Table of Contents
What Is Acceptance Credit?
An Acceptance Credit is a type of letter or document promising credit that specifies the period of the bill of exchange and is accepted by the bank from whom it is discounted or drawn. The beneficiary is compensated promptly at the specified discount.
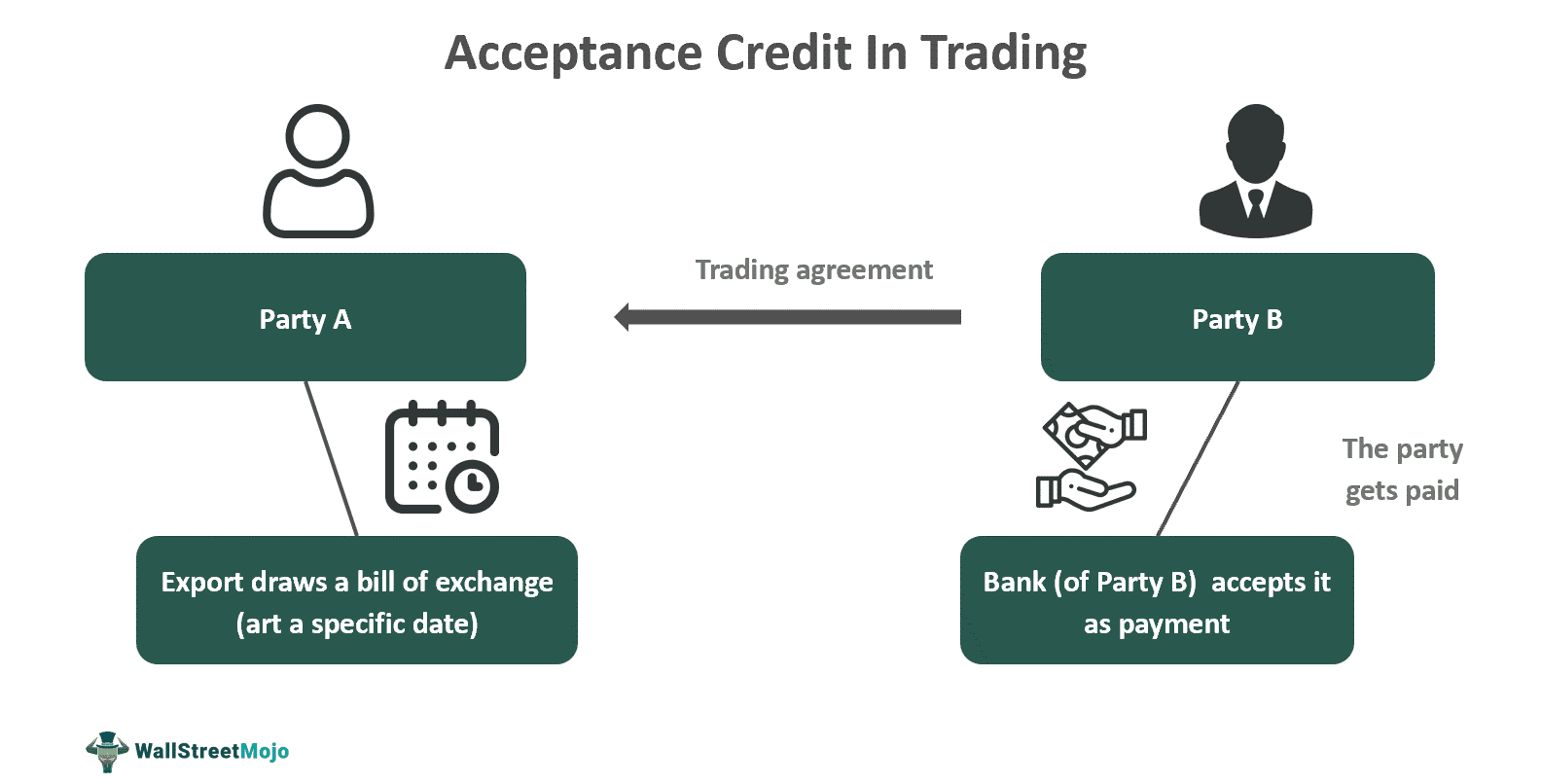
It is equivalent to a financing note after the terms of the advance instrument are met. Under the arrangement, a refund guarantee is made once the shipping company obtains the bank's documentation. The key component of this form of acceptance is the importer's pledge to reimburse the seller for the commodities purchased by a specified date.
Key Takeaways
- Acceptance credit is a financing method used in international trade, enabling creditworthy foreign importers to draw a bill of exchange, which can be discounted or matured.
