Table Of Contents
What Are Accounting Controls?
Accounting controls are the procedures and methods applied by an entity for financial statements' assurance, validity, and accuracy. Still, these accounting controls are applied for compliance, safeguard the company, and not comply with the laws, rules, and regulations.
There are various types of control applied within an organization. Also, there is no specific control policy that applies to every organization. The application of controls for each organization is designed and implemented to suit its needs, type of business, aspirations, goals, and other guidelines.
How Do Accounting Controls Work?
Accounting Controls are the measures and controls adopted by an organization that leads to increased efficiency and compliance and ensures that financial statements are accurate when presented to auditors, bankers, investors, and other stakeholders.
Internal accounting controls are not a recent development. These have been in place for a long time. The most significant advantage of accounting controls is that it restores the general public's faith in publicly listed companies. The wake of high-value scandals in the United States by companies like Tyco and Enron shook the general public's confidence in the accounting system.
SOX also known as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, was enacted by the United States Congress to protect the stakeholders from corporate accounting scandals. This also makes it a compulsion for organizations to follow corporate disclosure guidelines and other requirements. The point here is that accounting controls are nowadays an integrated part of any organization, without which the accounting system is like a car without brakes, and no one wants to take a ride in such a car. So any organization which aspires to grow big and better must have robust accounting control in place.
Types
There are three major categories of accounting internal controls.
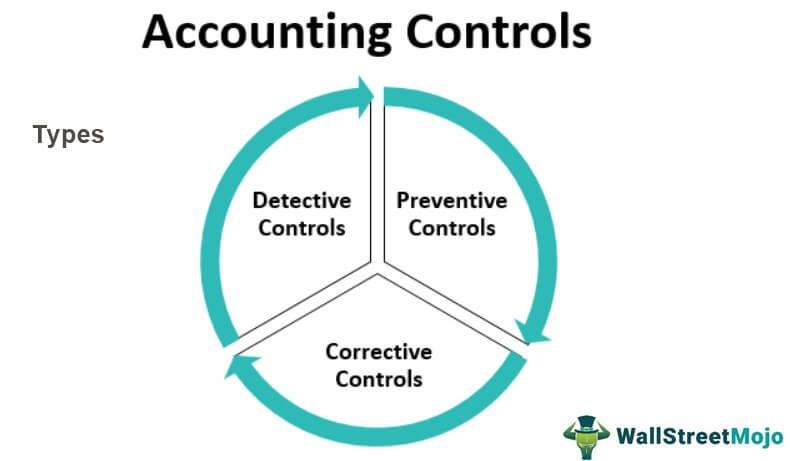
#1 - Detective Controls
As the name suggests, these controls are in place to detect any discrepancy and deviation from the policies in place. It also serves the purpose of the integrity check. Accounting controls for cash are examples that can be cited here.
For example – A surprise check of the actual cash balance in hand with the cashier and cash balance as per accounts will ensure if the cashier is doing his job accurately or not. It might also reflect any accounting posting error. In a computerized environment where the numbers are huge in volume and end to end processing of accounts is done by the system, in those cases, we might want to put a test invoice and track it till accounts finalization to see if it gives the desired result and it is compliant to regulations.
In the same way, comparing actual physical stock in the warehouse and closing stock as per books will show if there is an issue in the Inventory processing, any pilferage, or normal loss. Also, checking that all the assets appearing in the books are physically present ensures the safety of assets.
For example, we have understood that Detective Controls are applied irregularly and are more of an audit nature to identify errors or discrepancies.
#2 - Preventive Controls
The controls are applied daily within the organization to stop the errors or discrepancies from happening in the first place. We can say these are the rules which everyone within the organization has to abide by in their day-to-day job.
For example – in an accounting environment, when a person books an invoice, it goes to another person for peer review and approval. Once the invoice is accounted for, another team makes the payment. It is called segregation of duties, and it ensures that, daily, one person does not have control of booking and paying invoices.
Job rotation is a classic example of preventive control. In a big organization or at a critical place, the personnel is transferred regularly to ensure that any person does not have access to any data or asset for an extended period, which ensures that the person does not get involved in thefts or illegal activities.
In a computerized environment, backing up data daily on the cloud is also a Preventive control to avoid data loss.
#3 - Corrective Controls
These are the controls that come to the rescue when preventive and detective both the controls have failed to avoid an error. In an accounting environment posting an adjustment or rectification entry is an example of corrective controls. Once the books are closed after the financial year and auditors find an issue to be addressed. Reopening the financial yearbooks and making the adjustments an auditor asks for is also a part of corrective control.
In this case, the trial balance still agrees, and later on verification of ledgers, this error was identified. For example – While posting a journal entry, the accountant debited Mr. Tom instead of Mr. Robert for $ 500. The rectification entry here is to debit Mr. Robert and credit Mr. Tom by $500. It is called corrective control.
Examples
Let us understand the accounting controls definition better from the examples given below:
- Segregation of duties – processor and approver should be two different people.
- An independent user id and passwords should be provided to all the employees.
- Physical verification of Inventory and Assets should be done.
- Bank reconciliation and other Trial balance reconciliations should be done.
- Standard Operating Procedure documents should be made regarding process flow.
- Surprise check of petty cash and cash book balances.
Checklist For Accounting Controls
While implementing accounting measures for control in an organization, it is important to learn about the essential points to be kept in mind. Here is a checklist for the organizations to go through before they introduce the controls:
- Any change in one process impacts the other.
- The change should not be made in the middle of an accounting period, as it will affect the transaction flow.
- Any changes should be informed to auditors.
- Any change should also be documented and communicated well with all the stakeholders.
- It should be cost-effective.
Advantages
When there are controls implemented in an organization, the workflow becomes more efficient as everything is organized and handled in a proper manner. Below are some of the advantages of introducing accounting controls.
Below are some of the advantages of accounting controls.
- The action log identifies the person responsible for any error.
- Accuracy of financial statements and funds application
- Efficient use of the resources for the intended purpose
- Helpful in audit facilitation
- A strong foundation for a more significant growth
- Identification and rectification of any discrepancy identified
- Saving cost and resources
Disadvantages
Despite having a number of advantages, implementing controls may have some limitations, which organizations must be aware of as it may help them decide on which controls to introduce.
Below are some of the disadvantages of accounting controls.
- Sometimes irritating and time-consuming for employees
- The high cost of maintaining controls and standards
- Overdependent on financial statements and audit
- Duplication of work

