Table Of Contents
What Is A 409A Valuation?
A 409A valuation is a valuation of a company's common stock performed for tax purposes under section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code. This section of the IRC imposes strict rules on the timing and amount of deferred compensation payments made to employees, including the timing of stock options and other equity awards.
The purpose of it is to determine the market value of the firm's common stock. In addition, it sets the exercise price of stock options and other equity awards subject to section 409A. The valuation must be performed by a qualified appraiser and must be based on a reasonable valuation methodology.
Key Takeaways
- The 409A valuation determines the market value of a company's common stock for tax purposes, particularly for equity-based compensation plans such as stock options.
- It must comply with Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code, which sets out strict rules for the taxation of deferred compensation.
- The valuation process involves a detailed analysis of the company's financial statements, industry conditions, comparable companies, and other relevant factors to determine market value.
409A Valuation Explained
409A valuation report analyzes the company's financial statements, projections, market conditions, and other relevant factors. The significance of 409A valuation services lies in determining the market value of a firm's common stock for tax purposes.
Here are some of the crucial reasons why it is essential:
- Avoiding tax penalties: Section 409A imposes strict rules on the timing and amount of deferred compensation payments. It includes those made through stock options and other equity awards.
- Setting the exercise price for stock options: A 409A valuation methodology determines the market value of the firm's common stock. After which, it sets the exercise price of stock options and other equity awards subject to Section 409A. This is important to ensure that the exercise price is reasonable. This results in additional tax liabilities for the employee.
- Facilitating fundraising and M&A activities: Accurate valuations are essential for fundraising activities, as investors need to understand the potential value of their investment. Similarly, M&A transactions often involve the companies' valuations, and such valuations can provide a foundation for these discussions.
- Maintaining transparency and credibility: It can provide an objective and independent assessment of the value of a company's common stock. It can help keep transparency and credibility with investors, employees, and other stakeholders.
Requirements
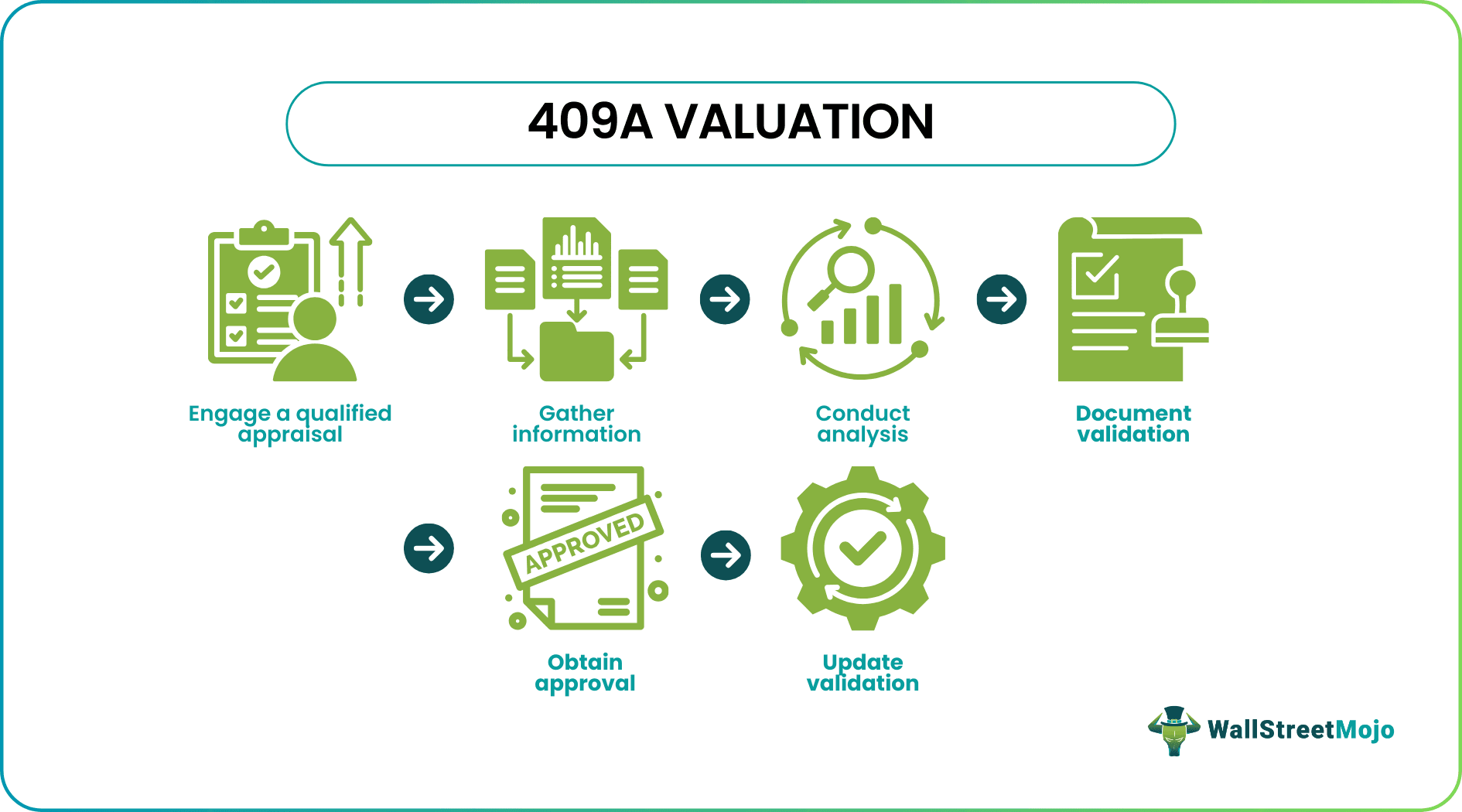
Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code sets forth specific requirements for 409A valuations. Here are some of the essential requirements:
- Timing of valuations: It must be performed at least once every 12 months or whenever a material event could impact the value of the company's common stock.
- Qualified appraiser: An appraiser performs the valuation with the requisite education, experience, and professional credentials to perform the valuation.
- Reasonable valuation methodology: The valuation must be based on an appropriate valuation methodology. It considers all relevant factors like the company's financial performance, market conditions, and growth prospects.
- Written valuation report: The valuation must be in a written statement. This includes a description of the methodology used, the assumptions made, and the data relied upon to perform the valuation.
