Table Of Contents
What Is Aave Protocol?
Aave Protocol is a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform that functions on the Ethereum blockchain and enables users to lend and borrow a diverse range of cryptocurrencies without any intermediaries. The platform uses smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer lending through an open-source protocol and allows users to earn interest on deposits or access loans.
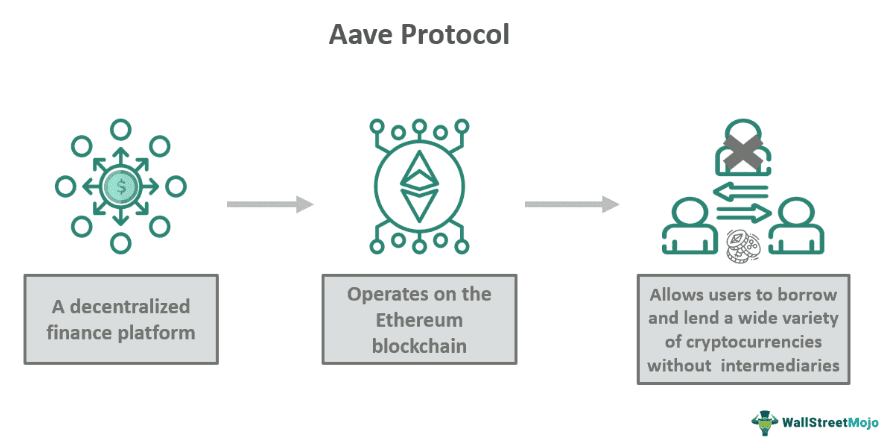
The protocol employs a pool-based system where users' deposits contribute to a shared liquidity pool from which borrowers can draw funds. The platform has gained traction for its user-friendly interface and a wide array of supported cryptocurrencies. Furthermore, it has been instrumental in promoting flexibility and accessibility within the DeFi space.
- The Aave Protocol is a decentralized financial network based on the Ethereum blockchain. It allows users to lend and borrow an extensive selection of cryptocurrencies without the use of any intermediaries.
- The platform facilitates peer-to-peer lending using an open-source protocol and allows users to earn interest on deposits or access loans.
- The protocol enables users to borrow various cryptocurrencies in exchange for collateral.
- However, smart contract vulnerabilities, human errors, as well as the potential of hacking or phishing attacks may compromise users' finances and personal information.
Aave Protocol Explained
Aave Protocol is an open-source lending and borrowing platform in the decentralized finance framework that is built on the Ethereum blockchain. It allows users to engage in a peer-to-peer financial ecosystem without the need for traditional intermediaries. The protocol operates through smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts facilitate lending and borrowing activities between users.
The platform allows individuals to deposit their cryptocurrency assets to earn interest and borrow funds against the assets. Additionally, the platform uses a pooled lending system. Moreover, the platform implements a unique feature known as "flash loans." They are uncollateralized loans that must be borrowed and repaid within the same transaction. The protocol has a user-friendly interface and supports an extensive range of cryptocurrencies.
While DeFi usually thrives on decentralized platforms, some regulated exchanges, such as Coinbase also provide limited access to DeFi tokens within a controlled environment.
History
The Aave protocol was founded in 2017 as ETHLend by Stani Kulechov. It initially focused on peer-to-peer lending services using Ethereum-based smart contracts. In 2018, the platform rebranded to Aave, meaning "ghost" in Finnish, and officially launched its first version in 2019. It quickly gained attention within the decentralized finance ecosystem for its innovative features and approach to lending and borrowing on the blockchain. Aave also introduced the concept of "flash loans." It allows users to borrow funds without collateral if the borrowed amount is repaid within the same transaction.
The Aave Protocol continued to evolve and enhance its protocol by launching Aave V2 in 2020. Version 2 brought improvements in efficiency and scalability. Furthermore, it introduced features like the ability to switch between fixed and variable interest rates.
Platforms like Kraken are often considered by traders for their security features and diverse asset listings.