- It is available in two types: Confirmed and unconfirmed. In the former, the advising bank guarantees payment to the exporting company, regardless of whether the issuing financial institution defaults on its commitments.
- The latter provides no particular assurances from the advising bank.
- It minimizes payment risks by offering a sense of security to sellers. It enhances cash flow, offers flexibility, bridges gaps in creditworthiness, and facilitates smoother cross-border trade relationships.
Acceptance Credit Explained
Acceptance Credit is a method of financing the sale of goods, especially in international trade, where a commercial bank or merchant bank extends credit to a foreign importer deemed creditworthy. In this arrangement, the importer, after receiving the products, pays the exporter at the policy/bond maturity date agreed upon. The payment can be made in the form of a letter of credit, cash against products, or cash against paperwork, depending on the agreement between the exporter and the importer. The maturity date of the assurance that will be issued can be any date beginning with the date of acceptance, as specified by the parties, with no time limit.
An acceptance of credit is established that offers the exporter an option to draw a bill of exchange. Once the bank accepts it, the bill can be discounted on the money market or left to mature. The seller can cash it immediately by discounting the accepted bill with another bank or discount house. The nominated bank then pays the bill of exchange upon maturity and is then reimbursed by the issuing bank, which the buyer later reimburses. The exporter needs to make a payment to the bank as a fee, which is called an acceptance commission for the service. Payment is made via an administrative order that authorizes payments on or after a specific date.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Types
Types of the arrangement are given below:
#1 - Confirmed Letter Of Credit
In the case of confirmed acceptance credit, the advising bank guarantees payment to the exporting company, regardless of whether the issuing financial institution defaults on its commitments. The confirming bank ensures payment as long as the terms of the letter of credit are adhered to. Confirmed type of credit acceptance is more expensive to establish because the issuing bank effectively guarantees payment.
#2 - Unconfirmed Letter Of Credit
An unconfirmed letter of credit provides no particular assurances from the advising bank. In case of unconfirmed acceptance credit, if the seller goes bankrupt or faces any other issues, payment may not be made. Possible reasons for non-payment include non-delivery of the shipment, intervention by customs authorities, or other unforeseen circumstances.
Examples
Let us look into a few examples to understand the concept better
Example #1
In this American acceptance credit example, Company A, a US-based machinery manufacturer, and Company B, a UK-based importer, agree to use acceptance credit as payment terms for a shipment of specialized machinery. Company B, an overseas buyer, arranges for its UK bank to provide acceptance credit on behalf of Company B, guaranteeing payment upon presentation of necessary documents. This arrangement allows company A to manufacture and ship the machinery to company B in the UK, facilitating smooth shipment and receipt. Once the shipment arrives and the required documents are presented to company B's bank, the bank honors the acceptance credit commitment, ensuring payment is received. This not only provides financial security for company A but also fosters international trade relationships between the US and the UK. By utilizing acceptance credit, both companies can engage in cross-border trade with confidence, mitigating payment risks and ensuring a smooth transaction process. This example demonstrates how acceptance of credit arrangements supports the efficient and secure exchange of goods between companies operating in different countries.
Example #2
Imagine a manufacturer of electronic goods, company A, exports a large shipment to a retailer, company B. To ensure a secure transaction, Company A requests acceptance credit as payment. Company B, unfamiliar with Company A's credibility, seeks confirmation from a financial institution. The bank issues a letter guaranteeing payment upon compliance with agreed terms and documentation submission. The shipment was successfully delivered to Company B, and Company A promptly presented the necessary documents. However, investigations reveal that company B had violated acceptance credit terms by misrepresenting the shipment's value and submitting forged shipping documents. This breach put the bank at risk of financial loss. The bank initiated legal proceedings against Company B, causing significant media attention and tarnishing Company B's reputation.
Benefits
Some of the benefits provided by the letter are given as follows:
- Reduces the potential of non-payment for sellers, minimizing payment risk.
- Offers sellers a sense of security by ensuring payment for their products or services.
- Enhances cash flow for sellers through the use of discounted drafts.
- Provides buyers with flexibility in managing their working capital as payment is deferred to a later date.
- Streamlines international trade transactions, making them more efficient.
- Cultivates trust and confidence between buyers and sellers in commercial dealings.
- Facilitates smoother cross-border trade relationships.
- It lessens the requirement for upfront payment, fostering business expansion and development.
- Bridges gaps in creditworthiness or trade history between parties.
- Supports effective cash flow management for both buyers and sellers.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

