Table Of Contents
What Is Activity Based Costing?
Activity-based costing (also known as ABC costing) refers to the allocation of costs (charges and expenses) to different heads or activities or divisions according to their actual use or on account of some basis for allocation, i.e. (cost driver rate, which is calculated by total cost divided by total no. of activities) to arrive at a profit.
Examples include square footage that is used per product, and the same would be used to allocate the rent of the factory as well as the maintenance cost of the firm; similarly, the number of purchase orders (i.e., PO) used to allocate the purchasing expenses of the purchasing department.
Activity Based Costing Explained
The activity based costing is a process of accounting for the indirect costs of goods and services of a business, in a more precise manner. It is based on the activities that influence those costs in order to products those products. Big and established corporations that have many lines of business, products and services leading to a complex cost structure, frequently use this method.
Activity based costing equation is quite different from the traditional methods, which have a comparatively simple procedure. Even though the process is very efficient, implementing it may be time consuming and complex. However, it successfully provides a clearer picture of the cost.
Features
Let us look at the various features of the activity based costing system in details.
- Cost drivers – They are the factors that help in identifying the cost with the particular activity. In case of manufacturing a product, the cost drivers can be the number of orders to be processed, the number of machines required, the labor hours spent on them, etc.
- The activities – These are the various tasks, actions of procedures that use up the different types of resources available in an organization. Such activities may be administrative in nature or any other operational process inside the organization.
- Resource cost – These are all the costs that are either direct or indirect in nature, which are linked to each activity. The direct costs can be identified very easily, but the indirect ones are shared across different activities and need to be proportionally allocated for each product or service.
Thus, the above are the important features of activity based costing system.
Formula

The activity based costing equation can be explained with the following core concepts.
- Cost Pool: This is an item for which measurement of the cost would require, e.g., a product
- Cost Driver: It is a factor that will cause a change in the cost of that activity. There are two kinds of cost drivers:
- 1) Resource Cost Driver: It measures the number of resources that activity consumes. It will be used to assign the cost of a resource to an activity. E.g., Electricity, Staff wages, Advertising, etc.
- 2) Activity Cost Driver: This is the measure of the intensity of demand and the frequency placed on the activities by the cost pools. It will assign the activity costs to a product or a customer. E.g., Material ordering costs, Machine setup costs, Inspection and testing charges, Material handling and storing costs, etc.
Steps
It is important to understand the different steps involved in the process.
- The first step is to identify the different activities that takes place inside the business. This should include both production related and administration related ones. In this step, the various tasks are segregated as per the activity they perform.
- The next step is to identify the various cost drivers. For each activity, the factors affecting the cost will be identified. For this, the management should also understand how much resource each activity is consuming, in the form of raw material, time, labor and machine hours, etc.
- Next, each cost will be assigned to each activity. Assigning the direct cost is easy, but for indirect cost, the procedure is complex, because it has to be allocated based on the cost drivers.
- The final step is to allocate the cost that relate to the particular product or service. This can be done only after the cost is allocated to all the concerned activities. Every product or service will involve usage of some or part of an activity that will have a type category of cost attached to it.
Thus, through the above steps, all types of costs are determined in a more accurate and precise manner which make this process very useful for organizations involving a wide variety of production processes.
Examples
Let’s see some simple to advanced examples to understand it better.
Example # 1
BAC ltd is considering shifting from the traditional costing method to the ABC-based costing method, and it has the following details. Using ABC costing formula, find out the new overhead rates for the company.

We have two activities. The first one is a machine set-up activity, and the second one is inspecting the same. So the driver's areas, the number of machine setup would increase, the cost would also increase, and similarly, as the number of inspecting hours increases, that would lead to an increase in inspection cost. Hence, we need to allocate those costs based on their cost drivers.
Using the ABC formula: Cost Pool total / Cost driver
Calculation of Machine Setup Cost

Machine setup cost / Number of Machine setups
=2,00,000 / 340
Machine Setup Cost = 588.24
Calculation of Inspection Cost

Inspection cost /Inspection hours
=1,40,000 / 7500
Inspection Cost= 18.67
Example # 2
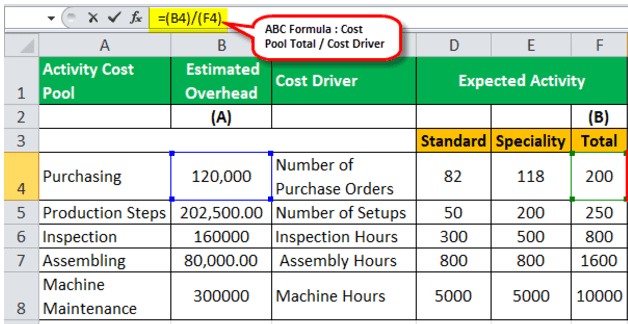
The following details pertain to different activities and their costs for Gamma Ltd. You are required to calculate the overhead rate for each activity.
Below is the given data for calculation.

