It is very important to understand the concept of the AC formula because it helps a company determine the contribution margin of a product, which eventually helps in the break-even analysis. The break-even analysis can decide the number of units required to be produced by the company to be able to book a profit. Further, the application of AC in the production of additional units eventually adds to the company's bottom line in terms of profit since the additional units would not cost the company an additional fixed cost. Another advantage of AC is that it is GAAP compliant.
Table Of Contents
What Is Absorption Costing?
Absorption costing is one approach that is used for the valuation of inventory or calculation of the cost of the product in the company where all the expenses incurred by the company are taken into consideration, i.e., it includes all the direct and indirect expenses incurred by the company during the specific period.

In simple terms, "absorption costing" refers to adding up all the costs of the production process and then allocating them to the products individually. This method of costing is essential as per the accounting standards to produce an inventory valuation captured in an organization's balance sheet.
Absorption Costing Explained
The term absorption costing refers to the method in which the entire production cost is allocated to each and every output proportionately. The cost will include both fixed and variable. It is a very common method used widely in the business especially in the manufacturing sector, and in this way the company is able to determine the cost of individual product and services.
As per this method of full absorption costing, the total product cost is calculated by adding variable costs, such as direct labor cost per unit, direct material cost per unit, and variable manufacturing overhead per unit, and fixed costs, such as fixed manufacturing overhead per unit.
The main idea and intention behind using such a absorption costing method for costing purpose is to imply that a product, when produced, absorbs both fixed and variable cost up to a certain extent. It does not depend on the fact that the unit of the product has been sold or it is still lying in the storage as inventory or finished product ready to be sold. Based on what happens to the product, it will be considered under the inventory calculation or considered under sales revenue and profit calculation.
This method of full absorption costing becomes very important is there is the need to follow the accounting principles for external reporting purposes. It is also used for decision making purposes and analysis of the same. This not only helps the management in evaluation of the financial condition of the business but also estimate the cost and plan production accordingly.
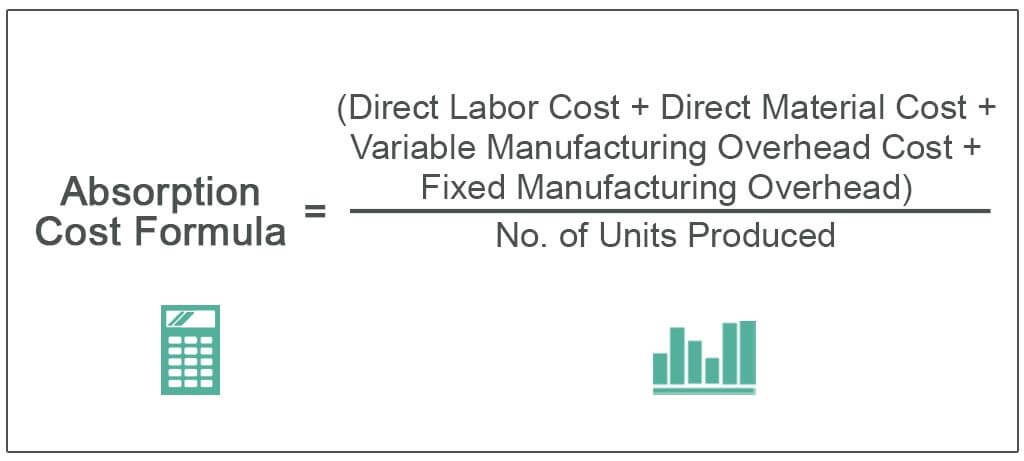
Formula
Absorption cost formula = Direct labor cost per unit + Direct material cost per unit + Variable manufacturing overhead cost per unit + Fixed manufacturing overhead per unit
Absorption costing equation can also be modified to,
Absorption cost formula = (Direct labor cost + Direct material cost + Variable manufacturing overhead cost + Fixed manufacturing overhead) / No. of units produced.
The formula for AC can be computed by using the following steps:
- Firstly, the direct labor cost per unit is directly attributable to the production. The direct labor cost can be determined based on the labor rate, level of expertise, and the no. of hours put in by the labor for production. However, the labor cost can also be taken from the income statement.
