entire value stream to identify waste and improvement opportunities.
#6 - Cost-Benefit Analysis
This involves comparing the costs of implementing a change with the benefits it will provide to determine if it is a worthwhile investment.
These techniques are used individually or in combination. As a result, organizations can identify and eliminate waste, improve efficiency, and increase profitability.
Examples
Let us look at the following example to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Consider that a company providing IT support services to clients wants to improve its profitability by reducing costs and increasing the value of its services. Therefore, the company uses ABM to analyze its activities and identify opportunities for improvement.
Through activity analysis, the company finds that much time is spent on resolving password reset requests. The company identifies bottlenecks in the password reset process and eliminates non-value-added steps using process mapping and value stream mapping.
As a result of these improvements, the company can reduce the time it takes to resolve password reset requests, increase customer satisfaction, and allocate resources to more valuable activities. This leads to increased profitability for the company.
Example #2
Let's take the example of a manufacturing company that produces specialty chemicals. The company wants to improve its profitability by reducing costs and increasing the value of its products.
To implement ABM, the company uses a combination of activity analysis, activity-based costing (ABC), and process mapping. The company identifies significant time spent on product testing and quality control through activity analysis.
Using ABC, the company determines that the testing and quality control activities drive the cost of producing its chemicals. To reduce costs, the company implements process improvements such as automation of testing processes, reducing the testing frequency for certain products, and optimizing the inventory levels of raw materials.
In addition to cost reduction, the company also wants to increase the value of its products. Using value stream mapping, the company identifies that certain customers are willing to pay a premium for faster delivery times. To increase the value of its products, the company implements improvements such as optimizing its supply chain to reduce lead times and offering expedited shipping options to customers for a fee.
Through these improvements, the company can reduce its production costs, increase the value of its products, and allocate resources to more valuable activities. This leads to increased profitability and a stronger competitive position for the company in the market.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Let us understand the pros and cons of Activity-based management as a concept.
Advantages
- Improved Cost Management: ABM helps organizations identify and analyze activities and allocate costs based on the resources consumed by each activity. This provides a more accurate picture of the true cost of producing products or providing services, which can lead to better cost management.
- Increased Efficiency: ABM can help organizations to identify areas of inefficiency in their processes and activities and make improvements to increase efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Customer Value: ABM can help organizations identify which activities add value to their customers and which do not. By focusing on value-added activities, organizations can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Better Decision Making: ABM provides a more accurate and detailed view of an organization's operations, allowing for better decision-making based on data and facts rather than assumptions and guesswork.
Disadvantages
- Time-Consuming: ABM can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Especially in the initial stages when activities and processes are analyzed and mapped. This can be a disadvantage for organizations with limited resources.
- Costly: Implementing ABM may require significant investments in technology, training, and resources, which can disadvantage smaller organizations with limited budgets.
- Complexity: The complexity of ABM can be a disadvantage for organizations that are not prepared for it. Identifying and analyzing activities is complicated and requires specialized skills and knowledge.
- Resistance to Change: ABM may require changes to an organization's processes and culture, which can be difficult and meet with resistance from employees who are comfortable with the status quo.
Activity-Based Costing vs Activity-Based Management
| Criteria | Activity-Based Costing (ABC) | Activity-Based Management (ABM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Basis | A costing methodology that assigns costs to products or services based on the activities that go into producing them. | A management approach that focuses on managing and optimizing activities to improve performance and profitability. |
| 2. Purpose | To accurately determine the cost of products or services. | To improve performance and profitability by managing and optimizing activities. |
| 3. Scope | Costing methodology | Management approach |
| 4. Focus | Costs | Activities |
| 5. Key Methodologies | Identifying and analyzing activities, assigning costs, and allocating costs to products or services. | Identifying and analyzing activities, identifying opportunities for improvement, making process improvements, and allocating resources to more valuable activities. |
| 6. Benefits | Provides more accurate product or service cost information and helps identify process inefficiency. | Improves efficiency and productivity, enhances customer value, provides a more accurate view of operations, and enables better decision-making. |
| 7. Limitations | Implementing it can be time-consuming, expensive, and complex for smaller organizations. | Requires significant investment in technology, training, and resources, can be complex, and may meet with resistance to change from employees. |
| 8. Example | Assigning the cost of quality control to different products based on the time spent on each activity. | Optimizing the inventory levels of raw materials, automating testing processes, and offering expedited shipping options to customers for a fee. |
