Table Of Contents
What is Absorbed Overhead?
Absorbed overhead, a frequently used terminology in cost accounting, is the sum of the entire manufacturing overhead implemented to comparable products or other cost objects. This overhead is generally considered in the calculation using a predetermined overhead allocation rate.
Explanation
AAbsorbed overhead means the total amount of indirect cost, which has been assigned to various cost objects. Indirect cost is the type of cost we cannot directly trace to a product or an activity. Cost objects are various attributes for which cost is generally calculated, like customers, products, product lines, distribution channels, etc.
Absorption of overhead cost is a set requirement by both GAAP and IFRS. It is done to include the entire cost of overheads in the inventory details shown in the books of accounts of the business.
Formula
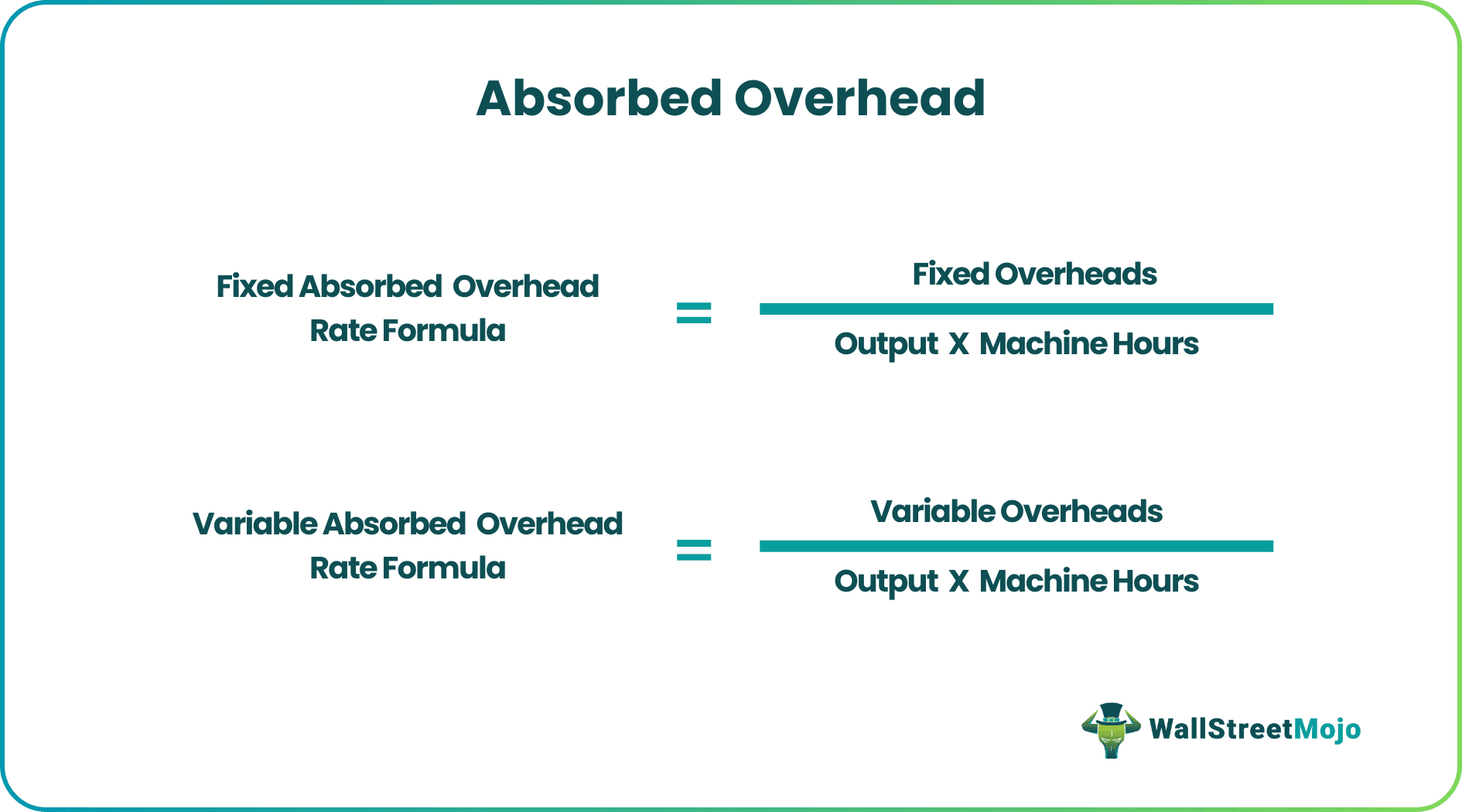
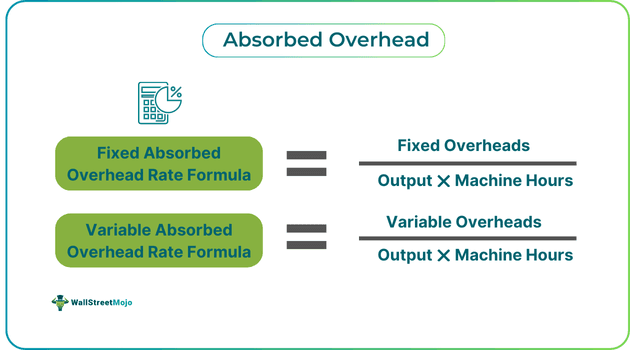
The formula of absorbed overhead is as follows:
We can have two broad types – Fixed and variable absorbed overhead rate.
