Table Of Contents
What is Activity Based Budgeting?
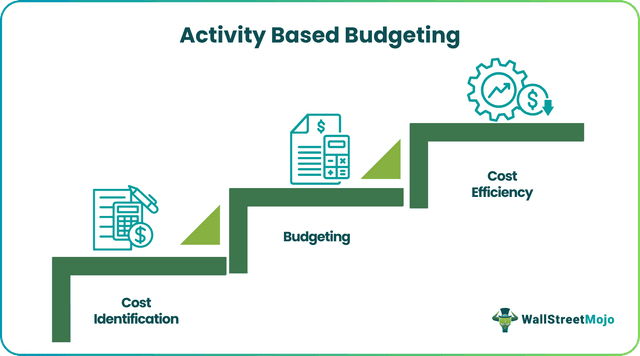
Activity-Based Budgeting is a budgeting process where the firm first identifies, analyzes, and researches the activities that determine the cost of the company and then prepares the budget based on the results. Unlike conventional budgets that merely readjust previous budgets and account for inflation, the activity-based budgeting features make it a more concentrated version.
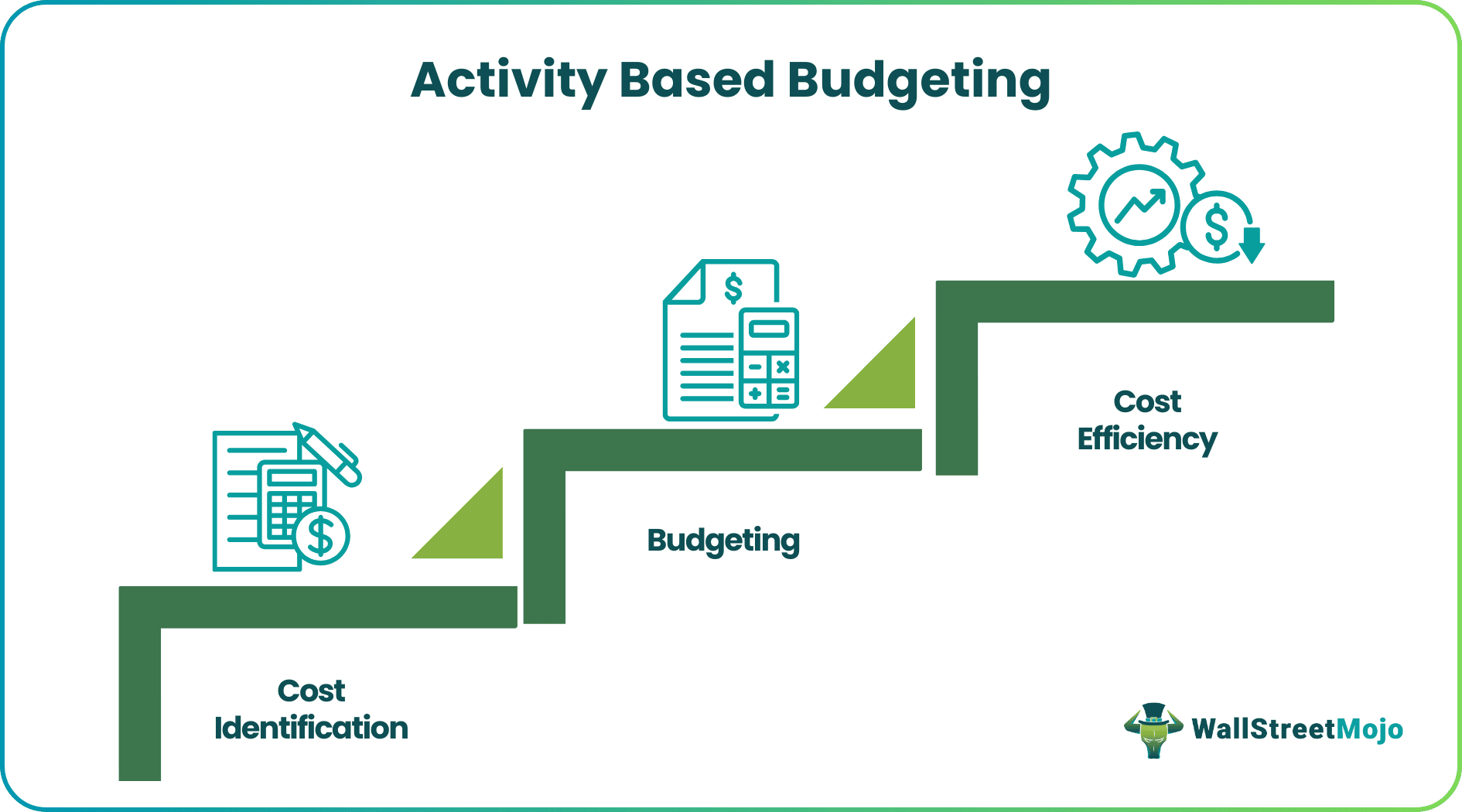
Every activity within an organization is liked to costs and scrutinizing them gives an opportunity to ensure no unnecessary expenditures are made. Using ABB, companies can significantly decrease their costs, and therefore, profit margins are increased. This is an appropriate form of creating a budget, especially for companies going through a transitional phase into new materials or new companies.
Activity Based Budgeting Explained
Activity-based budgeting or ABB is the process of structuring a company’s costs into different buckets and making sure expenses are made keeping cost efficiency in mind. Efficient spending ensures that a business can churn out more profits.
The traditional way of assigning cost or budget was to take the overhead cost of the last period and adjust the same for inflation and compute the total cost for the new order; hence it ignores the activities cost, wherein one could lead to no involvement in the process, and still, it was charged.
Hence, by implementing an activity-based budgeting template, the management can identify activities that are indeed involved in the production process and accordingly price the product and save cost and hence increase the firm's revenue.
The very purpose of orchestrating a business, irrespective of the scale of operations and experience is to make profits to sustain and grow. Therefore, all companies calculate their costs and use the formula to curate their own ABB.
The formula is represented as follows,
Activity-Based Budgeting Formula = Cost Pool in the Designated Diver /Cost Driver in Units
Process
Despite the fact that a singular activity-based budgeting template might not work for all organizations due to the difference in their scales of operations, nature of business, and experience in their niche, there are a few common factors that are invariably important in the process of curating a fool-proof ABB. Let us understand them through the points below.
- Identification of Cost Drivers: The cost drivers are the expenditures that form the majority chunk of the expenses of an organization. These could be wages, rent, electricity, etc for a factory unit.
- Projection: It is important to determine and project the number of requirements within each cost driver. For instance, it becomes easy to calculate the minimum requirement of the workforce for a singular product line, therefore, it can be translated into total working hours, per week or month based on the company’s lookout.
- Calculation: Calculating the per unit cost within each driver can give the company an overall idea of the quantum of spending within each cost driver and its overall expenditure. They can use this data to curate a budget and promote efficiency within their set-up.
Examples
Let us understand activity-based budgeting features and related concepts with the help of a few examples. These examples will give us a practical outlook on the concept and help us understand its ebbs and flows.
Example #1
Washington Inc. has decided to switch from a traditional budgeting system to activity-based budgeting. Based on the below information, you must compute the budgeted cost based on those drivers.
| Activity | Last Year Actual Cost |
|---|---|
| Machine Set up | 400000 |
| Inspection Cost | 280000 |
| Number of Machine Setups | 700 |
| Inspection Hours | 15500 |
Solution
The company has shifted from a traditional base to an activity budgeted way; hence, we can see that two activities are driving the cost.
We can calculate the overhead cost using the ABC formula: Cost Pool total / Cost driver.
We have = Machine setup cost / Number of Machine setups & Inspection cost / Inspection hours
Calculation of Machine Set-Up Per Unit