Lending Assets On Aave
The lending process on the platform begins by accessing the Aave user interface or using a Web3 wallet like MetaMask to connect to the Aave Protocol. After connecting, users can select the specific cryptocurrency they wish to lend. The platform supports a wide range of assets. Users can then deposit their chosen assets into the Aave liquidity pools. These pools act as a collective storehouse for funds, which borrowers can use as collateral to borrow other assets. After depositing their assets, lenders start earning interest on their holdings.
Moreover, the lenders receive aToken that represents their share in the pool and the accrued interest. These aTokens are set at 1:1 to the deposited assets. They continuously increase in quantity as the lender earns interest. They can be stored or used as collateral for borrowing other assets within the Aave platform.
Borrowing Assets On Aave
To initiate a borrowing transaction on the Aave Protocol, users must have deposited assets into the Aave platform's liquidity pools. These deposited assets act as collateral and provide the security necessary for the borrowing process. Users can choose from an array of supported assets, including Ethereum (ETH), stablecoins, and various other cryptocurrencies.
After selecting the desired asset to borrow, users must ensure that they maintain a sufficient collateral-to-debt ratio as required by the protocol. This ratio determines the maximum amount that can be borrowed against the deposited collateral. When the borrower specifies the amount and accepts the borrowing terms, the borrowed assets are then transferred to their wallet or account.
Examples
Let us study the following examples to understand the Aave Protocol:
Example #1
Suppose Jim owns 10 Ethereum (ETH) and wants to earn interest. He deposited the ETH into the Aave Protocol. As a lender, he received aTokens that represented his deposited ETH and the interest earned. A few days later, Sam wanted to borrow ETH and offered collateral. He was allowed to borrow 5 ETH. When Sam returned the 5 ETH along with interest within the agreed period, he was able to retrieve his collateral. Additionally, Jim, being a lender, earned interest from the borrowed amount.
Example #2
On November 4, 2023, the Decentralised Finance (DeFi) protocol Aave suspended some markets following complaints of a problem impacting a particular feature. Many networks were impacted by the halt, including the Aave v2 Ethereum Market and some Aave v2 assets on Avalanche. Furthermore, a few assets on Optimism, Arbitrum, and Polygon had been frozen. Aave did not specify which assets were impacted or which issue triggered the incident. Additionally, Aave emphasized that no funds were in danger in any of its markets. The protocol claimed that the problem did not affect the Aave v3 marketplaces on Ethereum, Base, or Metis. Aave v2 marketplaces on Polygon and Avalanche were also unaffected.
Benefits
Some Aave Protocol benefits include the following:
- Aave operates on the Ethereum blockchain. It allows global access to its lending and borrowing services without the need for a traditional financial intermediary. This decentralized nature allows users worldwide to participate in financial activities without geographical restrictions.
- The protocol allows users to borrow various cryptocurrencies against deposited collateral. It offers flexibility in accessing liquidity without selling their assets. Borrowers can choose from a diverse range of assets supported by the platform.
- This protocol utilizes variable interest rates. It provides users with benefits or adjustments based on market conditions, demand, and supply within the platform.
- The protocol involves its community in governance through its native token, AAVE. Token holders can vote and decide on the platform's future developments and changes.
- Smart contracts govern the protocol's operations. These contracts provide transparency and security while automating the lending and borrowing processes.
Risks
The risks associated with the Aave Protocol are:
- The smart contracts this protocol operates on may contain vulnerabilities. Exploiting these vulnerabilities might lead to financial losses or security breaches.
- The value of the assets held in Aave liquidity pools may fluctuate significantly. This volatility may impact the value of deposited collateral or borrowed assets. Sudden market movements can result in losses for borrowers or lenders.
- The protocol uses variable interest rates that can change according to the supply and demand dynamics within the platform. Fluctuations in interest rates affect the earnings of lenders or repayment costs for borrowers.
- Regulatory changes or crackdowns could impact the platform's operations or lead to changes in user access and usability.
- Human errors and the risk of hacking or phishing attacks cause threats to users' funds and personal information.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How are interest rates determined on the Aave Protocol?
2. Does the Aave Protocol charge fees for lending or borrowing?
3. Are there gas fees associated with transactions on Aave Protocol?

Get in Touch with our Experts!