- Secondly, identify the material type required and then determine the amount required for the production of a unit of product to calculate the direct material cost per unit. However, the direct raw material cost can also be taken from the income statement.
- Thirdly, determine which part of the manufacturing overhead is variable. The manufacturing overhead is available in the income statement.
- Next, determine which part of the manufacturing overhead is fixed in nature and divide the value by the number of units produced to arrive at a per-unit cost.
- Finally, the formula for absorption cost is derived by adding direct labor cost per unit, direct raw material cost per unit, variable manufacturing overhead per unit, and fixed manufacturing overhead per unit, as shown above.
Marginal Costing vs. Absorption Costing Explained in Video
Examples
Let us understand the concept of absorption costing equation with the help of some suitable examples.
Example #1
Let us take the example of company XYZ Ltd which manufactures clothes for people of the elite class residing in a modern city. Do the calculation of Absorption Costing. The managerial accountant has provided the following information, and the finance director of the company has vetted the same:
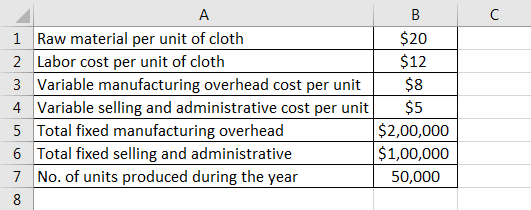
It is to be noted that selling and administrative costs (both fixed and variable) are recurring and, as such, are expensed in the period they occurred. However, these costs are not included in the calculation of product cost per the AC.
Therefore, the calculation of AC is as follows,
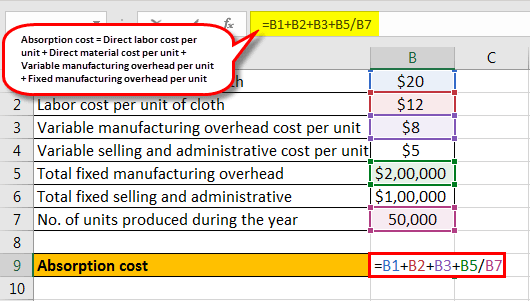
Absorption cost Formula = Direct labor cost per unit + Direct material cost per unit + Variable manufacturing overhead cost per unit + Fixed manufacturing overhead per unit
= $20 + $12 + $8 + $200,000 / 50,000
AC will be -
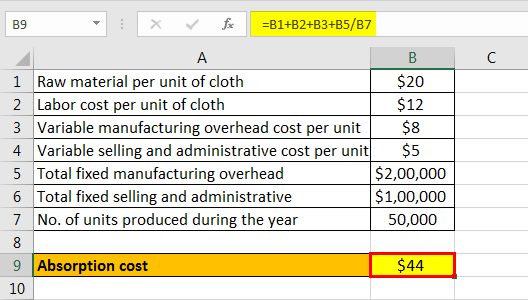
- Ab cost = $44 per unit of cloth
Example #2
Let us take the example of company ABC Ltd, a manufacturer of mobile phone covers. The company recently received an order for 2,500,000 mobile covers at a total contract price of $5,000,000. However, the company is not sure whether the order is a profitable proposition. Do the calculation of Absorption Costing to find whether the order is profitable or not. The following are the excerpts from the entity’s income statement for the calendar year ending in December 2017:
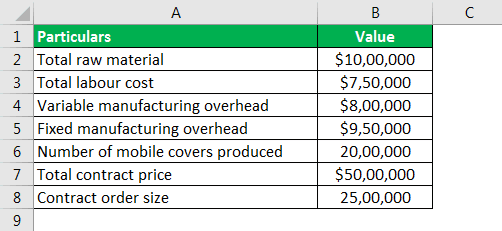
Now, based on the above information, do the calculation.
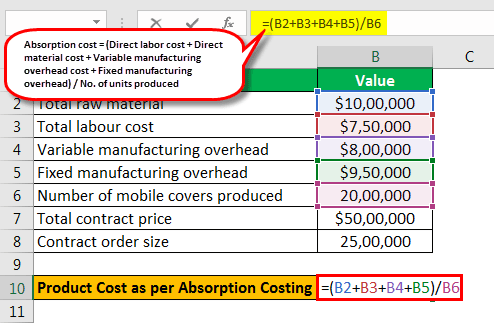
Absorption cost formula = (Direct labor cost + Direct material cost + Variable manufacturing overhead cost + Fixed manufacturing overhead) / No. of units produced.