We are here given five activities; hence, we need to allocate those costs based on their cost drivers.
Using the ABC formula: Cost Pool total / Cost driver
Each activity pool’s total cost is divided by its cost driver to arrive at different rates.
Overhead Rate for the Purchasing Activity

Overhead Rate for the Purchasing Activity = 1,20,000 / 200
Activity-Based Costing for Purchasing will be –

Overhead Rate for the Purchasing Activity =600.00
Similarly, calculate the ABC Cost Formula for all the cost pool activities.

Total Estimated Overhead = 862500.00
Example # 3
Mamata Inc., a manufacturing company of drugs, is considering switching from its traditional cost method to a newly implemented system by their production head. It is activity-based costing so that the two products, Z serum, and W serum, can be sold at their reasonable cost and make them price competitive in the market.
Below are the production details that have been derived from the production sheet.

You must arrive at a product-based total cost using the ABC formula.
We are here given six activities; hence, we need to allocate those costs based on their cost drivers.
Using the ABC formula: Cost Pool total / Cost driver
Each activity pool's total cost is divided by its cost driver to arrive at different rates.
Overhead Rate for the Purchasing Activity

Overhead Rate for the Purchasing Activity = 60000/1000
For Purchasing, it will be –

Overhead Rate for the Purchasing Activity = 60.00
Similarly, calculate the ABC Cost Formula for all the cost pool activities.

And the total estimated overhead is 506250.00
After arriving at different rates, we now have to arrive at product level total cost. It would be nothing but multiplying different overhead rates as arrived above with their actual cost drivers.

Advantages
Some advantages of the process of activity based costing method are as follows:
- It is a type of cost allocation process that identifies all kinds of company's costs and allocates them to the costs of the products based on actual consumption.
- It will enhance the process of cost in 3 different ways. First, it will expand the number of cost pools, which can later be used to assign those overhead costs. So, it pools costs by activity instead of accumulating them in one organization-wide pool. Second, instead of volume measures like direct labor costs or machine hours, it will create new bases to assign these overhead costs to items upon these activities, which shall generate costs. Lastly, it makes the cost traceable to these activities.
- Since the cost drivers are identified properly with accuracy, it helps in optimum resource allocation and in the process improve the entire business operation procedure.
- It leads to better accountability and identification of areas of mismanagement and wastage. The inefficiencies are errors that can be minimized and controlled only if they are identified properly.
Disadvantages
Some disadvantages of the activity based costing method are as follows:
- The process is complex and time consuming, which means it may not be easy to manage it and may not be suitable for organizations which are small or in the growth stage, because their line of production will be comparatively simple.
- The process requires resources for data collection, implementation, training and follow-ups, etc.
- The data collected may not always be accurate, leading to lack of useful information or misrepresentation of the cost structure and allocation. This compromises accuracy in the process.
- The process itself involves cost for implementation. The employees need to be trained and skilled to effectively carry out the procedure. This may be challenging due to high level of responsibility required to break down, manage and implement the process.
Activity Based Costing Vs Traditional Costing
Both are two distinct costing methods used in organizations and projects. But there are some differences between them, as follows.
- The activity based costing approach allocates the cost based on different activities that influence the resource consumption for producing that particular product or service because it assumes that different products have different resource utilization pattern. But the latter follows a very simple process of allocating costs related to machine hours, labor, or raw material consumption for each product.
- The former is suitable for organizations having a wide range of products and area of operation whereas the latter is suitable for simple organization structure that has one line of business.
- The former is a complex and time-consuming process which need identification of activities and cost drivers and establishing a relation between them. But the latter is a simple and traditional process, where the overheads are standard in nature.
- The former is considered to be more accurate than the latter because it precisely identifies the cost drivers for each activity related to the product or service.
- For the activity based costing approach, the overheads are more transparent and can be identified easily compared to the latter which facilitates the decision-making process for the management.
However, both are useful for determining the costs, but should be selected based on the need, cost structure, production process, lines of business, etc.