- Board approval: The company's board of directors must provide the valuation report. This must approve the valuation in good faith.
- Consistency with equity awards: The market value determined by the 409A valuation cost must be consistent with the exercise price of any stock options and other equity awards the company grants.
Examples
Let us understand it in the following ways.
Example #1
Suppose a start-up technology company that is preparing to issue stock options to its employees as a form of compensation. Before giving these options, the company engages a qualified appraiser to perform a 409A valuation to determine the market value of its common stock. The company's board of directors reviews and approves the valuation report. The exercise price of the stock options is at par or above the market value.
Example #2
Recently in 2018, 409A valuation was in the news in the case of Theranos, a now-defunct blood testing company subject to a federal investigation into its business practices. As part of this investigation, it was apparent that Theranos had falsely claimed that its technology could conduct a wide range of medical tests with just a few drops of blood.
In addition, Theranos inflated the value of its common stock through fraudulent valuations, which were used to justify high valuations in fundraising rounds and to award stock options to employees. As a result, the company and its founder, Elizabeth Holmes, are facing criminal charges related to these allegations.
409A Valuation vs Post-Money Valuation vs Venture Capital Valuation
409A Valuation, Post-Money Valuation, and Venture Capital Valuation are different methods of valuing a company that serves other purposes. For example, a 409A valuation determines the market value of a company's common stock for tax purposes, a post-money valuation determines the overall value of a company after a financing round, and a venture capital valuation assesses the company's value to invest.
Here are the critical differences between the three valuations:
409A Valuation
- A valuation method used to determine the market value of a company's common stock for tax purposes.
- Ensures that the exercise price of equity awards granted to employees is reasonable, which could trigger additional tax liabilities.
- It is a detailed analysis of the company's financial statements, industry conditions, comparable companies, and other relevant factors required to arrive at a market value.
- They comply with Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code.
Post-Money Valuation
- A valuation method, such as a venture capital investment, determines a company's overall value after a financing round.
- It takes the pre-money valuation (the company's value before the investment) and adds the investment amount.
- Essential for both the company and the investors, as it provides a baseline for future financing rounds and potential exit events such as acquisitions or IPOs.
Venture Capital Valuation
- Venture capital investors use a valuation method to assess the value of a company they are considering investing in.
- It involves a detailed analysis of the company's financial statements, management team, industry conditions, and growth prospects to arrive at a valuation.
- They determine whether the investment will likely generate a sufficient return on investment for the investor, typically through an exit event such as an acquisition or IPO.
- Typically results in a higher valuation than a 409A or post-money valuation, as venture capitalists are willing to pay a premium for the potential return on investment.