AC = ($1,000,000 + $750,000 + $800,000 + $950,000) ÷ 2,000,000
AC will be -
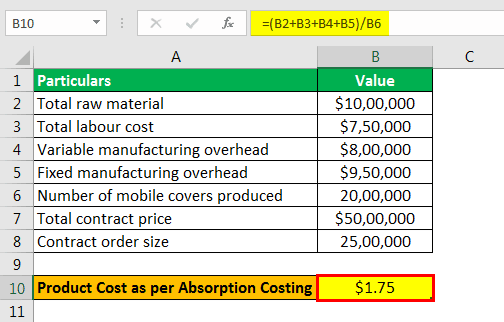
- AC = $1.75 per mobile case
As per the contract pricing, the per-unit price = $5,000,000 / 2,500,000 = $2.00 per mobile case
Since this method shows lower product costs than the pricing offered in the contract, the order should be accepted.
Advantages
Since this method is widely used by many manufacturing companies, it is necessary yo know the advantages and disadvantages of the same. Let us look at the advantages first.
- Absorption costing method is a method of compliance with the accounting principles like the GAAP, and therefore it can be used for external reporting purposes. Thus, this gives a clear, transparent and accurate view of the financial condition of the company which is used by both management and stakeholders.
- It helps in making the inventory valuation method very simple and efficient because it also takes into consideration the fixed overhead, making the components of cost more stable and beneficial, especially for companies that have various levels of production process in their operations.
- Absorption costing method help to match the amount of cost with the revenue earned from the business. This supports the matching principle that is followed in any business enterprise, because here the cost is aligned with the revenue earned from selling the goods and services.
Disadvantages
Here are some disadvantages of the method.
- The most important disadvantage is that the profit figure calculated using this method may be misleading in the sense that since the fixed cost part remain unchanged and is spread over the entire production volume, in case of high production, the overall cost will show a less value and result in high profits and low production will show a high amount of cost and depict low profits, all because of the fixed cost that remain the same.
- In this method, since the inventory valuation includes the fixed cost of production, this will influence the company management to increase the production to very high levels and bring down the overall cost of production by reducing the fixed cost. This may encourage overproduction and put strain on the resources.
- From the above points it is implied that this method, in a way will encourage negative decision making on the part of management. If the profitability assessment is incorrect and over production is encouraged within the entity, this can be used to create a false impression about the company and present it to the stakeholders. This will impact the decisions like pricing production planning, continuation of product lines and investment plans for long term.
Therefore, it is necessary to analyse and evaluate the pros and cons of the process and then decide whether it is suitable for the business. The company management should use it with diligence and responsibility so as not to create any negative effect in the decision making process.
Relevance And Use
Absorption Costing Vs Variable Costing
Both the above methods are accounting techniques that companies use to allocate the cost of production over the total number of units produced. However, there are some differences between them as follows.
- The primary difference is that under the absorption costing format, both fixed and variable costs are included in the production of goods and services and under the latter, only the variable costs are included in the production cost calculation.
- In case of the former the fixed manufacturing overhead cost becomes a part of the cost of inventory and is recorded in the books as product cost, which is not the case in variable costing. Here it is treated as an expense and are not made a part of the inventory.
- From the above points it can be derived that in case of the absorption costing format, the inventory value is inflated due to inclusion of the fixed cost in it, but this is not the case with the variable costing method. Therefore, this makes a lot of difference in the inventory valuation of the products and services of the enterprise.
- This also leads to differences in the income statement and profit calculation. In case of the former, the income shows a higher amount when the production is higher, because of distribution of fixed cost. But for the latter, the income statement shows a higher profit with rise in sales, not production.
- The latter is considered a better method in case of internal decision making since it provides a clearer picture of the company condition with regard to cost and return, as compared to the former.
- The former is more in line with the external reporting purpose since it complies with the accounting principles, which is not the case with the latter.
Thus, the following are some of the noteworthy differences between the above two concepts.