=400000/700
- =571.43
Calculation of Inspection Cost Per Unit

- = 280000 / 15500
- = 18.06 per hour inspection cost
Hence, in ABB, the cost is determined at the activity level and not an ad-hoc rate, which was done in a traditional method where only inflation was accounted for.
Example #2
Vista Inc was losing the auction due to its higher cost than peers. The management then decided to start budgeting the cost for their new orders using Activity Based Budgeting.
| Activity Cost Driver | Last Year Cost | Cost Driver | Last Year | Expected Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purchasing | 900000 | Number of Purchase Orders | 41 | 59 |
| Production Steps | 1518750 | Number of Setups | 25 | 30 |
| Inspection | 1200000 | Inspection Hours | 150 | 200 |
| Assembling | 600000 | Assembly Hours | 400 | 400 |
| Machine Maintainance | 2250000 | Machine Hours | 2500 | 2600 |
Solution
The expected activity for the next order is given based on it, and you are required to estimate the total cost that can be provided as a bid.
In this example, we are given all the actual costs and drivers for the same, and we can use the below formula to compute the cost that was incurred in the last order; the same is assumed to remain the same, and hence we can estimate for the new order as well.
Using the Activity Based Budgeting formula: Cost Pool total / Cost driver
Below are the calculations for each activity and are as per the last order.

The total cost for the new order and budgeted cost will be -

The above shall reflect true cost instead of a traditional way of doing the same.
Stages
The activity-based budgeting templates usually work in three stages and each of them are discussed through the points below.
- Identify the activities by conducting detailed research, and along with that, also one needs to identify their cost drivers, which again requires proper knowledge of the process.
- Now, either forecast the number of units produced for the next period or there could be a new order coming up and compute the overhead per driver at this stage.
- In the final stage, one needs to Calculate the cost driver rate and multiply the same for the new order or the new production units, which shall give one the total estimated or budgeted cost.
- But before the above, one needs to determine whether the required time and cost are adequately available with the management or the company.
- Does the company have the required resources, software, and workforce to capture the same daily?
- Cost-benefit analysis needs to be done before implementing the same, as the management should be that the benefits outweigh the cost.
- Can operational managers be recruited at reasonable remuneration?
Advantages
Let us discuss the advantages of following an activity-based budgeting template through the points below.
- The budgeting process can have more control when Activity-based budgeting (ABB) systems are used in the company instead of a traditional way of budgeting.
- Expenses and Revenue planning will occur at an accurate level, which shall provide meaningful details regarding the estimated and future financial projections.
- Last but not least, the company can have better control and align its annual budget with the overall firm's goals by implementing Activity Based Budgeting.
- It helps improve the business process by identifying unnecessary activities, which leads to an increase in cost as a lot of research is done here.
Disadvantages
Despite the various advantages mentioned above, there are a few factors that prove to be a disadvantage. Let us understand them through the explanation below.
- The main disadvantage of Activity Based Budgeting is that it is more expensive to implement and comparatively more costly than the traditional way of budgeting.
- Furthermore, technical details are required to maintain capture costs at a particular level.
- This process also involves a lot of assumptions to be made, which shall consume more time of management and can lead to inaccuracy of cost at certain times as well, which shall depict the incorrect cost of the product.
- It also requires a deep understanding of the process.