Fixed Absorbed Overhead Rate = Fixed Overheads / (Output * Machine Hours)
Variable Absorbed Overhead Rate = Variable Overheads / (Output * Machine Hours)
Example
Let's take an example.
Let us assume a company manufactures only a single type of product. The company follows a standard absorption costing system and goes for the absorption of production overhead based on its machine hours utilized. The budgeted details from the last year are mentioned as follows:
- Output generated = 5000 units
- Variable overheads = $10,000
- Fixed overheads = $8,000
- Machine hours = 0.20 hours per unit
Solution:
The total budgeted hours we can calculate as 5000 units * 0.20 hours per unit = 1000 hours
To calculate the absorption rates now, let us use the fixed and variable absorption overhead formulas, which are as follows:
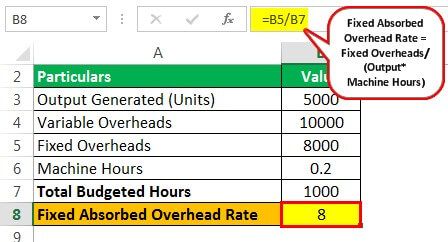
Fixed absorbed overhead rate = $8000/1000 = $8 per machine hour
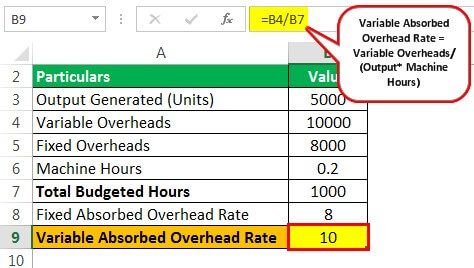
Variable absorbed overhead rate = $10,000/1000 = $10 per machine hour
Thus, to arrive at a standard cost per unit:
- Fixed overhead = 0.2 *8 = $1.6 / unit
- Variable overhead = 0.2*10 = $2 / unit
Methods of Absorbed Overhead
There are a total of seven methods of overhead absorption, which are as follows:
#1 - Direct Material Cost Method
Here the direct material cost serves as the basis of absorption. It is calculated by the formula given below. This method is suitable when the material price does not vary a lot or where material cost forms the major cost component.
Direct Material Percentage Rate = (Factory Overhead / Direct Material Cost) * 100
#2 - Direct Labor Cost Method
Here the direct labor cost serves as the basis of absorption. It is calculated by the formula given below. This method is suitable when wages do not vary significantly or where direct wages form the major cost component. Also, this method is applied when there is efficiency and productivity in the workforce.
Direct Labor Percentage Rate = (Factory Overhead /Direct Wages) * 100
#3 - Prime Cost Percentage Method
Here the overhead is divided by the department's direct material and direct labor costs. This method is simple and easy to calculate. The formula for the same is as below:
Prime Cost Percentage Rate = (Factory Overhead / Prime Cost) * 100
#4 - Direct Labor Hour Method
This is calculated by dividing the factory overhead by direct labor hours. This method is best for cases when production is carried out manually or even for cases where production is not uniform. The formula is as follows:
Labor Hour Rate = Factory Overhead / Labor Hours
#5 - Machine Hour Rate Method
This applies to those industries where the manual job is negligible and machines are extensively used for production. The formula goes as follows:
Machine Hour Rate = Factory Overhead / Machine Hours
#6 - Rate per Unit Production Method
This is used in industries where the output is measured in physical units like weight or some numbers. This is applicable in cases where only one type of product is being produced and production is uniform. The formula for the same is as follows:
Overhead Absorption Rate per Unit = Factory Overhead / Units of Production
#7 - Sales Price Method
Under this method, the overhead budget is divided by the sales price per production unit. The formula for the same is as follows:
Sales Price Recovery Rate = (Factory Overhead / Sales Value Unit of Production) * 100
Advantages of Absorbed Overhead
- It aligns with GAAP and results more accurately than the variable costing method.
- It considers all production costs and is unlike the variable costing methods where only variable cost is considered.
- When production is done to have sales in the future, it will show better results than variable costing.
- It eradicates the separation of cost into fixed and variable elements.
- It helps to calculate gross and net profit separately in income statements.
Disadvantages of Absorbed Overhead
- It isn't easy to compare and control the cost.
- It is not helpful in managerial decisions where decisions related to the selection of product mix or decision to buy or manufacture need to be taken.
- Some criticize this method because of the inclusion of fixed costs, which is not justified.
- Here the fixed overheads are apportioned by arbitrary methods.
- It is not helpful in the preparation of a flexible budget.


